

An overview of craniofacial reconstruction technology application in physical anthropology
Received date: 2019-10-25
Revised date: 2019-12-22
Online published: 2020-09-11
Facial appearances are one of the most important features of humans. Facial shapes relied heavily on the geometric shape of skulls, craniofacial morphology relationship between skulls and faces and gender, age, ethnic, body mass index (BMI), nutritional status, etc. After the humans’ skeletons are excavated from archaeological sites, facial soft-tissue tissues and muscles usually have been disappeared. It has become one of hot topics for anthropologists and arachnologists to predict the facial appearances of these unidentified skulls. Traditional craniofacial reconstruction (CFR) methods are based on manual technologies that anthropologists collaborated with artists to model a facial appearance on a skull replica with plasticine. During recent thirty years, the improvement of medical image acquisitions technologies and the progress in computer technologies have had a great impact on CFR, and computerized CFR has become one of cutting-edge technologies in the interdisciplinary study of information science, physical anthropology and forensic science. The purpose of this paper is to give an overview of existing manual CFR methods, computerized CFR methods and assessment methods by summarizing the research methods of related literatures. Finally, this paper reviews the progresses of CFR application in physical anthropology and gives some suggestions for further research.
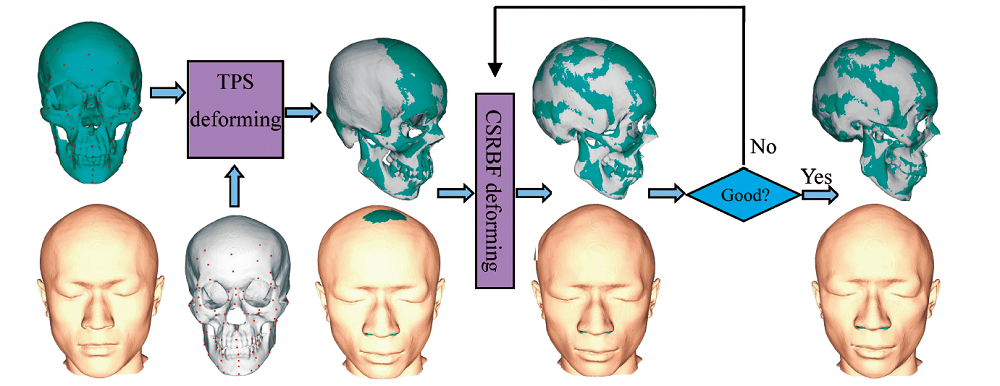
Key words: Cranioface; Reconstruction; Soft-tissue; Assessment
Wuyang SHUI , Qingqiong DENG , Xiujie WU , Yuan JI , Xiaoqun LI , Mingquan ZHOU . An overview of craniofacial reconstruction technology application in physical anthropology[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021 , 40(04) : 706 -720 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0028
| [1] | 周明全, 耿国华, 李康, 等. 颅面形态信息学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016 |
| [2] | Wilkinson C. Computerized forensic facial reconstruction[J]. Forensic Sci Med Pathol, 2005, 1(3):173-177 |
| [3] | Stephan CN. Facial approximation—from facial reconstruction synonym to face prediction paradigm[J]. Journal of forensic sciences, 2015, 60(3):566-571 |
| [4] | Wilkinson C. Facial reconstruction—anatomical art or artistic anatomy?[J]. J Anat, 2010, 216(2):235-250 |
| [5] | Claes P, Vandermeulen D, De Greef S, et al. Computerized craniofacial reconstruction: conceptual framework and review[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2010, 201(1-3):138-145 |
| [6] | Lee WJ, Wilkinson C, Hwang HS. An accuracy assessment of forensic computerized facial reconstruction employing cone-beam computed tomography from live subjects[J]. J Forensic Sci, 2012, 57(2):318-327 |
| [7] | Taylor KT. Forensic Art and Illustration[M]. New York: CRC Press, 2001 |
| [8] | Gerasimov M. The Face Finder[M]. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Co., 1971 |
| [9] | Wilkinson C. Forensic Facial Reconstruction[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004 |
| [10] | Hayes S, Sutikna T, Morwood M. Faces of Homo floresiensis (LB1)[J]. J Archaeol Sci, 2013, 40(12):4400-4410 |
| [11] | Omstead J. Facial reconstruction[J]. Totem: The University of Western Ontario Journal of Anthropology, 2002, 10(1):37-46 |
| [12] | Maltais Lapointe G, Lynnerup N, Hoppa RD. Validation of the new interpretation of Gerasimov’s nasal projection method for forensic facial approximation using CT data[J]. J Forensic Sci, 2016, 61(S1):S193-S200 |
| [13] | 李一波, 王扬扬, 姬晓飞, 等. 计算机辅助颅面复原技术研究[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2006, 11(10):1369-1379 |
| [14] | 徐长苗, 梁荣华. 计算机辅助技术的三维颅面复原研究现状与进展[J]. 刑事技术, 2008, 2:26-28 |
| [15] | 张继宗. 中国法医人类学三十年[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(3):256-263 |
| [16] | Nelson LA, Michael SD. The application of volume deformation to three-dimensional facial reconstruction: a comparison with previous techniques[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 1998, 94(3):167-181 |
| [17] | 周明全, 耿国华, 范江波. 计算机辅助的颅骨面貌复原技术[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 27(5):375-378 |
| [18] | Stephan CN, Caple JM, Guyomarc’h P, et al. An overview of the latest developments in facial imaging[J]. Forensic sciences research, 2019, 4(1):10-28 |
| [19] | Stephan CN, Simpson EK. Facial soft tissue depths in craniofacial identification (part I): An analytical review of the published adult data[J]. J Forensic Sci, 2008, 53(6):1257-1272 |
| [20] | Stephan CN, Simpson EK. Facial soft tissue depths in craniofacial identification (part II): An analytical review of the published sub-adult data[J]. J Forensic Sci, 2008, 53(6):1273-1279 |
| [21] | Aulsebrook WA, Beckerb PJ, Iscan MY. Facial soft-tissue thicknesses in the adult male Zulu[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 1996, 79(2):83-102 |
| [22] | 税午阳, 周明全, 纪元, 等. 面部软组织厚度测量及其在面貌复原中的应用[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(3):345-353 |
| [23] | Stephan CN, Preisler R. In vivo facial soft tissue thicknesses of adult Australians[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2018, 282:220.e1-220.e12 |
| [24] | Claes P, Vandermeulen D, De Greef S, et al. Craniofacial reconstruction using a combined statistical model of face shape and soft tissue depths: methodology and validation[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2006, 159S:S147-S158 |
| [25] | Utsuno H, Kageyama T, Uchida K, et al. Pilot study of facial soft tissue thickness differences among three skeletal classes in Japanese females[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2010, 195(1-3):165.e1-165.e5 |
| [26] | Kurkcuoglu A, Pelin C, Ozener B, et al. Facial soft tissue thickness in individuals with different occlusion patterns in adult Turkish subjects[J]. HOMO-Journal of Comparative Human Biology, 2011, 62(4):288-297 |
| [27] | 陈廷瑜, 余家树, 钟山, 等. 中国土家族人群头面部软组织厚度的测量[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2005, 20(4):213-215 |
| [28] | Phillips VM, Smuts NA. Facial reconstruction: utilization of computerized tomography to measure facial tissue thickness in a mixed racial population[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 1996, 83(1):51-59 |
| [29] | Wilkinson C, Rynn C, Peters H, et al. A blind accuracy assessment of computer-modeled forensic facial reconstruction using computed tomography data from live subjects[J]. Forensic Sci Med Pathol, 2006, 2(3):179-187 |
| [30] | Dong Y, Huang L, Feng Z, et al. Influence of sex and body mass index on facial soft tissue thickness measurements of the northern Chinese adult population[J]. Forensic Sci Int 2012, 222(1-3):396.e1-396.e7 |
| [31] | Chen F, Chen Y, Yu Y, et al. Age and sex related measurement of craniofacial soft tissue thickness and nasal profile in the Chinese population[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2011, 212(1-3):272.e1-272.e6 |
| [32] | Sipahioglu S, Ulubay H, Diren HB. Midline facial soft tissue thickness database of Turkish population: MRI study[J]. Forensic Sci Int. 2012, 219(1-3):282. e1-282.e8 |
