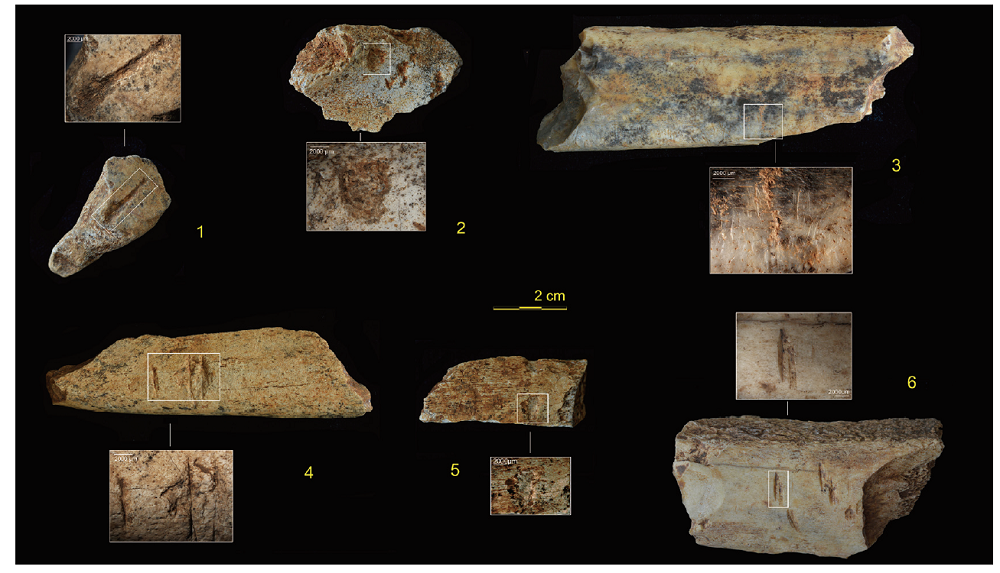
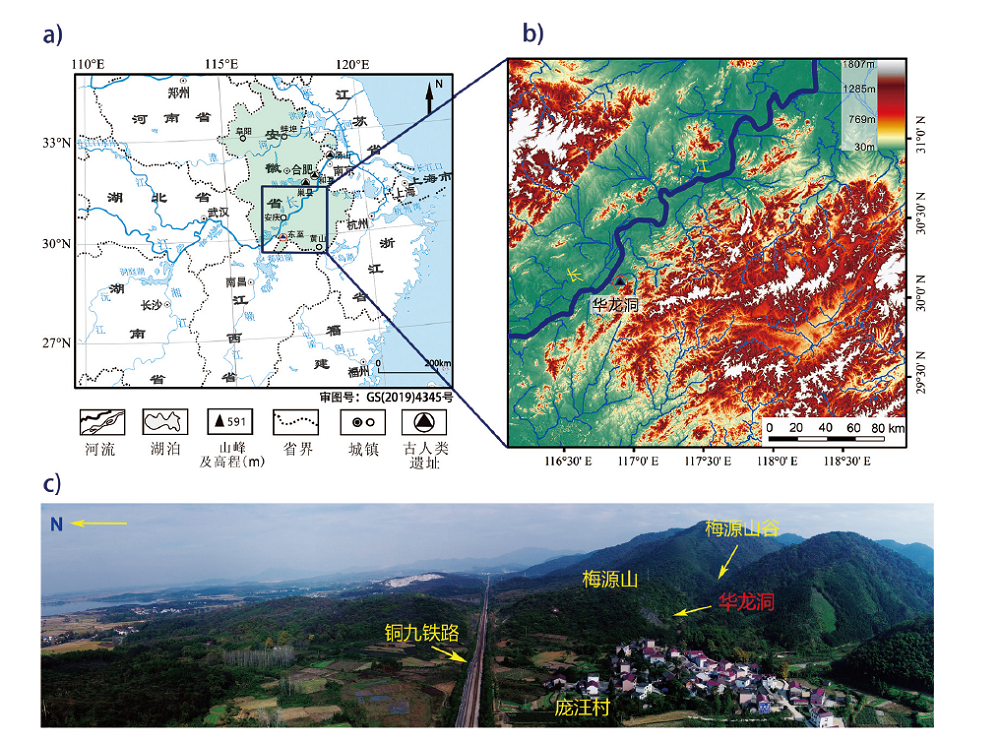
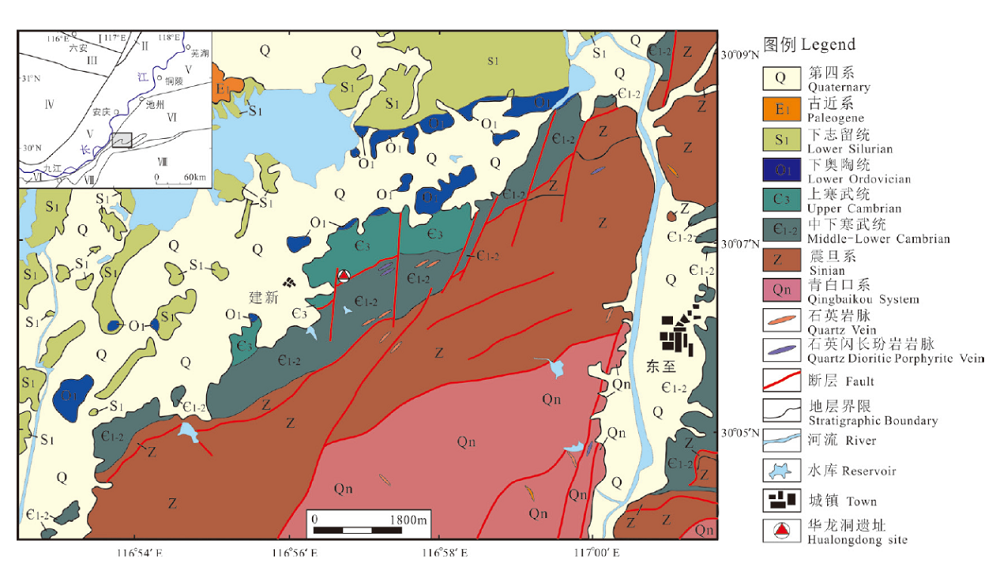
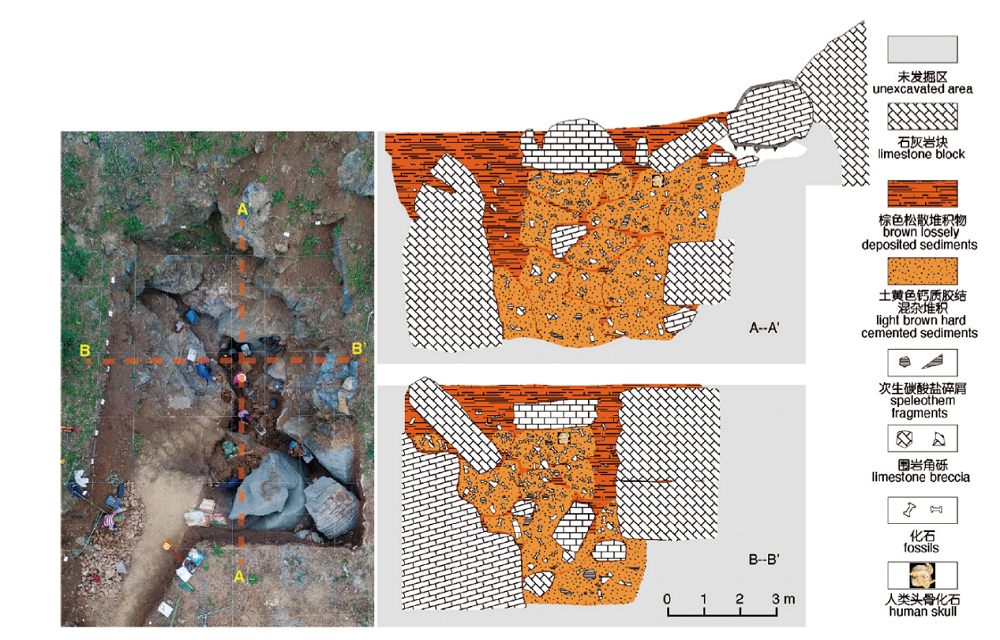
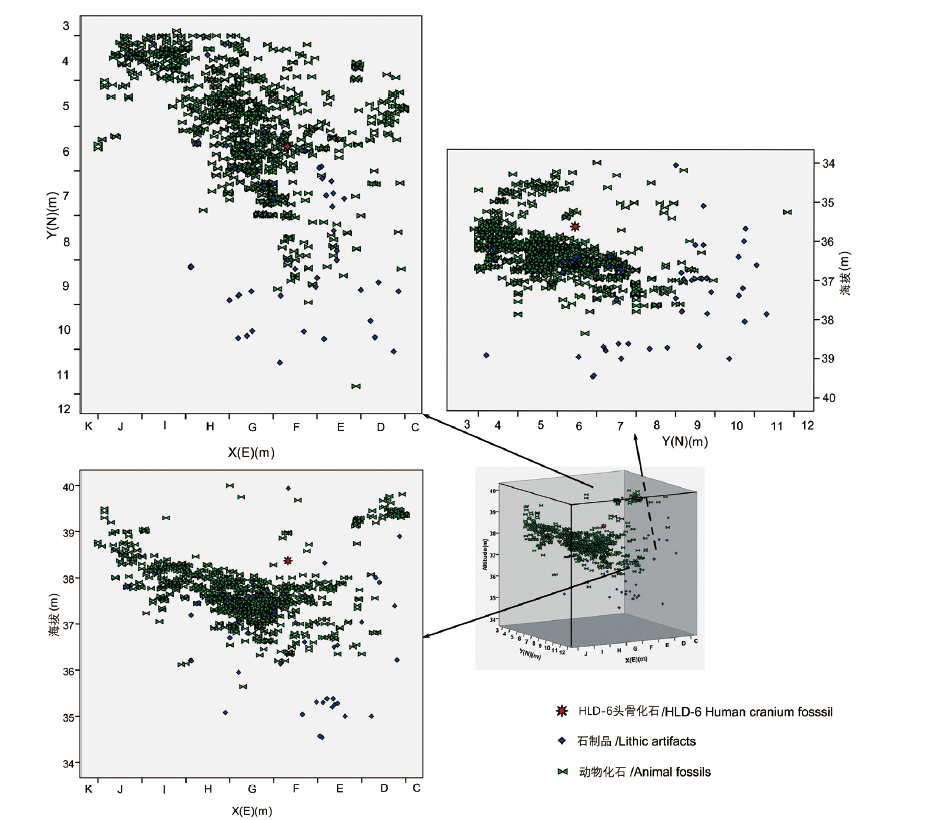
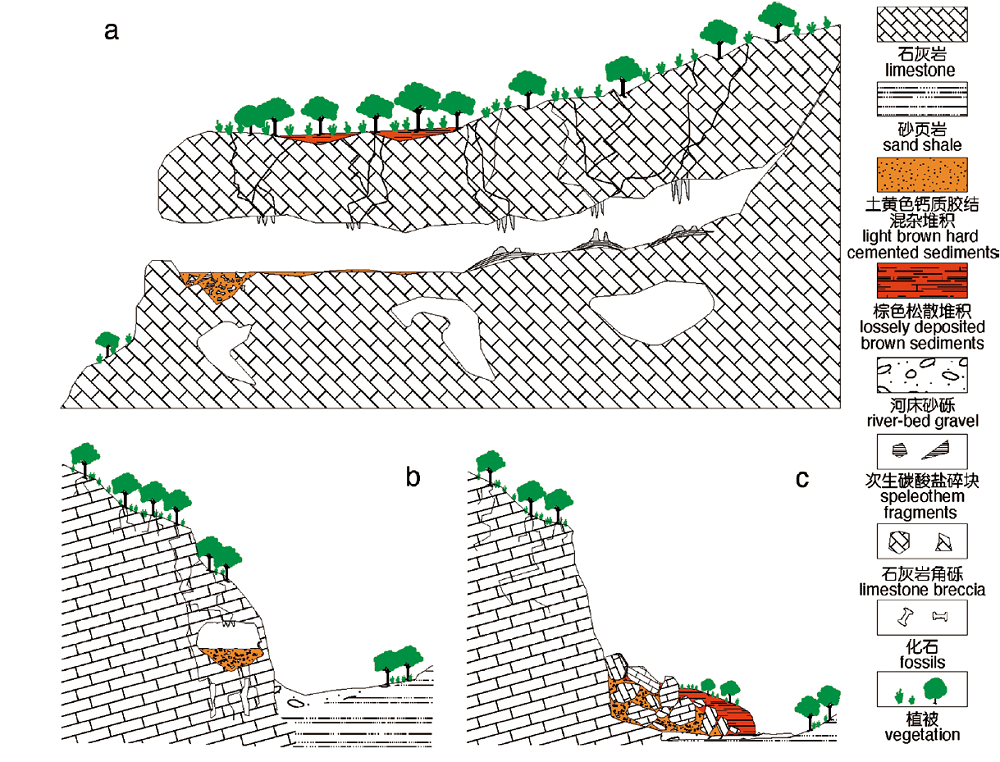
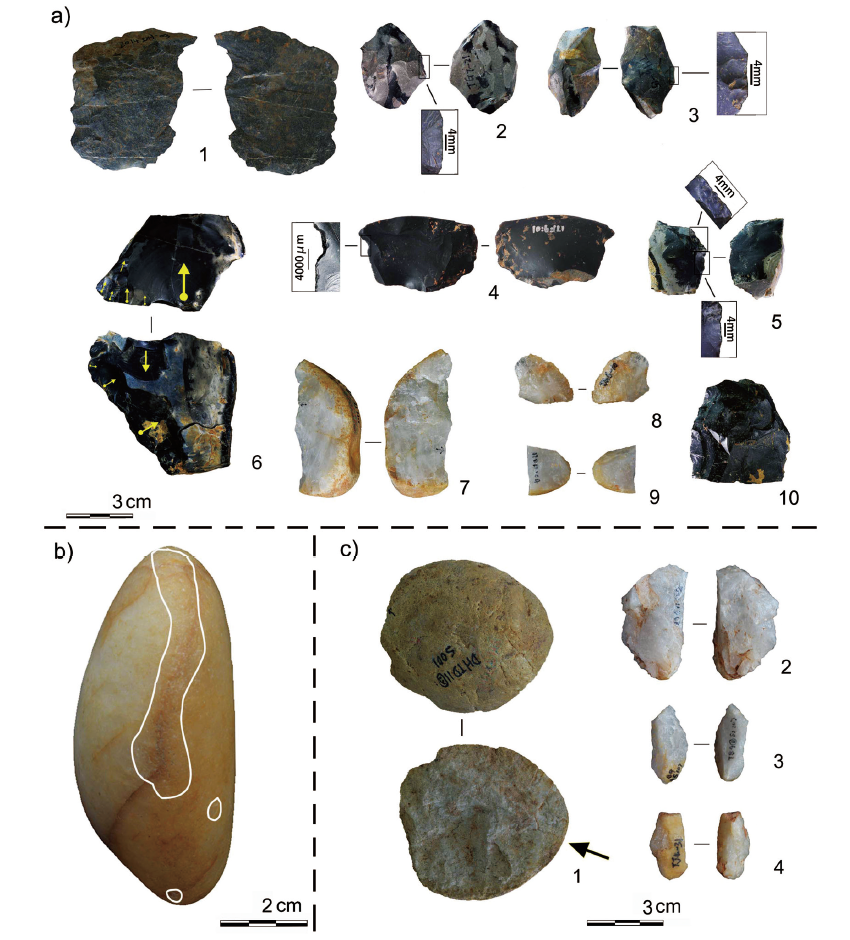
| [1] |
O'Connor S, Barham A, Aplin K, et al. Cave stratigraphies and cave breccias: Implications for sediment accumulation and removal models and interpreting the record of human occupation[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2017, 77: 143-159
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2016.05.002
URL
|
| [2] |
Goldberge P, Sherwood SC. Deciphering human prehistory through the geoarchaeological study of cave sediments[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology, 2006, 15: 20-36
doi: 10.1002/evan.20094
URL
|
| [3] |
中国科学院地质研究所岩溶研究组. 中国岩溶研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1979: 1-6
|
| [4] |
北京地方志编辑委员会. 北京志·世界文化遗产卷·周口店遗址志[M]. 北京: 北京出版社, 2004: 1-486
|
| [5] |
Liu W, Martinón-Torres M, Cai YJ, et al. The earliest unequivocally modern humans in southern China[J]. Nature, 2015, 526: 696-699
doi: 10.1038/nature15696
URL
|
| [6] |
宫希成, 郑龙亭, 邢松, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞出土的人类化石[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(4): 427-436
|
| [7] |
陈胜前, 罗虎. 安徽东至县华龙洞旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2013, (4): 7-13
|
| [8] |
Wu XJ, Pei SW, Cai YJ, et al. Archaic human remains from Hualongdong, China, and Middle Pleistocene human continuity and variation[J]. PNAS, 2019, 116: 9820-9824
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902396116
URL
|
| [9] |
Wu XJ, Pei SW, Cai YJ, et al. Morphological description and evolutionary significance of 300 ka hominin facial bones from Hualongdong, China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2021, 161: 103052
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2021.103052
URL
|
| [10] |
潘桂棠, 肖庆辉. 中国大地构造图(1:2500000)说明书[R]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015: 1-160
|
| [11] |
安徽省地质矿产局. 安徽省岩石地层[M]. 全国地层多重划分对比研究(34), 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1997
|
| [12] |
都洵, 张永康. 东南区区域地层[M]. 全国地层多重划分对比研究(30), 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1998
|
| [13] |
安徽省地质矿产局区域地质调查队. 中华人民共和国区域地质调查报告:1:5万香隅坂幅(H-50-66-D)、张溪镇幅(H-50-67-A)、东至县幅(H-50-66-C)(地质部分)[R]. 合肥:安徽省地质矿产局, 1991, 1-139
|
| [14] |
李潇丽, 董哲, 裴树文, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞洞穴发育与古人类生存环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3): 169-179
|
| [15] |
中国科学院地质研究所岩溶研究组. 中国岩溶研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1979, 148-278
|
| [16] |
同号文, 吴秀杰, 董哲, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞古人类遗址哺乳动物化石的初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(2): 284-305
|
| [17] |
董哲, 裴树文, 盛锦朝, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞古人类遗址2014-2016年出土的石制品[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(4): 778-788
|
| [18] |
Gao X, Norton CJ. A critique of the Chinese “Middle Palaeolithic”[J]. Antiquity, 2002, 76(292): 397-412
doi: 10.1017/S0003598X00090517
URL
|
| [19] |
Pei SW, Xie F, Deng CL. et al. Early Pleistocene archaeological occurrences at the Feiliang site, and the archaeology of human origins in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12 (11): e0187251
|
| [20] |
Schick KD, Dong ZA. Early Palaeolithic of China and Eastern Asia[J]. Evolutional Anthropology, 1993, 2(1): 22-35
|
| [21] |
Binford LR, Ho CK. Taphonomy at a distance: Zhoukoudian, "The Cave Home of Beijing Man"[J]. Current Anthropology, 1985, 26: 413-442
doi: 10.1086/203303
URL
|
| [22] |
Boaz NT, Ciochon R, Xu Q. et al. Mapping and taphonomic analysis of the Homo erectus loci at Locality 1 Zhoukoudian, China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2004, 46: 519-549
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2004.01.007
URL
|
| [23] |
Vals A, Dirks PHGM, Backwell LR, d’Errico F. et al. Taphonomic analysis of the faunal assemblage associated with the hominins (Australopithecus sediba) from the Early Pleistocene cave deposits of Malapa, South Africa[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10: e0126904
|
| [24] |
Mangano G. An exclusively hyena-collected bone assemblage in the Late Pleistocene of Sicily: taphonomy and stratigraphic context of the large mammal remains from San Teodoro Cave (North-Eastern Sicily, Italy)[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2011, 38: 3584-3595
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2011.08.029
URL
|
| [25] |
Brain CK. The Hunters or the Hunted? An Introduction to African Cave Taphonomy[M]. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press, 1981
|
| [26] |
Marean CW, Ehrhardt CL. Palaeoanthropological and palaeoecological implications of the taphonomy of a sabertooth's den[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 1995, 29: 515-547
doi: 10.1006/jhev.1995.1074
URL
|
| [27] |
Brugal JP, Jaubert J. Les gisements paléontologiques pléistocènes à indices de fréquentation humaine: un nouveau type de comportement de prédation?[J]. Paléo, 1991, 3: 15-41
doi: 10.3406/pal.1991.1034
URL
|
| [28] |
Villa P, Soressi M. Stone tools in carnivore sites: The case of Bois Roche[J]. Journal of Anthropological Research, 2000, 56: 187-215
doi: 10.1086/jar.56.2.3631362
URL
|
| [29] |
Stewart M, Andrieux E, Clark-Wilson R, et al. Taphonomy of an excavated striped hyena (Hyaena hyaena) den in Arabia: implications for paleoecology and prehistory[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2021, 13: 179
doi: 10.1007/s12520-021-01439-5
URL
|
| [30] |
Leslie DE. A dtriped Hyena scavenging event: implications for Oldowan hominid behavior[J]. Field Notes: A Journal of Collegiate Anthropology, 2016, 8 (1): 122-138
|