

Stratigraphy and chronology of the Gaolingpo site in the Bose Basin, South China
Received date: 2017-09-07
Online published: 2020-07-17
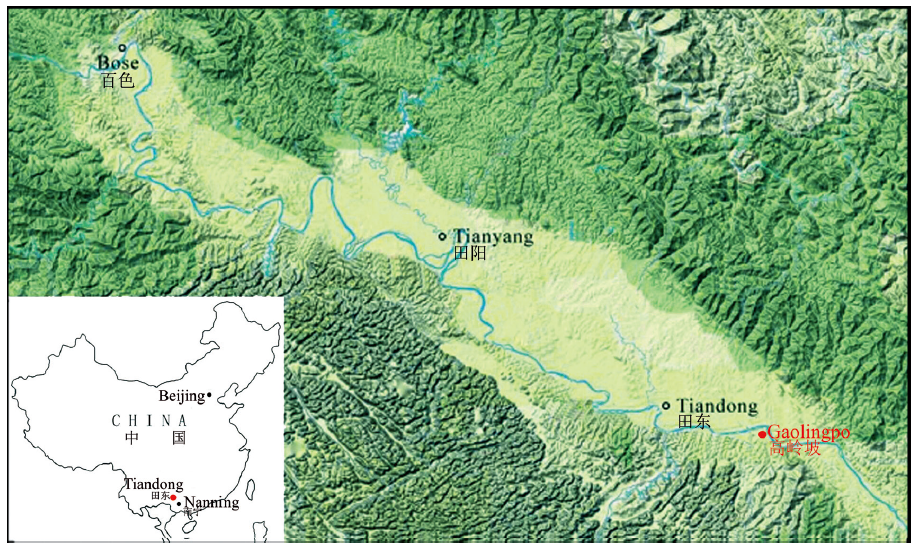
The Palaeolithic industry in the Bose Basin, Guangxi, South China is well known in the international Paleolithic community for its handaxes dating back to 803 kaBP. Seven fluvial terraces were developed in the basin, but the fourth terrace is the most important archaeologically because handaxes and tektites were recovered from this terrace. Since the first site was discovered in 1973, additional sites of the Bose Palaeolithic industry have been investigated and excavated, most of which are located on the fourth terrace. Previous studies concluded that there is only one industrial phase within the depositional sequence of terrace four and its age is 803 kaBP. However, before 2013 no attempt had been made to excavate to the basal gravels from top of the fourth terrace, and therefore the depositional sequence was not completely investigated. Until now, the stratigraphy and the layers from which the stone artifacts derived in terrace four were not clear. In 2013-2014, we conducted an excavation over an area of 200m 2at the Gaolingpo site, which is one of the most important Palaeolithic sites in the Bose Basin. We excavated to the basal gravel deposits from the top of this terrace, and a section of more than 7m thick was exposed, with the stratigraphic layers of Pleistocene and Holocene deposits clearly presented. Furthermore, more than 800 stone artifacts including choppers, picks, and scrapers were recovered from several stratigraphic layers, which have different ages and characteristics. Based on stratigraphic analysis and the stone artifacts, three stages of Palaeolithic cultural remains from the Gaolingpo site are established. The first stage has an age of at least 803 kaBP, the second stage can be dated to 15 kaBP, and the third stage is 10 kaBP.
Key words: Bose Basin; South China; Stratigraphy; Chronology; Cultural sequence; Palaeolithic
Guangmao XIE , Qiang LIN , Minghui YU , Xiaoying CHEN , Zhanghua HU , Huayu LU , Qiuyan HUANG . Stratigraphy and chronology of the Gaolingpo site in the Bose Basin, South China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2020 , 39(01) : 106 -117 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2018.0046
| [1] | 李炎贤, 尤玉柱 . 广西百色发现的旧石器[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1975,13(4):225-228 |
| [2] | 覃圣敏, 覃彩銮, 梁旭达 , 等. 广西新州打制石器地点的调查[J]. 考古, 1983(10):865-868 |
| [3] | 何乃汉, 邱中郎 . 百色旧石器的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1987,6(4):289-297 |
| [4] | 黄慰文, 冷健, 员晓枫 , 等. 对百色石器层位和时代的新认识[J]. 人类学学报, 1990,9(2):105-112 |
| [5] | 曾祥旺 . 广西百色市百谷屯发现的旧石器[J]. 考古与文物, 1996(6):1-8 |
| [6] | Hou YM, Potts R, Yuan BY , et al. Mid-Pleistocene Acheulean-like stone technology oftheBose Basin, South China[J]. Science, 2000,287:1622-1626 |
| [7] | 林强 . 广西百色田东坡西岭旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2002,21(1):59-64 |
| [8] | 谢光茂, 林强, 黄启善 . 百色旧石器 [M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2003: 104-108 |
| [9] | 王頠, 莫敬尤, 黄志涛 . 广西百色盆地大梅南半山遗址发现与玻璃陨石共生的手斧[J]. 科学通报, 2006,51(18):2161-2165 |
| [10] | Xie GM, Bodin E . Les industries paleolithiques du bassin de Bose(Chine du Sud)[J]. L’Anthropologie, 2007,111:182-206 |
| [11] | 裴树文, 陈福友, 张乐 , 等. 百色六怀山旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2007,26(1):1-15 |
| [12] | 谢光茂, 林强 . 百色上宋遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2008,27(1):13-22 |
| [13] | 谢光茂, 林强, 黄鑫 . 百色田东百渡旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2010,29(4):355-371 |
| [14] | 闫少鹏 . 田东坡洪遗址A区发掘简报[A]. 广西考古文集(第4辑), 科学出版社, 2010, 36-62 |
| [15] | 王頠 . 广西百色盆地枫树岛旧石器遗址 [M] . 北京: 科学出版社, 2014 |
| [16] | 邱立诚 . 田阳那满旧石器时代遗址发掘报告[A]. 广西考古文集(第4辑), 科学出版社, 2010: 83-116 |
| [17] | 袁宝印, 侯亚梅, 王頠 , 等. 百色旧石器遗址的若干地貌演化问题[J]. 人类学学报, 1999,18(3):215-224 |
| [18] | 侯亚梅, 高立红, 黄慰文 , 等. 百色高岭坡旧石器遗址1993年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2011,30(1):1-12 |
| [19] | 高立红, 袁俊杰, 侯亚梅 . 百色盆地高岭坡遗址的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2014,33(2):137-148 |
| [20] | 黄志涛 . 广西玻璃陨石初步研究[J]. 地质地球化学, 1995(4):50-54 |
| [21] | Chardin PT, Young CC, Pei WC , et al. On the Cenozoic Formations of Kwangsi and Kwangtung[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of China. 1935,14:179-205 |
| [22] | Derevianko AP, Su NK, Tsybankov AA , et al. The origin of bifacial industry in East and Southeast Asia [M]. Novosibirsk: IAET SB RAS Publishing, 2016 |
| [23] | Ghosh AK, Das R . Palaeolithic Industries of West Bengal[J]. Bulletin of the Cultural Research Institute, 1996,5(1-2):83-93 |
| [24] | 谢光茂, 林强, 韦江 . 百色盆地旧石器时代考古发掘取得重大突破[N]. 中国文物报, 2007-05-04 |
| [25] | Wang W, Bae CJ . How old are the Bose (Baise) Basin (Guangxi, Southern China) bifaces?---The Austalasian tektites question revisited[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015,80:171-174 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |