

Chronology of lithic artifact sites and hominin distribution from Early to Middle Pleistocene in China
Received date: 2020-11-25
Revised date: 2021-01-29
Online published: 2021-06-24
Hominin fossils and Paleolithic sites of Early and Middle Pleistocene in China can provide information to understand hominin behavioral and living environments, while a chronological framework is the basis for analyzing hominin evolution, migration, and relationship with climate change during the Pleistocene era. In the past 20 years, hominin records in China steadily increased because of the Paleolithic excavation and the advancement of dating techniques, providing amplified materials for establishing age frameworks. This study analyzed 95 Early to Middle Pleistocene sites with numerical age estimates. The distribution patterns are shown under the loess-paleosol chronology constraints and a relatively continuous chronology of hominin activities is established from approximately 2 MaBP to the last interglacial period. These sites are mainly distributed in four regions of the Nihewan Basin and the adjacent Zhoukoudian, Qingling Mountains Range, and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and South China, where the maximum intensity of hominin activities occurred in order during the Early Pleistocene, Middle Pleistocene, and in the late part of Middle Pleistocene, respectively. Various excavated sites still lack chronological study or encounter issues in dating. Therefore, improvement of chronological study is necessary.
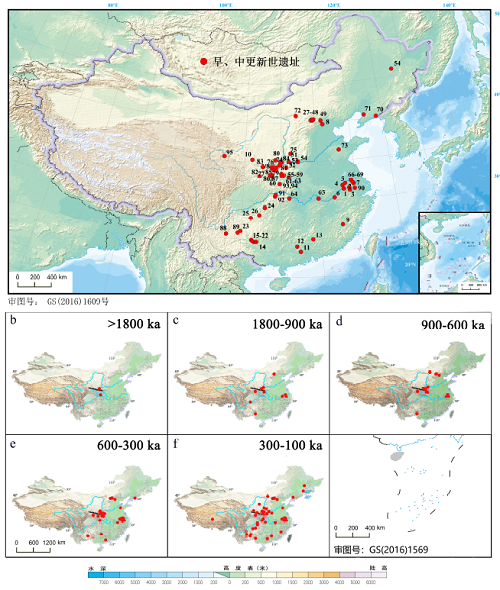
Ying LU , Xuefeng SUN , Shejiang WANG , Huayu LU . Chronology of lithic artifact sites and hominin distribution from Early to Middle Pleistocene in China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021 , 40(03) : 411 -426 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0038
| [1] | Sun X, Lu H, Wang S, et al. Hominin distribution in Glacial-Interglacial Environmental changes in the Qinling Mountains Range, Central China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018,198:37-55 |
| [2] | Bae CJ, Li F, Cheng LL, et al. Hominin distribution and density patterns in Pleistocene China: Climatic influences[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018,512:118-131 |
| [3] | Yang SX, Yue JP, Zhou XY, et al. Hominin site distributions and behaviours across the Mid-Pleistocene climate transition in China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020,248:106614 |
| [4] | 钱方, 周国兴. 元谋第四纪地质与古人类[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991 |
| [5] | Zhu RX, Potts R, Pan YX, et al. Early evidence of the genus homo in east Asia[J]. Journal of Human Evolution. 2008,55(6):1075-1085 |
| [6] | 贾兰坡. 蓝田猿人头骨发现经过及地层概况[J]. 科学通报, 1965,6:477-481 |
| [7] | An ZS, Ho CK. New magnetostratigraphic dates of Lantian Homo erectus[J]. Quaternary Research, 1989,32(2):213-221 |
| [8] | Zhu ZY, Dennell R, Huang WW, et al. New dating of the homo erectus cranium from Lantian (Gongwangling), China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015,78:144-157 |
| [9] | 阎桂林. 湖北“郧县人”化石地层的磁性地层学初步研究[J]. 地球科学, 1993,18(2):221-226 |
| [10] | Lumley H, Li TY. Le Site de l’Homme de Yunxian. Quyuanhekou, Quingqu, Yunxian Province du Hubei[M]. Paris: CNRS éditions, 2008 |
| [11] | 陈铁梅, 周力平. 周口店北京猿人遗址的年代综述兼评该遗址的铝铍埋藏年龄[J]. 人类学学报, 2009,28(3):285-291 |
| [12] | 黄万波, 方笃生, 叶永相. 安徽和县猿人化石及有关问题的初步研究[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1982,20(3):248-256 |
| [13] | Grün R, Huang PH, Huang W, et al. ESR and U-series analyses of teeth from the palaeoanthropological site of Hexian, Anhui Province, China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 1998,34(6):555-564 |
| [14] | 吴汝康, 李星学, 等(主编). 南京直立人[M]. 南京: 江苏科技出版社, 2002 |
| [15] | Wu XZ, Athreya S. A description of the geological context, discrete traits, and linear morphometrics of the Middle Pleistocene hominin from Dali, Shaanxi Province, China[J]. American journal of Physical Anthropology, 2013,150(1):141-157 |
| [16] | Shen GJ, Ku TL, Cheng H, et al. High-precision U-series dating of Locality I at Zhoukoudian , China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2001,41(6):679-688 |
| [17] | Shen G, Gao X, Gao B, et al. Age of Zhoukoudian Homo erectus determined with 26Al/10Be burial dating [J]. Nature, 2009,458(7235):198-200 |
| [18] | Xiao J, Jin C, Zhu YZ. Age of the fossil Dali Man in north-central China deduced from chronostratigraphy of the loess-paleosol sequence[J]. Quaternary Science Review. 2002,21(20-21):2191-2198 |
| [19] | Yin GM, Bahain JJ, Shen GJ, et al. ESR/U-series study of teeth recovered from the palaeoanthropological stratum of the Dali Man site (Shaanxi Province, China)[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2011,1(6):98-105 |
| [20] | Sun XF, Yi SW, Lu HY, et al. TT-OSL and post-IR IRSL dating of the Dali Man site in central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017,434(A):99-106 |
| [21] | Zhang JF, Huang WW, Hu Y, et al. Optical dating of flowstone and silty carbonate-rich sediments from Panxian Dadong Cave, Guizhou, southwestern China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015,30(B):479-486 |
| [22] | 刘武, 吴秀杰, 邢松, 等. 中国古人类化石[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014 |
| [23] | 孙雪峰, 陆莹, 文少卿. 中国古人类遗址年代学问题[J]. 科学通报, 2020,65(20):2136-2144 |
| [24] | 朱照宇, 黄慰文, 吴翼, 等. 黄土高原黄土地层古人类遗迹年代研究新进展[J]. 科学通报, 2019,64(25):2641-2653 |
| [25] | Ao H, Shen GJ, Granger D, et al. Isochron 26Al/10Be burial dating of the Lantian Hominin site at Gongwangling in Northwestern China [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2017,41:174-179 |
| [26] | 高星. “元谋人”的年龄及相关的年代问题讨论[J]. 人类学学报, 2015,34(4):442-450 |
| [27] | Luo L, Granger DE, Tu H, et al. The first radiometric age by isochron 26Al/10Be burial dating for the Early Pleistocene Yuanmou hominin site, southern China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2020,55:101022 |
| [28] | 宫希成, 郑龙亭, 邢松, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞出土的人类化石[J]. 人类学学报, 2014,33(4):427-436 |
| [29] | Wu XJ, Pei S, Cai Y, et al. Archaic human remains from Hualongdong, China, and Middle Pleistocene human continuity and variation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2019,116:9820-9824 |
| [30] | Chen FH, Welker F, Shen C, et al. A Late Middle Pleistocene Denisovan mandible from the Tibetan plateau[J]. Nature, 2019,569:409-412 |
| [31] | 卫奇, 裴树文, 贾真秀, 等. 泥河湾盆地黑土沟遗址[J]. 人类学学报, 2016,35(1):43-62 |
| [32] | 唐锐枰, 葛俊逸, 庞海娇, 等. 泥河湾黑土沟剖面磁组构特征及古湖水文环境变化[J]. 科学通报, 2020,65:1027-1045 |
| [33] | Huang S, Wang W, Bae CJ, et al. Recent Paleolithic field investigations in Bose Basin (Guangxi, China)[J]. Quaternary International, 2012,281:5-9 |
| [34] | Xu G, Wang W, Bae C J, et al. Spatial distribution of Paleolithic sites in Bose Basin, Guangxi, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2012,281(19):10-13 |
| [35] | Wang W, Bae CJ. How old are the Bose (Baise) Basin (Guangxi, southern China) bifaces? The Australasian tektites question revisited[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015,80:171-174 |
