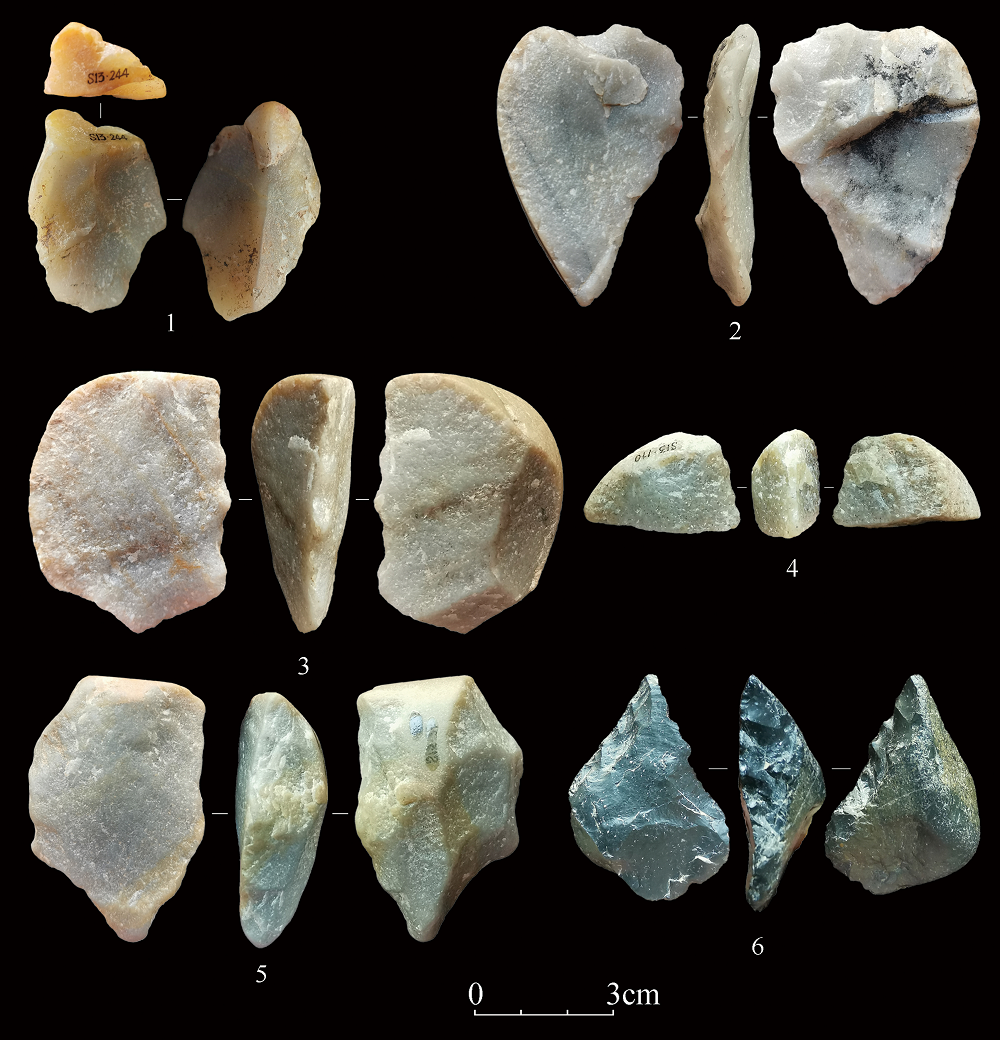
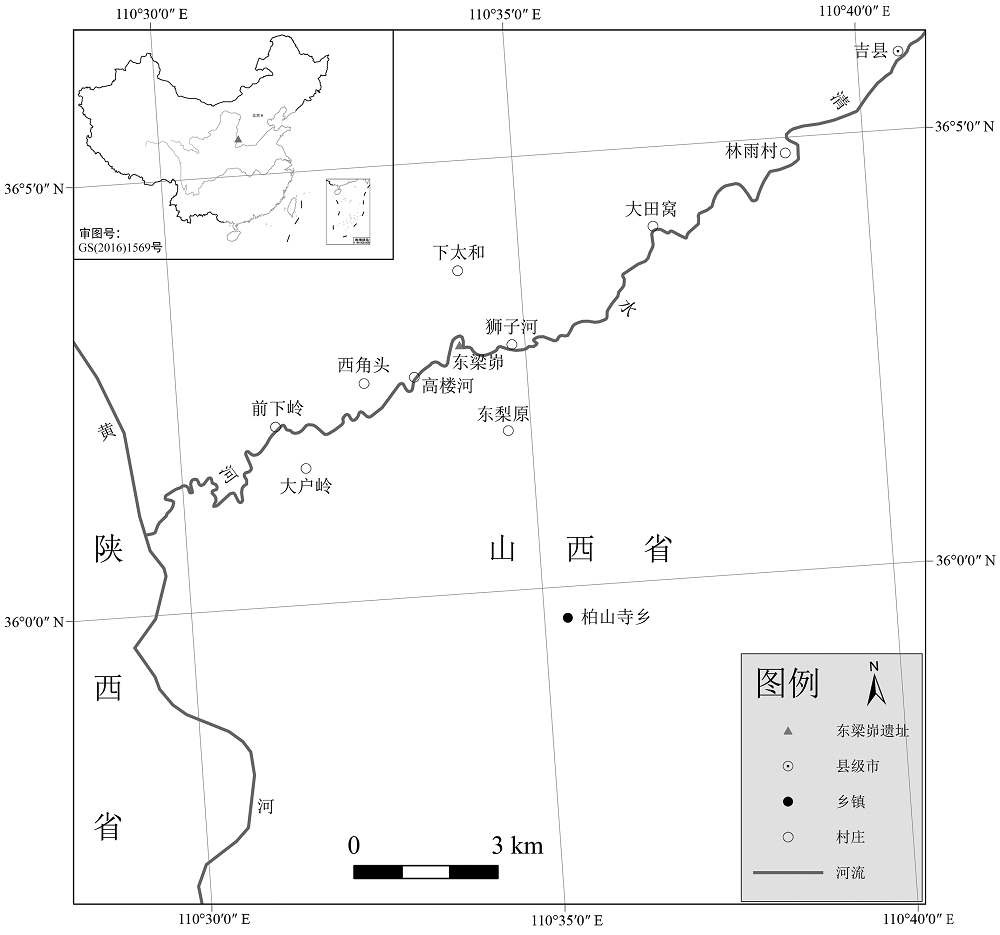
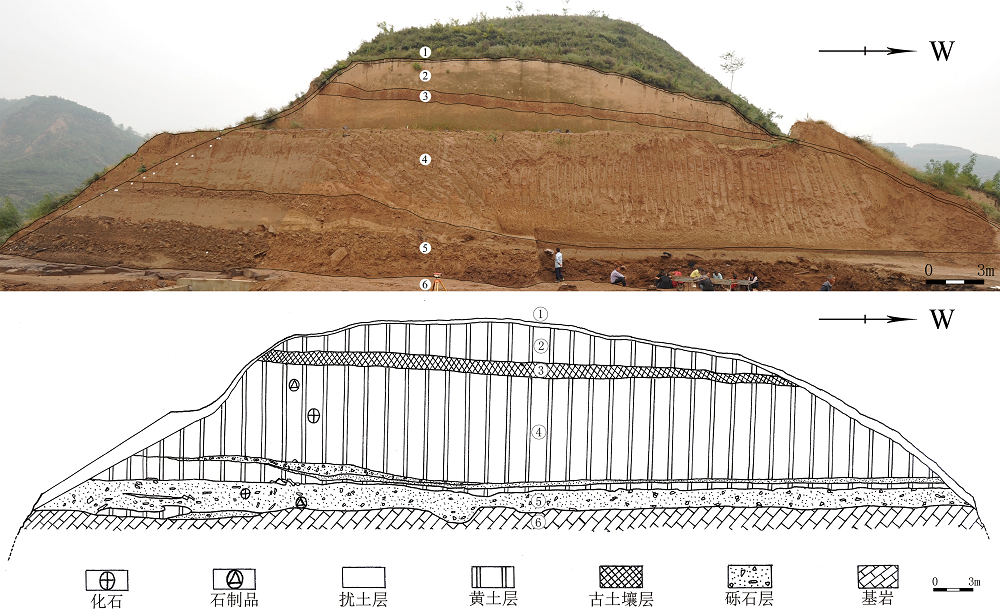
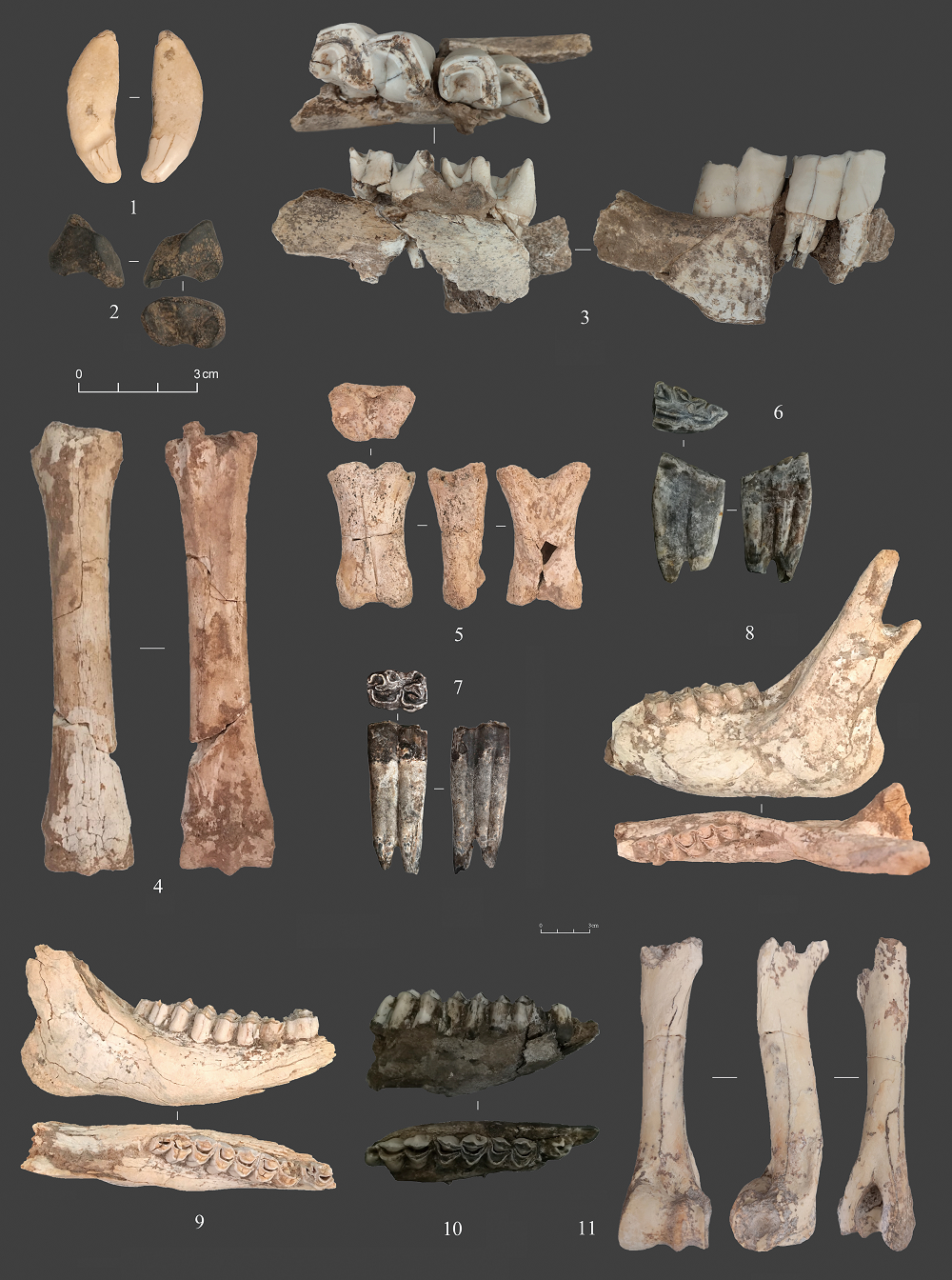
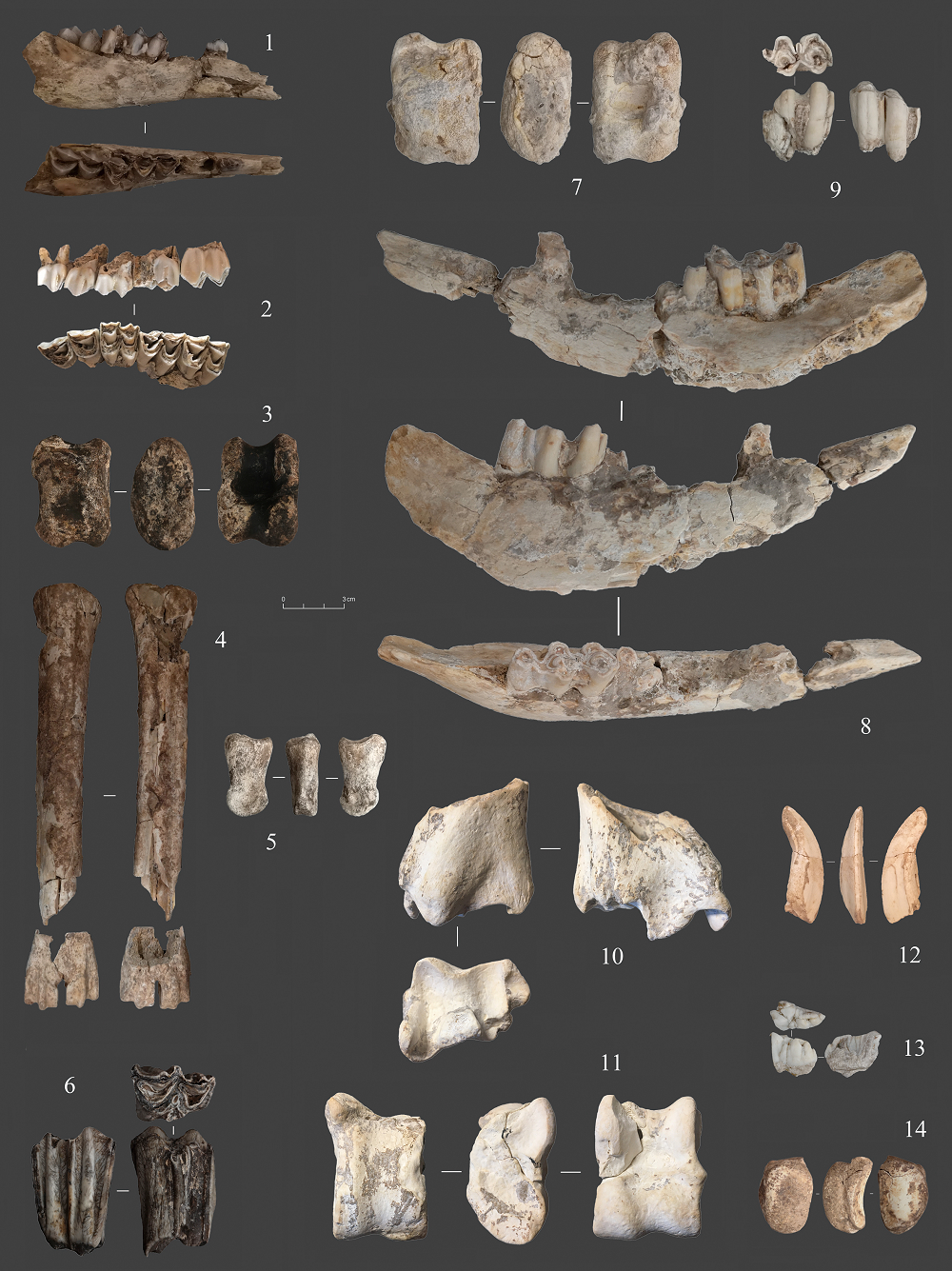
| [1] |
HUAN Faxiang, YANG Shixia, CHEN Wei, CHEN Weiju, ZHU Lidong, ZHANG Yuxiu.
A restudy of stone artifacts from the Fulin site in Hanyuan, Sichuan
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023, 42(02): 177-190.
|
| [2] |
LIN Yi, LIU Tuo, GU Wanfa, WANG Songzhi, WANG Youping.
Sources of lithic raw materials of the Fangjiagou site in Dengfeng county, Henan Province
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023, 42(01): 25-35.
|
| [3] |
NIU Dongwei, YAN Xiaomeng, MA Dongdong, XU Zhe, PEI Shuwen.
A report on the 2019-2020 paleolithic survey in Yuxian Basin
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(05): 936-944.
|
| [4] |
DONG Zhe, ZHAN Shijia.
A preliminary report on the survey and excavation at Anyouzhuang Paleolithic site in Ningguo city, Anhui province
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(02): 334-341.
|
| [5] |
MU Zhanxiong, CHEN Guoke, DU Shuisheng, WANG Hui.
A preliminary report of the 2018 excavation at the Loufangzi site in Huan county, Gansu province
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(01): 121-134.
|
| [6] |
LI Jingya, ZHAO Jingfang, SONG Guoding.
Report of the stone artifacts from the Liangjiagang Locality 2 and the Donggang Paleolithic site in Danjiangkou reservoir region
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(01): 108-120.
|
| [7] |
GAO Lihong, HOU Yamei, HUANG Qiuyan, LI Jinyan, LU ZhengQin, HUANG Dejiang.
A report of the trial excavation of the Liulinling Paleolithic site in the Bose Basin
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(01): 135-147.
|
| [8] |
LIU Yang, YANG Jungang, BAO Lei, QIU Weili, HOU Yamei, YIN Chunlei.
A preliminary research of the Locality 10 of Wulanmulun River in Ordos, Inner Mongolia
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021, 40(04): 568-574.
|
| [9] |
MA Dongdong, NIU Dongwei, PEI Shuwen, LI XiaoLi, YANG Haiyong, WANG Fagang.
A preliminary report on the Paleolithic survey of 2017-2018 in Yuxian Basin
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021, 40(01): 128-136.
|
| [10] |
ZHAO Qingpo, SONG Guoding, MU Junhong.
Stone artifacts collected from the Kengnan site in Xichuan, Henan Province
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021, 40(01): 146-156.
|
| [11] |
ZHAN Shijia, DONG Zhe, QIAN Yaopeng.
A preliminary report on the Paleolithic survey in Jinghe River basin, Shaanxi Province in 2019
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021, 40(01): 157-164.
|
| [12] |
WANG Yinghua, SUN Zudong, SHAN Mingchao, HE Jia, LIU Wang, CHEN Fuyou.
A preliminary report on the survey and test excavation of the Mogushanbei site in Zhalainuoer district, Inner Mongolia
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2020, 39(02): 173-182.
|
| [13] |
ZHANG Peiqi, ZHANG Xiaoling, Sam LIN, GUO Jialong, WANG Huimin, Nicolas ZWYNS, PENG Fei, GAO Xing.
A preliminary analysis of the stone artifacts from the 2014~2015 excavation of Shuidonggou Locality 2, Ningxia Autonomous Region
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2020, 39(01): 30-41.
|
| [14] |
REN Haiyun, WANG Xiaoyi, WANG Xiaojuan, ZHANG Guanghui.
A study of stone artifacts excavated at the Bicun site in Xingxian county
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2020, 39(01): 52-63.
|
| [15] |
BIE Jingjing, WANG Shejiang, XIA Nan, LU Huayu, WANG Xianyan, YI Shuangwen, XIA Wenting, ZHANG Gaike, Mathew L FOX, ZHANG Hongyan, ZHUO Haixin, ZHANG Wenchao.
Lithic artifacts excavated from the Jinshuihekou site in the Hanzhong Basin, Shaanxi Province, China
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2019, 38(03): 344-361.
|