| [33] | Short LJ, Khambay B, Ayoub A, et al. Validation of a computer modelled forensic facial reconstruction technique using CT data from live subjects: a pilot study[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2014, 237:147. e1-147.e8 |
| [34] | Hwang HS, Park MK, Lee WJ, et al. Facial soft tissue thickness database for craniofacial reconstruction in Korean adults[J]. J Forensic Sci, 2012, 57(6):1442-1447 |
| [35] | Bulut O, Sipahioglu S, Hekimoglu B. Facial soft tissue thickness database for craniofacial reconstruction in the Turkish adult population[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2014, 242:44-61 |
| [36] | Baillie LJ, Mirijali SA, Niven BE, et al. Ancestry and BMI Influences on Facial Soft Tissue Depths for A Cohort of Chinese and Caucasoid Women in Dunedin, New Zealand[J]. J Forensic Sci, 2015, 60(5):1146-1154 |
| [37] | Drgáčová A, Dupej J, Velemínská J. Facial soft tissue thicknesses in the present Czech Population[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2016, 260:106.e1-106.e7 |
| [38] | 郭莹, 宋军学, 姚霁航, 等. 基于BMI指数的吉林省长春地区汉族青年面部软组织厚度超声测量及性别差异比较[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2013, 39(5):980-985 |
| [39] | Jia L, Qi B, Yang J, et al. Ultrasonic measurement of facial tissue depth in a Northern Chinese Han population[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2016, 259:247.e1-247.e6 |
| [40] | Wang J, Zhao X, Mi C, et al. The study on facial soft tissue thickness using Han population in Xinjiang[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2016, 266:585.e1-585.e5 |
| [41] | 陈守榕, 邓国顺. 中国汉族成年女性与6个民族成年女性头面部软组织厚度的分析[J]. 人类学学报, 1996, 15(2):178-180 |
| [42] | Shui WY, Zhou MQ, Deng QQ, et al. Densely Calculated Facial Soft Tissue Thickness for Craniofacial Reconstruction in Chinese Adults[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2016, 266:573.e1-573.e12 |
| [43] | Berar M, Tilotta FM, Glaunès JA, et al. Craniofacial reconstruction as a prediction problem using a Latent Root Regression model[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2011, 210(1-3):228-236 |
| [44] | Prieels F, Hirsch S, Hering P. Holographic topometry for a dense visualization of soft tissue for facial reconstruction[J]. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2009, 5:11-16 |
| [45] | Vanezis P, Blowes RW, Linney AD, et al. Application of 3-D computer graphics for facial reconstruction and comparison with sculpting techniques[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 1989. 42(1-2):69-84 |
| [46] | Vanezis P, Vanezis M, McCombe G, et al. Facial reconstruction using 3-D computer graphics[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2000, 108(2):81-95 |
| [47] | Shrimpton S, Daniels K, De Greef S, et al. A spatially-dense regression study of facial form and tissue depth: towards an interactive tool for craniofacial reconstruction[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2014, 234:103-110 |
| [48] | De Greef S, Vandermeulen D, Claes P, et al. The influence of sex, age and body mass index on facial soft tissue depths[J]. Forensic Sci Med Pathol, 2009, 5:60-65 |
| [49] | De Greef S, Claes P, Vandermeulen D, et al. Large-scale in-vivo Caucasian facial soft tissue thickness database for craniofacial[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2006, 159S:S126-S146 |
| [50] | Guyomarc’h P, Santos F, Dutailly B, et al. Facial soft tissue depths in French adults: variability, specificity and estimation. Forensic Sci Int, 2013, 231(1-3):411.e1-e10 |
| [51] | 热孜万古丽·夏米西丁, 耿国华, 邓擎琼, 等. 改进的基于特征点软组织厚度的颅面复原方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2016, 33(10):3191-3195 |
| [52] | Pei Y, Zha H, Yuan Z. The Craniofacial Reconstruction from the Local Structural Diversity of Skulls[J]. Comput Graph Forum, 2008, 27(7):1711-1718 |
| [53] | Gietzen T, Brylka R, Achenbach J, et al. A method for automatic forensic facial reconstruction based on dense statistics of soft tissue thickness[J]. PloS one, 2019. 14(1):e0210257 |
| [54] | Deng QQ, Zhou MQ, Shui WY, et al. A novel skull registration based on global and local deformations for craniofacial reconstruction[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2011, 208(1-3):95-102 |
| [55] | Quatrehomme G, Cotin S, Subsol G, et al. A fully three-dimensional method for facial reconstruction based on deformable models[J]. J Forensic Sci, 1997, 42(4):649-652 |
| [56] | Vandermeulen D, Claes P, Loeckx D, et al. Computerized craniofacial reconstruction using CT-derived implicit surface representations[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2006, 159S:S164-S174 |
| [57] | Shui WY, Zhou MQ, Deng QQ, et al. 3D craniofacial reconstruction using reference skull-face database[A]. In: IEEE International Conference on Image and Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ)[C]. 2010: 1-7 |
| [58] | Turner WD, Brown RE, Kelliher TP, et al. A novel method of automated skull registration for forensic facial approximation[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2005, 154(2-3):149-158 |
| [59] | Jiang L, Ma X, Lin Y, et al. Craniofacial reconstruction based on MLS deformation[J]. Wseas Transactions on Computers, 2010, 9(7):758-767 |
| [60] | 梁荣华, 叶钱炜, 古辉, 等. 特征点自动标定的颅面复原及其评估方法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2013, 25(3):322-330 |
| [61] | 税午阳, 周明全, 武仲科, 等. 数据配准的颅骨面貌复原方法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2011, 23(4):607-614 |
| [62] | Miranda GE, Wilkinson C, Roughley M, et al. Assessment of accuracy and recognition of three-dimensional computerized forensic craniofacial reconstruction[J]. Plos One, 2018, 13(5):e0196770 |
| [63] | Kähler K, Haber J, Seidel H. Reanimating the dead: reconstruction of expressive faces from skull data[J]. ACM T Graphic, 2003, 22(3):554-561 |
| [64] | Berar M, Desvignes M, Bailly G, et al. 3D semi-landmarks based statistical face reconstruction[J]. Journal of computing and information technology, 2006, 14(1):31-43 |
| [65] | Hu Y, Duan F, Yin B, et al. A hierarchical dense deformable model for 3D face reconstruction from skull[J]. Multimed Tools Appl, 2013, 64(2):345-364 |
| [66] | Zhang YF, Zhou MQ, Geng GH, et al. Face Appearance Reconstruction Based on a Regional Statistical Craniofacial Model (RCSM)[A]. In: IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition[C]. 2010: 1670-1673 |
| [67] | Duan FQ, Huang DH, Tian Y, et al. 3D face reconstruction from skull by regression modeling in shape parameter spaces[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 151(2):674-682 |
| [68] | Deng QQ, Zhou MQ, Wu ZK, et al. A regional method for craniofacial reconstruction based on coordinate adjustments and a new fusion strategy[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2016, 259:19-31 |
| [69] | Shui WY, Zhou MQ, Maddock S, et al. A PCA-Based method for determining craniofacial relationship and sexual dimorphism of facial shapes[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2017, 90:33-49 |
| [70] | Li Y, Chang L, Qiao X, et al. Craniofacial reconstruction based on least square support vector regression[A]. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC)[C]. 2014: 1147-1151 |
| [71] | Paysan P, Lüthi M, Albrecht T, et al. Face Reconstruction from Skull Shapes and Physical Attributes[C]. Springer: Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Pattern Recognition, 2009: 232-241 |
| [72] | 赵俊莉, 武仲科, 刘翠婷, 等. 形状空间下的3D面貌相似性比较[J]. 光学精密工程, 2015, 23(4):1138-1145 |
| [73] | 李红艳, 武仲科, 周明全, 等. 基于等测地区域的三维面貌相似度评价方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2012, 38(13):7-21 |
| [74] | Zhao JL, Liu CT, Wu ZK, et al. Craniofacial Reconstruction Evaluation by Geodesic Network[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2014: No.943647 |
| [75] | Bulut O, Jessica LCY, Koca F, et al. Comparison of three-dimensional facial morphology between upright and supine positions employing three-dimensional scanner from live subjects[J]. Leg Med, 2017, 27:32-37 |
| [76] | 税午阳, 吴秀杰. 奇和洞古人类头骨面貌的三维虚拟复原[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(8):745-754 |
| [77] | Verzé L. History of facial reconstruction[J]. Acta Biomed, 2009, 80:5-12 |
| [78] | Fatuzzo G, Sequenzia G, Oliveri SM. Virtual anthropology and rapid prototyping: A study of Vincenzo Bellini’s death masks in relation to autopsy documentation[J]. Digital Applications in Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, 2016, 3(4):117-125 |
| [79] | Hayes S. Faces in the museum: revising the methods of facial reconstructions[J]. Mus Manag Curatorship, 2016, 31(3):218-245 |
| [80] | Kustar A. The facial restoration of Antal Simon, a Hungarian priest-teacher of the 19th c[J]. HOMO-Journal of Comparative Human Biology, 2004, 55(1-2):77-90 |
| [81] | Benazzi S, Fantini M, Crescenzio FD, et al. The face of the poet Dante Alighieri reconstructed by virtual modelling and forensic anthropology techniques[J]. J Archaeol Sci, 2009, 36(2):278-283 |
| [82] | Benazzi S, Bertelli P, Lippi B, et al. Virtual anthropology and forensic arts: the facial reconstruction of Ferrante Gonzaga[J]. J Archaeol Sci, 2010, 37(7):1572-1578 |
| [83] | Marić J, Bašića Ž, Jerković I, et al. Facial reconstruction of mummified remains of Christian Saint-Nicolosa Bursa[J]. J Cult Herit, 2020, 42:249-254 |
| [84] | 吴汝康, 吴新智, 王存义. 中国猿人女性头象的复原[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1959, 3(1):147-150 |
| [85] | 张建军. 谈谈我国古人类化石面貌复原像[J]. 大自然, 2011, 3:24-26 |
| [86] | 张建军. 从北京猿人到南京猿人的面貌复原[J]. 化石, 2015, 2:66-69 |
| [87] | Silvestri M, Tomezzoli G. 3D Facial Reconstruction of an Ancient Female Skull from Oberkassel bei Bonn (Germany)[A]. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Topical Conference Ancient Inhabitants of Europe[C]. 2006, 229-235 |
| [88] | Lee WJ, Yoon AY, Mi KS, et al. The archaeological contribution of forensic craniofacial reconstruction to a portrait drawing of a Korean historical figure[J]. J Archaeol Sci, 2014, 49:228-236 |
| [89] | Hamre SS, Ersland GA, Daux V, et al. Three individuals, three stories, three burials from medieval Trondheim, Norway[J]. PloS one, 2017, 12(7):e0180277 |
| [90] | Gualdi-Russo E1, Zaccagni L, Russo V. Giovanni Battista Morgagni: facial reconstruction by virtual anthropology[J]. Forensic Sci Med Pathol, 2015, 11(2):222-227 |
| [91] | 朱泓, 周慧, 林雪川. 老山汉墓女性墓主人的种族类、DNA分析和颅像复原[J]. 文物, 2004, 2:21-27 |
| [92] | 郭剑峰. 公主重生记颅面复原技术再现盛唐公主真容[J]. 科技潮, 2011, 11:22-25 |
| [93] | Cui YM, Wu XZ. A geometric morphometric study of a Middle Pleistocene cranium from Hexian, China[J]. J Hum Evol, 2015, 88:54-69 |
| [94] | Li ZY, Wu XJ, Zhou LP, et al. Late Pleistocene archaic human crania from Xuchang, China[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328):969-972 |
| [95] | Li X, Yin Z, Wei L, et al. Symmetry and template guided completion of damaged skulls[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2011, 35(4):885-893 |
| [96] | 税午阳, 周明全, 杜国光, 等. 颅骨三维模型制作和数据库的构建[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2016, 31(1):1-4 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |