

A report on 2019 excavation of the Gezishan Locality 15 in Qingtongxia of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region
Received date: 2019-01-11
Revised date: 2019-04-22
Online published: 2020-09-10
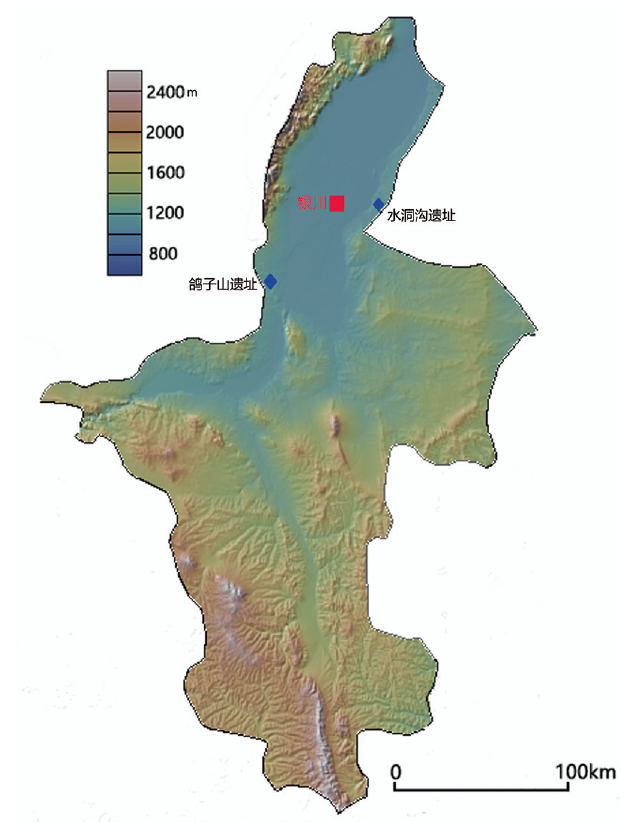
This paper describes the excavation, stratigraphy, and lithic assemblages of locality 15, a Late Pleistocene to Holocene site from the Gezishan site complex. A trench about 16m2was excavated in 2015. Four layers were exposed within more than three meters of sandy sediments. 155 lithic artifacts and three fragile fragments of mammal fossils were unearthed. The lithic assemblages are simple core-and-flake technology. Quartzite pebbles provided the largest number of knapped pieces. Retouched tools are rare but are dominated by scrapers. Considering the gaps in chronology and local environmental change during the Pleistocene and Holocene, the relationship between human activity and climate change should be further investigated in this region.
Key words: Terminal Paleolithic; Ningxia; Gezishan site; Flake assemblage; Gobi
Jialong GUO , Yueyin YAO , Huimin WANG , Decheng LIU , Xiaomei NIAN , Fei PENG . A report on 2019 excavation of the Gezishan Locality 15 in Qingtongxia of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2019 , 38(02) : 182 -190 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2019.0030
| [1] | Andrews RC. The New Conquest of Central Asia: a Narrative of the Explorations of the Central Asiatic Expeditions in Mongolia and China, 1921-1930[M]. The American Museum of Natural History, New York, 1932 |
| [2] | 王晓琨. 内蒙古旧石器时代考古简史[J].内蒙古考古与文物, 2008(2):60-67 |
| [3] | 内蒙古自治区文物考古研究所, 国家博物馆, 阿拉善右旗文物管理所, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善右旗史前文化调查简报. 草原文物, 2014,2:9-15 |
| [4] | 高星, 裴树文, 彭菲, 等. 2004年新疆旧石器考古调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2018,37(4):499-509 |
| [5] | Janz L, Elston RG, Burr GS. Dating North Asian surface assemblages with ostrich eggshell: implications for palaeoecology and extirpation[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2009,36(9):1982-1989 |
| [6] | Janz L, Feathers JK, Burr GS. Dating surface assemblages using pottery and eggshell: Assessing radiocarbon and luminescence techniques in Northeast Asia[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015,57:119-129 |
| [7] | 王惠民, 余军. 青铜峡鸽子山遗址调查报告[C].宁夏考古文集, 宁夏人民出版社, 1994: 1-19 |
| [8] | Madsen DB, Jingzen L, Elston RG, et al. The loess/paleosol record and the nature of the Younger Dryas climate in Central China[J]. Geoarchaeology, 1998,13(8):847-869 |
| [9] | Elston RG, Cheng X, Madsen DB, et al. New dates for the north China Mesolithic[J]. Antiquity, 1997,71(274):985-993 |
| [10] | Nian XM, Zhang WG, Wang ZH, et al. The chronology of a sediment core from incised valley of the Yangtze River delta: Comparative OSL and AMS14C dating[J]. Marine Geology, 2018,395:320-330 |
| [11] | Nian XM, Zhang WG, Sun QL. Optical dating of Holocene sediments from the Yangtze River (Changjiang) Delta, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2018,467:251-263 |
| [12] | Murray AS, Wintle AG. Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2000,32(1):57-73 |
| [13] | de la Torrea I, Mora R. Unmodified lithic material at Olduvai Bed I: Manuports or ecofacts?[J] Journal of Archaeological Science, 2005(32):273-285 |
| [14] | Zhang XL, Ha BB, Wang SJ, et al. The earliest human occupation of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau 40 thousand to 30 thousand years ago. Science, 2018,362(6418):1049-1051 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |