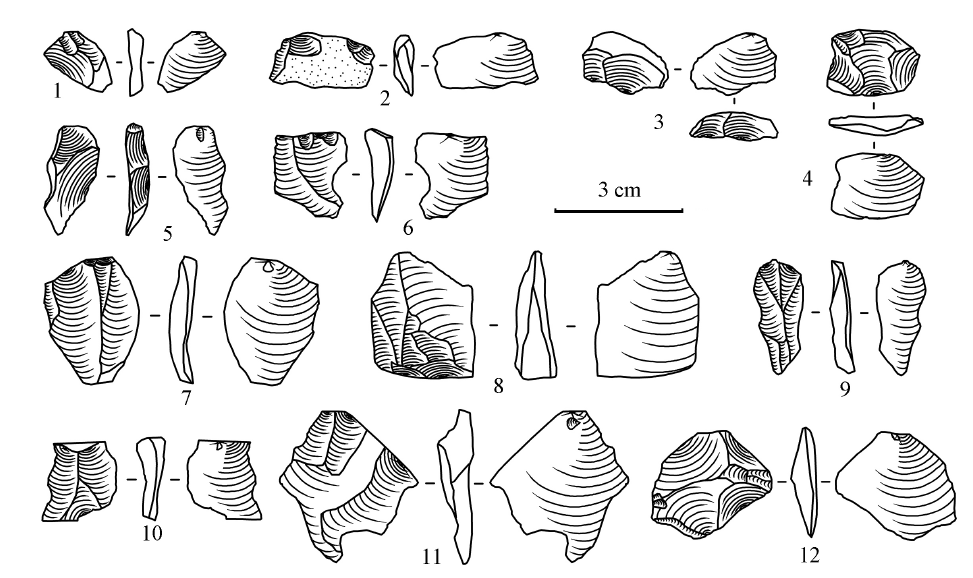
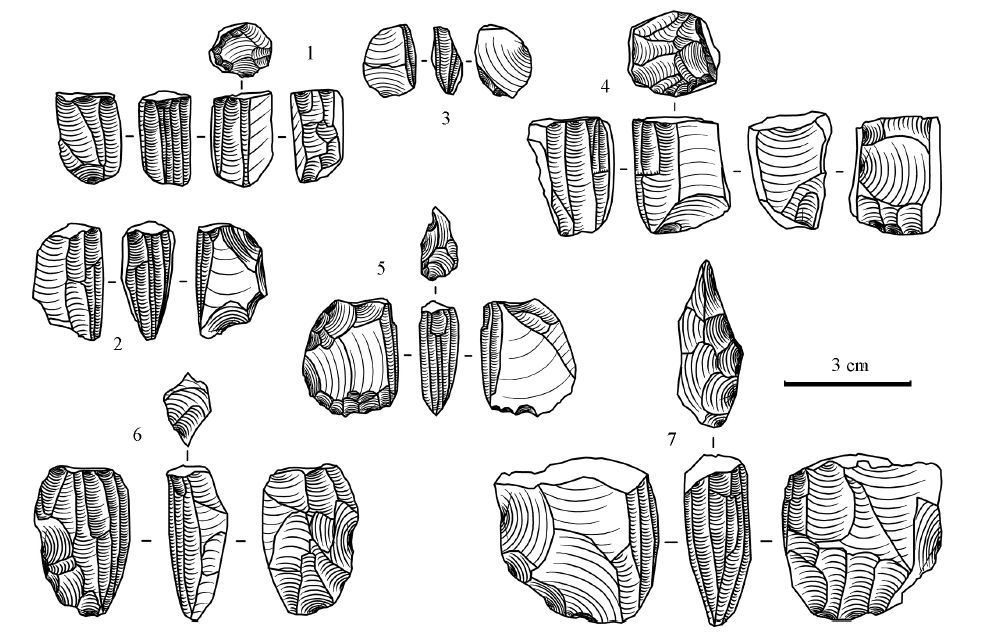
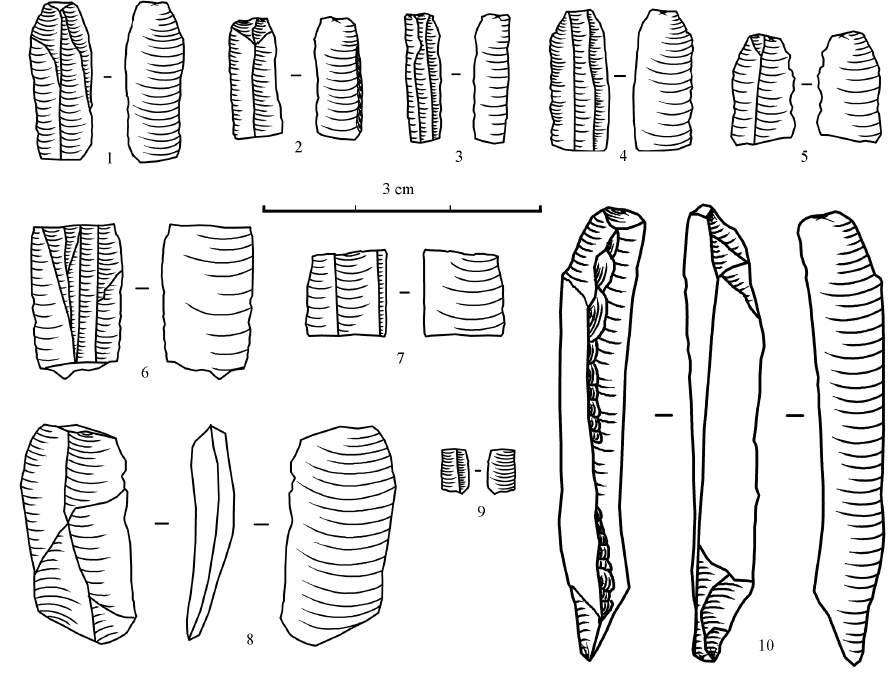
| [1] |
Hou GL, Lai ZP, Cao GC, et al. The earliest prehistoric pottery in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its archaeological implications[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 30:431-437
doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.05.005
URL
|
| [2] |
张东菊, 董广辉, 王辉, 等. 史前人类向青藏高原扩散的历史过程和可能驱动机制[J]. 中国科学, 2016, 46(8): 1007-1023
|
| [3] |
Brantingham PJ, Gao X. Peopling of the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. World Archaeology, 2006, 38(3): 387-414
doi: 10.1080/00438240600813301
URL
|
| [4] |
安志敏, 尹泽生, 李炳元. 藏北申扎、双湖的旧石器和细石器[J]. 考古, 1979(6): 481-494
|
| [5] |
吕红亮. 更新世晚期至全新世中期青藏高原的狩猎采集者[J]. 藏学学刊, 2014(11): 1-27
|
| [6] |
高星, 周振宇, 关莹. 青藏高原边缘地区晚更新世人类遗存与生存模式[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(6): 969-977
|
| [7] |
Madsen DB, Ma Haizhou, Brantingham PJ, et al. The Late Upper Paleolithic occupation of the northern Tibetan Plateau margin[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2006, 33:1433-1444
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2006.01.017
URL
|
| [8] |
盖培, 王国道. 黄河上游拉乙亥中石器时代遗址发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 1983, 2(1): 49-59
|
| [9] |
汤惠生, 周春林, 李一全, 等. 青海昆仑山山口发现的细石器考古新材料[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(3): 247-253
doi: 10.1360/972012-550
URL
|
| [10] |
仪明洁, 高星, 张晓凌, 等. 青藏高原边缘地区史前遗址2009年调查试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(2): 124-136
|
| [11] |
侯光良, 杨石霞, 鄂崇毅, 等. 青藏高原东北缘江西沟2号遗址2012年出土石制品初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(4): 553-564
|
| [12] |
韩芳, 蔡林海, 杜玮, 等. 青南高原登额曲流域的细石叶工艺[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(1): 53-69
|
| [13] |
西藏自治区文物管理委员会. 西藏昌都卡若遗址试掘简报[J]. 文物, 1979(9): 22-28
|
| [14] |
西藏自治区文管会文物普查队. 西藏仲巴县城北石器地点[J]. 考古, 1994(7): 577-586
|
| [15] |
中国社会科学院考古研究所西藏工作队,西藏自治区文物管理委员会. 西藏贡嘎县昌果沟新石器时代遗址[J]. 考古, 1999(4): 1-10
|
| [16] |
侯光良, 许长军, 樊启顺. 史前人类向青藏高原东北缘的三次扩张与环境演变[J]. 地理学报, 2010, 65(1): 65-72
doi: 10.11821/xb201001007
URL
|
| [17] |
陈宥成, 曲彤丽. 旧大陆视野下的中国旧石器晚期小型两面器溯源[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(1): 21-29
|
| [18] |
柿子滩考古队. 山西吉县柿子滩旧石器时代遗址S14地点2002~2005年发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2013(2): 3-13
|
| [19] |
北京大学中国考古学研究中心, 郑州市文物考古研究院. 河南新密李家沟遗址南区2009年发掘报告[J]. 古代文明, 2013, 9:208-239
|
| [20] |
陈宥成, 曲彤丽. 中国早期陶器的起源及相关问题[J]. 考古, 2017(6): 82-92
|
| [21] |
中国社会科学院考古研究所,四川工作队. 四川广元中子铺细石器遗存[J]. 考古, 1991(4): 289-299
|
| [22] |
中国社会科学院考古研究所华南一队,贵州省文物考古研究所,平坝县文物管理所. 贵州平坝县牛坡洞遗址2012~2013年发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2015(8): 16-36
|
| [23] |
仪明洁. 旧石器时代晚期末段中国北方狩猎采集者的适应策略——以水洞沟第12地点为例[D]. 中国科学院大学博士学位论文, 2013: 38-53
|