| [36] | Langbroek M. Do tektites really date the bifaces from the Bose (Baise) Basin, Guangxi, southern China?[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015,80:175-178 |
| [37] | Hou Y, Potts R, Yuan B, et al. Mid-Pleistocene Acheulean-like stone technology of the Bose Basin, South China[J]. Science, 2000,287(5458):1622-1626 |
| [38] | Wang W, Bae CJ, Huang SM, et al., Middle Pleistocene bifaces from Fengshudao (Bose Basin, Guangxi, China)[J], Journal of Human Evolution, 2014,69:110-122 |
| [39] | 高星. 七十年的探索历程——中国旧石器时代考古学的回顾与展望[N]. 中国文物报,2019-9-6(005) |
| [40] | Maxwell SJ, Hopley PJ, Upchurch P, et al. Sporadic sampling, not climatic forcing, drives observed early hominin diversity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2018,115(19):4891-4896 |
| [41] | Han F, Bahain J, Deng C L, et al. The earliest evidence of hominid settlement in China: Combined electron spin resonance and uranium series (ESR/U-series) dating of mammalian fossil teeth from Longgupo cave[J]. Quaternary International, 2017,432(A):75-83 |
| [42] | Zhu RX, Potts R, Xie F, et al. New evidence on the earliest human presence at high northern latitudes in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2004,431(7008):559-562 |
| [43] | Wang W, Richard P, Hou YM, et al. Early Pleistocene hominid teeth recovered in Mohui cave in Bubing Basin, Guangxi, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bullient, 2005,50(23):2777-2782 |
| [44] | Shao QF, Bahain J, Wang W, et al. Coupled ESR and U-series dating of early Pleistocene Gigantopithecus faunas at Mohui and Sanhe Caves, Guangxi, southern China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015,30(B):524-528 |
| [45] | 于汇历, 董为. 黑龙江阿城交界洞穴遗址的哺乳动物群[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011,31(4):675-675 |
| [46] | 汪英华. 大窑遗址四道沟地点年代测定及文化分期[J]. 草原文物, 2002,1:6-11 |
| [47] | 辽宁省博物馆本溪市博物馆. 庙后山——辽宁省本溪市旧石器文化遗址[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1986 |
| [48] | 张丽, 沈冠军, 傅仁义, 等. 辽宁本溪庙后山遗址铀系测年初步结果[J]. 东南文化, 2007,3:54-57 |
| [49] | 郑公望, 康永洙. 金牛山人遗址下部地层的热释光断代[J]. 人类学学报, 1994,13(3):257-259 |
| [50] | Chen T M, Yang Q, Wu E. Antiquity of Homo sapiens in China[J]. Nature, 1994,6466:55-56 |
| [51] | Han F, Sun C, Bahain J, et al. Coupled ESR and U-series dating of fossil teeth from Yiyuan hominin site, northern China[J]. Quaternary International. 2016,400:195-201 |
| [52] | Guo Y, Sun C, Luo L, et al. 26Al/10Be burial dating of the Middle Pleistocene Yiyuan hominin fossil site, Shandong Province, Northern China[J]. Scientific Reports. 2019,9:6961 |
| [53] | Nian X, Li F, Chen F, et al. Optically stimulated luminescence ages for human occupation during the penultimate glaciation in the western Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2016,31(8):e2917 |
| [54] | 同号文, 胡楠, 韩非. 河北阳原泥河湾盆地山神庙咀早更新世哺乳动物群的发现[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011,31(4):643-653 |
| [55] | Liu P, Deng CL, Li SH, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Huojiadi Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010,298(3-4):399-408 |
| [56] | Wang HQ, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Donggutuo and Maliang Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin,North China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2005,64(1):1-11 |
| [57] | 王红强, 邓成龙, 朱日祥, 等. 泥河湾盆地岑家湾旧石器遗址的古地磁定年[J]. 中国科学, 2006,36(3):273-279 |
| [58] | Deng CL, Xie F, Liu CC, et al. Magnetochronology of the Feiliang Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin and implications for early human adaptability to high northern latitudes in East Asia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007,34:L14301 |
| [59] | Ao H, An ZS. High-resolution record of geomagnetic excursions in the Matuyama chron constrains the ages of the Feiliang and Lanpo paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012,13(8):1-1 |
| [60] | 贾真秀, 裴树文, 马宁, 等. 泥河湾盆地麻地沟E6和E7旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2016,35(3):343-358 |
| [61] | 裴树文, 贾真秀, 马东东, 等. 泥河湾盆地麻地沟E5旧石器地点的遗址成因与石器技术[J]. 人类学学, 2016,35(4):493-508 |
| [62] | Pei S, Deng C, de la Torre L, et al. Magnetostratigraphic and archaeological records at the Early Pleistocene site complex of Madigou (Nihewan Basin): Implications for human adaptations in, North China[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2019,530:176-189 |
| [63] | Liu CR, Yin GM, Deng CL, et al. ESR dating of the Majuangou and Banshan paleolithic sites in the Nihewan basin, north China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2014,73(4):58-63 |
| [64] | 卫奇, 裴树文, 敖红, 等. 泥河湾盆地葡萄园旧石器遗址[J]. 人类学学报, 2016,35(3):321-330 |
| [65] | Zhu RX, Hoffman KA, Potts R, et al. Earliest presence of humans in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2001,413(6854):413-417 |
| [66] | Deng CL, Wei Q, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic age of the Xiantai Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin and implications for early human colonization of Northeast Asia[J]. Earth Planet Science Letter, 2006,244(1-2):336-348 |
| [67] | 王法岗. 泥河湾盆地南山边遗址发现的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2016,35(3):331-342 |
| [68] | Ao H, Mark JD, Wei Q, et al. New evidence for early humans in North China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013,3:2403 |
| [69] | 朱日祥, 邓成龙, 潘永信. 泥河湾盆地磁性地层定年与早期人类演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007,27(6):922-944 |
| [70] | 陈曦, 赵海龙, 张贝, 等. 泥河湾盆地石沟遗址B区掘告[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017,37(4):895-907 |
| [71] | 刘连强, 王法岗, 杨石霞, 等. 泥河湾盆地马梁遗址第10地点2016年出土石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2018,3:419-427 |
| [72] | 庞其清, 牛树银, 孙爱群, 等. 泥河湾盆地晚新生代介形类生物地层和旧石器文化遗存地层及环境演化的探讨[J]. 石家庄经济学院学报, 2017,40(1):13-40 |
| [73] | 左天文, 成洪江, 刘平, 等. 泥河湾盆地后沟旧石器遗址的磁性地层学定年[J]. 中国科学, 2012,42(1):94-102 |
| [74] | Guo YJ, et al. Luminescence Ages for Three‘Middle Paleolithic’Sites in the Nihewan Basin, Northern China, and Their Archaeological and Palaeoenvironmental Implications[J]. Quaternary Research, 2016,85(3):456-470 |
| [75] | 刘春茹, 尹功明, 高璐, 等. 泥河湾盆地东坡遗址ESR 年代学初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2009,29(1):166-172 |
| [76] | 李文朋, 刘春茹, 牛东伟, 等. 怀来盆地珠窝堡遗址ESR年代学初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018,38(3):680-687 |
| [77] | 贾兰坡, 盖培, 尤玉桂. 山西峙峪旧石器时代遗址发掘报告[J].考古学报, 1972(1):39-58 |
| [78] | Liu Y, Hu Y, Wei Q. Early to Late Pleistocene human settlements and the evolution of lithic technology in the Nihewan Basin, North China: A macroscopic perspective[J]. Quaternary International, 2013,295:204-214 |
| [79] | 袁宝印, 夏正楷, 牛平山. 泥河湾裂谷与古人类[M].地质出版社, 2011, 132-188 |
| [80] | Yang SX, Deng C, Zhu RX, et al. The Paleolithic in the Nihewan Basin, China: Evolutionary history of an Early to Late Pleistocene record in Eastern Asia[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology Issues News and Reviews. 2019,29(2):125-142 |
| [81] | 蔡保全, 李强, 郑绍华. 泥河湾盆地马圈沟遗址化石哺乳动物及年代讨论[J]. 人类学学报, 2008,27(2):127-140 |
| [82] | Gao X, Wei Q, Shen C, et al. New Light on the Earliest Hominid Occupation in East Asia.[J]. Current Anthropology, 2005,46:115-121 |
| [83] | Shen C, Zhang XL, Gao X. Zhoukoudian in transition: Research history, lithic technologies, and transformation of Chinese Palaeolithic archaeology[J]. Quaternary international, 2016,400:4-13 |
| [84] | 陈铁梅, 原思训, 高世君, 等. 许家窑遗址哺乳动物化石的铀子系法年代测定[J]. 人类学学报, 1982,1:91-95 |
| [85] | 邓成龙, 郝青振, 郭正堂, 等. 中国第四纪综合地层和时间框架[J]. 中国科学, 2019,49(1):334-356 |
| [86] | 王法岗, 李锋. “许家窑人”埋藏地层与时代探讨[J]. 人类学学报, 2020,39(2):161-172 |
| [87] | Li Z, Xu Q, Zhang S, et al. Study on stratigraphic age, climate changes and environment background of Houjiayao site in Nihewan Basin[J]. Quatern Int, 2014,349:42-48 |
| [88] | 戴尔俭, 计宏祥. 陕西蓝田发现之旧石器[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1964,8(2):152-161 |
| [89] | 戴尔俭. 陕西蓝田公王岭及其附近的旧石器[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1966,10(1):32-36 |
| [90] | 吴新智, 袁振新, 韩德芬, 等. 陕西蓝田公王岭猿人地点1965年发掘报告[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1966,10(1):25-31 |
| [91] | 黄慰文, 祁国琴. 梁山旧石器遗址的初步观察[J]. 人类学学报, 1987,6(3):236-244 |
| [92] | 薛祥煦. 陕西洛南人牙化石及其地质时代[J]. 人类学学报, 1987,6(4):284-288 |
| [93] | 李天元, 王正华, 李文森, 等. 湖北省郧县曲远河口化石地点调查与试掘[J]. 江汉考古, 1991,2:1-14 |
| [94] | Li TY, Etler DA. New Middle Pleistocene Hominid crania from Yunxian in China[J]. Nature, 1992,357:404-407 |
| [95] | 王社江, 黄培华. 洛南盆地旧石器遗址地层划分及年代研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2001,20(3):229-237 |
| [96] | 王社江, 张小兵, 沈辰, 等. 洛南花石浪龙牙洞1995年出土石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2004,23(2):93-110 |
| [97] | 王社江, 沈辰, 胡松梅, 等. 洛南盆地1995—1999年野外地点发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2005,24(2):87-103 |
| [98] | 王社江, 鹿化煜, 张红艳, 等. 东秦岭南洛河中游地区发现的旧石器和黄土堆积[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008,28(6):988-999 |
| [99] | 王社江, 刘顺民. 东秦岭山地商洛市和山阳县新发现的两处旧石器地点[J]. 考古与文物,2011, 1: 24-28+52 |
| [100] | 王社江, 张小兵, 鹿化煜, 等. 丹江上游商丹盆地新发现的旧石器及其埋藏黄土地层[J]. 人类学学报, 2013,32(4):421-431 |
| [101] | 冯小波. 郧县人遗址石核的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2004,23(1):1-12 |
| [102] | 陕西省考古研究院, 商洛地区文管会, 洛南县博物馆. 花石浪(I):洛南盆地旷野类型旧石器地点群研究 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007 |
| [103] | 陕西省考古研究院. 花石浪(II):洛南花石浪龙牙洞遗址发掘报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008 |
| [104] | 裴树文, 高星, 冯兴无, 等. 三峡地区更新世人类适应生存方式[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006,26(4):534-542 |
| [105] | 杜水生, 刘富良, 朱世伟, 等. 河南卢氏发现黄土旧石器[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008,28(6):1000-1006 |
| [106] | 杜水生, 刘富良, 朱世伟, 等. 洛宁县发现黄土石器工业[J]. 考古与文物, 2010,2:14-17 |
| [107] | 鹿化, 张红艳, 王社江, 等. 东秦岭南洛河上游黄土地层年代的初步研究及其在旧石器考古中的意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007,27(4):559-567 |
| [108] | 鹿化煜, 张红艳, 孙雪峰, 等. 中国中部南洛河流域地貌、黄土堆积与更新世古人类生存环境[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012,32(2):167-177 |
| [109] | 周振宇, 王春雪, 高星. 丹江口北泰山庙旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2009,28(3):246-261 |
| [110] | 李浩, 李超荣, 冯兴无. 2004年丹江口库区调查发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2012,31(2):113-126 |
| [111] | 李浩, 李超荣, Kathleen K, 等. 丹江口库区第四级阶地旧石器遗址调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2017,36(2):145-153 |
| [112] | Sun XF, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Early human settlements in the southern Qinling Mountains, central China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017,164:168-186 |
| [113] | 王社江, 鹿化煜, 张红艳, 等. 陕西蓝田地区新发现黄土地层中的旧石器及其年代[J]. 科学通报, 2014,59:1318-1326 |
| [114] | Zhuo HX, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Chronology of newly-discovered paleolithic artifact assemblages in Lantian (Shaanxi province), central China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2016,86:316-325 |
| [115] | Lu HY, Zhuo HX, Zhang WC, et al. Earth surface processes and their effects on human behavior in monsoonal China during the Pleistocene-Holocene epochs[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2017,27(11):1311-1324 |
| [116] | 李超荣, 冯兴无, 李浩. 1994年丹江口库区调查发现的石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2009,28(4):337-354 |
| [117] | 夏文婷, 王社江, 夏楠, 等. 汉中盆地龙岗寺遗址第3地点出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2018,37(4):33-45. |
| [118] | 别婧婧, 王社江, 夏楠, 等. 陕西汉中洋县金水河口旧石器遗址出土石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2019,38(3):344-361 |
| [119] | Lu HY, Sun X, Wang S, Cosgrove R, et al. Ages for hominin occupation in Lushi Basin, middle of South Luo River, central China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2011,60(5):612 |
| [120] | Lu H, Zhang H, Wang S, et al. Multiphase timing of hominin occupations and the paleoenvironment in Luonan Basin, Central China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2011,76(1):142-147 |
| [121] | 邢路达, 王社江, 张改课, 等. 陕西洛南盆地夜塬地点发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2015,34(1):1-13 |
| [122] | 于青瑶, 王晓勇, 刘全玉, 等. 洛南盆地槐树坪地点2013年出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2017,36(2):154-164 |
| [123] | Lu HY, Zhang HY, Sun XF, et al. Landform, Loess Deposit and Paleoenrivonmental Changes in the South Luohe River (Central China) during the Hominin Occupations[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012,32:167-177 |
| [124] | 徐行华, 孙雪峰, 宁有丰, 等. 铀系不平衡测年法在我国秦岭南麓黄土钙结核中的应用[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020,40(1):40-48 |
| [125] | 王社江, 鹿化煜. 秦岭地区更新世黄土地层中的旧石器埋藏与环境[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2016,46:881-890 |
| [126] | Sun XF, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Ages of Liangshan Paleolithic sites in Hanzhong Basin, Central China. Quaternary Geochronology 2012,10:380-386 |
| [127] | Sun XF, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. TT-OSL dating of Longyadong Middle Paleolithic site and paleoenvironmental implications for hominin occupation in Luonan Basin (central China)[J]. Quaternary Research, 2013,79:168-174 |
| [128] | Sun XF, Li YH, et al. Pedostratigraphy of aeolian deposition near the Yunxian Man site on the Hanjiang River terraces, Yunxian Basin, central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016,400:187-194 |
| [129] | Wang KX, Xu XH, Sun XF, et al. Cosmogenic nuclide burial dating of Liuwan Paleolithic site in the Luonan Basin, Central China[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2019,29(3):406-416 |
| [130] | 安芷生, 高万一, 祝一志, 等. “蓝田人”的磁性地层年龄[J]. 人类学学报, 1990,9:1-7 |
| [131] | 程国良, 李瑞林. 林金禄蓝田人地层年代的探讨[A].见:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所(编).古人类论文集 [C]. 北京:科学出版社, 1978: 151-157 |
| [132] | 马醒华, 钱方, 李普, 等. “蓝田人”年代的古地磁学研究[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1978,16:238-243 |
| [133] | Tu H, Shen G, Granger D, et al. Isochron, 26Al/10Be burial dating of the Lantian hominin site at Gongwangling in Northwestern China [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2017: S1871101417300079 |
| [134] | Bahain JJ, Shao Q, Han F, et al. Contribution des méthodes ESR et ESR/U-Th à la datation de quelques gisements pléistocènes de Chine[J]. L’Anthropologie, 2017,121:215-233 |
| [135] | Sun X, Lu H, Wang S, Cosgrove R, et al. Age of newly discovered paleolithic assemblages at Liuwan site Luonan Basin, central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014,347(347):193-199 |
| [136] | Zhu R, An Z, Potts R, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of early humans in china[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2003,61(3-4):341-359 |
| [137] | Kong P, Jia J, Zheng Y. Cosmogenic 26Al/10Be burial dating of the paleolithic at Xihoudu, North China [J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2013,64(5):466-470 |
| [138] | Shen GJ, Wang YR, Tu H, et al. Isochron 26Al/10Be burial dating of Xihoudu: Evidence for the earliest human settlement in northern China[J]. L Anthropologie, 2020,124(5):102790 |
| [139] | Li X, Ao H, Dekkers M J, et al. Early Pleistocene occurrence of Acheulian technology in North China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017,156(15):12-22 |
| [140] | Kong YF, Deng CL, Liu W, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the hominin occupation of Bailong Cave, central China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018,8:9699 |
| [141] | Liu X, Shen G, Tu H, et al. Initial 26Al/10Be burial dating of the hominin site Bailong cave in Hubei province, central China [J]. Quaternary International, 2015,389(2):235-240 |
| [142] | Han F, Shao Q, Bahain JJ, et al. Coupled ESR and U-series dating of Middle Pleistocene hominin site Bailongdong cave, China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2019,49:291-296 |
| [143] | Li H, Li CR, Kuman K, et al. The Middle Pleistocene handaxe site of Shuangshu in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, central China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2014,52:391-409 |
| [144] | Wang SJ, Huang PH. Stratigraphy and TL Dating of Paleolithic Sites in the Luonan Basin, China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2002(S1):67-77 |
| [145] | 杜水生, 杨丽荣, 刘富良, 等. 洛阳北窑遗址年代再研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011,31(1):16-21 |
| [146] | 陈铁梅, 原思训, 高世君. 铀子系法测定骨化石年龄的可靠性研究及华北地区主要旧石器地点的铀子系年代序列[J]. 人类学学报, 1984,3:259-269 |
| [147] | 王桂增, 黄慰文, 刘有民. 陕西岐山鱼家山旧石器地点的发现[A]. 见:中国地质科学院天津地质矿产研究所文集(5)[C]. 1983: 103-105 |
| [148] | 冯兴祥, 周华山, 巴志刚, 等. “豫灵人”头骨化石的发现与研究[J]. 地域研究与开发, 1993. 12(S1):1-7 |
| [149] | 董哲, 裴树文, 袁四方. 安徽水阳江流域2017年旧石器考古调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2019. 38(2):223-231 |
| [150] | 房迎三, 何未艾, 惠强, 等. 江苏金坛和尚墩旧石器遗址研究:地层、遗迹与年代[J]. 考古学研究, 2008,7:116-135 |
| [151] | 朱诚, 张杨阳, 马春梅, 等. 江苏金坛和尚墩旧石器遗址地层的古地磁年代与磁化率研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 2007,31(1):35-44 |
| [152] | Liu C, Xu X, Yuan B, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of the Qiliting section (SE China) and its implication for geochronology of the red soil sequences in southern China[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2010,174(1):107-117 |
| [153] | 刘彩彩, 邓成龙. 南方红土磁性地层年代学研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2011,18(4):158-170 |
| [154] | 赵其国, 杨浩. 中国南方红土与第四纪环境变迁的初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 1995,15(2):107-116 |
| [155] | 韩立刚. 安徽宣城孙埠镇洋山发现旧石器遗址[J]. 人类学学报, 2006,25(2):172-172 |
| [156] | 郑龙亭. 繁昌人字洞遗址发现、发掘与研究[A].见:安徽省古生物学会.第四届安徽科技论坛——地质古生物遗迹与生态环境保护学术讨论会论文(摘要)汇编[C].合肥:安徽省古生物学会, 2006: 9 |
| [157] | Chen Q, Chen TM, Yang Q. ESR Dating of Early Pleistocene Archaeological Sites in China[A]. In Shen C, Keates SG (eds). Current Research in Chinese Pleistocene Archaeology[M]. Oxford: BAR international series 1179, 2003, 119-126 |
| [158] | 周春林, 汪永进, 程海, 等. 论南京直立人化石的年代[J]. 人类学学报, 1999,18(4):255-262 |
| [159] | 房迎三, 何未艾, 沈冠军, 等. 江苏镇江莲花洞中、晚更新世人类化石地点的新材料[J]. 古生物学报, 2005,44(1):87-95 |
| [160] | Tu H, Shen GJ, Liu XB, et al. U-series dating of hominin fossil-bearing Panlong Cave in Guandong Province, southern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017,434(A):92-98 |
| [161] | 沈冠军, 李建坤, 吉学平. 宜良九乡张口洞的年代:中国 40~100 ka间人类活动的证据[J]. 科学通报, 2004,49(23):2464-2467 |
| [162] | Wei G, Huang W, Bo?da E, et al. Recent discovery of a unique paleolithic industry from the Yumidong Cave site in the three gorges region of Yangtze River, southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2015,434(A):107-120 |
| [163] | Shen GJ, Tu H, Xiao DF, et al. Age of Maba hominin site in southern China: Evidence from U-series dating of Southern Branch Cave[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2014,23:56-62 |
| [164] | Jones HL, Rink WJ, Schepartz LA, et al. Coupled electron spin resonance (ESR)/uranium-series dating of mammalian tooth enamel at Panxian Dadong, Guizhou Province, China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2004,5:965-977 |
| [165] | 沈冠军, 金林红. 桐梓人遗址岩灰洞的铀系年龄[J]. 人类学学报, 1991,10(1):65-72 |
| [166] | 沈冠军, 金林红. 贵州水城硝灰洞的铀系年龄[J]. 中国岩溶, 1992,11(2):155-161 |
| [167] | 原思训, 陈铁梅, 高世君. 华南若干旧石器时代地点的铀系年代[J]. 人类学学报, 1986,5(2):179-190 |
| [168] | 李建军, 陈子文, 余生富. 灵峰洞——福建省首次发现的旧石器时代早期遗址[J]. 人类学学报, 2001,20(4):247-255 |
| [169] | Gao X, Huang WB, Xu ZQ, et al. 120-150ka human tooth and ivory engravings from Xinglongdong cave, three-Gorges region, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bullient. 2004,49:175-180 |
| [170] | Peng HX, Ma ZB, Huang WP, et al. 230Th/U chronology of a paleolithic site at Xinglong Cave in the three-Gorge region of South China [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2014,14:1-9 |
| [171] | 张镇洪. “封开人”——迄今岭南地区最早的人类化石[J]. 岭南文史, 2004,3:15-15 |
| [172] | 彭菲, 裴树文, 马宁, 等. 三峡库区冉家路口旧石器遗址2007年发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2009,28(2):130-146 |
| [173] | Hu Y, Marwick B, Zhang JF, et al. Late Middle Pleistocene Levallois stone-tool technology in Southwest China[J]. Nature, 2019,565:82-85 |
| [174] | 李锋, 李英华, 高星. 贵州观音洞遗址石制品剥片技术辨析[J]. 人类学学报, 2020,39(1):1-11 |
| [175] | Wang W, Mo JY, Huang ZT. Recent discovery of handaxes associated with tektites in the Nanbanshan locality of the Damei site, Bose basin, Guangxi, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bullient, 2008,53:878-883 |
| [176] | 谢光茂, 林强, 余明辉, 等. 广西百色盆地高岭坡遗址的地层及年代[J]. 人类学学报, 2020,39(1):106-117 |
| [177] | 裴树文, 陈福友, 张乐, 等. 百色六怀山旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2007,26(1):1-15 |
| [178] | Huang SM, Wang W, Bae CJ, et al. Recent paleolithic field investigations in Bose Basin (Guangxi, China)[J]. Quaternary International, 2012,281:5-9 |
| [179] | 谢光茂, 林强, 黄鑫. 百色田东百渡旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2010,29(4):355-371 |
| [180] | 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1985 |
| [181] | 刘东生, 施雅风, 王汝建, 等. 以气候变化为标志的中国第四纪地层对比表[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000,20(2):108-128 |
| [182] | An ZS, Liu TS, L YC, et al. The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in Central China[J]. Quaternary International, 1990, (7-8):91-95 |
| [183] | 周力平, Shackleton NJ, Dodonov AE. 欧亚黄土中古地磁极性界线的地层学解释[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000,20(2):196 |
| [184] | 邓成龙, 刘青松, 潘永信, 等. 中国黄土环境磁学[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007,27(2):193-209 |
| [185] | 黄慰文. 中国旧石器文化序列的地层学基础[J]. 人类学学报, 2000,19(4):269-283 |
| [186] | 杨晓燕, 刘东生. 欧亚大陆的黄土带与旧石器早期人类活动[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008,28(6):978-987 |
| [187] | Ranov V. The ‘Loessic Palaeolithic’ in South Tadjikistan, Central Asia: Its industries, chronology and correlation[J]. Quaternary ence Reviews, 1995,14(7-8):731-745 |
| [188] | 刘东生. 黄土旧石器工业[A].见:徐钦琦,谢飞,王建(主编).史前考古学新进展——庆贺贾兰坡院士九十华诞国际学术讨论会文集[C] 北京:科学出版社, 1999: 52-62 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |