

ESR chronology of the Sankeshu Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, North China
Received date: 2020-11-06
Revised date: 2020-12-22
Online published: 2021-06-24
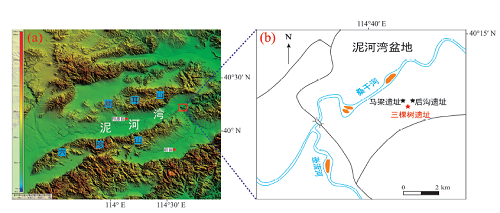
The Nihewan Basin has attracted much attention owing to its well-developed late Mesozoic lacustrine strata and abundant Paleolithic sites and mammalian fossils. More than 100 Paleolithic sites have been found in the basin, which is known in academic circles as the “Olduvai canyon of the East”. Suitable dating materials are lacking; therefore, few independent ages are associated with Middle Pleistocene sites. Sankeshu Paleolithic site is one such example. This situation leaves the study of Paleolithic sites without a sound chronological framework. Electron spin resonance (ESR) dating technology is a dating technology developed in 1960s and has been widely recognized in geological circles. The ESR dating method has obvious advantages for the dating of the Middle Pleistocene sites, especially for the 400-780 kaBP which can not be dated by the Luminescence method. In this paper, we use quartz Ti-Li center ESR method to date four sediment samples at different depths of the Sankeshu site. The age of Sankeshu site is 599±70 kaBP, which provides a necessary chronological basis for understanding the survival and evolution of ancient humans in the Nihewan Basin.
Key words: Nihewan Basin; Sankeshu site; Middle Pleistocene; Paleolithic; ESR; Quartz
Hao JI , Chunru LIU , Weijuan SONG , Chuanyi WEI , Hong AO , Jianping LI , Gongming YIN . ESR chronology of the Sankeshu Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021 , 40(03) : 427 -435 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0081
| [1] | Barbour GB. Preliminary observation in the Kalgan Area[M]. Bulletin of Geological Society of China, 1924,3(2):167-168 |
| [2] | Barbour GB. The deposits of the Sankanho Valley[M]. Bulletin of Geological Society of China, 1925,4(1):53-55 |
| [3] | 卫奇. 在泥河湾层中发现纳玛象头骨化石[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1976,14(1):53-58 |
| [4] | 卫奇. 泥河湾盆地发现177万年前的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2008,27(1):70-70 |
| [5] | 邓成龙, 郝青振, 郭正堂, 等. 中国第四纪综合地层和时间框架[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2019,49(1):330-352 |
| [6] | Zhu RX, Hoffman KA, Potts R, et al. Earliest presence of humans in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2001,413(6854):413-417 |
| [7] | Zhu RX, Potts R, Xie F, et al. New evidence on the earliest human presence at high northern latitudes in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2004,431(7008):559-562 |
| [8] | Deng CL, Wei Q, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic age of the Xiantai Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin and implications for early human colonization of Northeast Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006,244(1-2):336-348 |
| [9] | Deng CL, Xie F, Liu CC, et al. Magnetochronology of the Feiliang Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin and implications for early human adaptability to high northern latitudes in East Asia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007,34(14):1-6 |
| [10] | Deng CL, Zhu RX, Zhang R, et al. Timing of the Nihewan formation and faunas[J]. Quaternary Research, 2008,69(1):77-90 |
| [11] | 谢飞, 李珺, 刘连强. 泥河湾旧石器文化[M]. 石家庄: 花山文艺出版社, 2005: 1-278 |
| [12] | 裴树文. 泥河湾盆地大长梁旧石器地点[J]. 人类学学报, 2002,21(2):116-125 |
| [13] | 裴树文, 李潇丽, 刘德成, 等. 泥河湾盆地东谷坨遗址古人类生存环境探讨[J]. 科学通报, 2009,54(19):2895-2901 |
| [14] | Pei SW, Li XL, Liu DC, et al. Preliminary study on the living environment of hominids at the Donggutuo site, Nihewan Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009,54(21):3896 |
| [15] | Pei SW, Deng CL, Torre DL, et al. Magnetostratigraphic and archaeological records at the Early Pleistocene site complex of Madigou (Nihewan Basin): Implications for human adaptations in North China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019,530:176-189 |
| [16] | Wang HQ, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Donggutuo and Maliang Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2005,64(1):1-11 |
| [17] | Wang HQ, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. Paleomagnetic dating of the Cenjiawan Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, northern China[J]. Science in China Series D, 2006,49(3):295-303 |
| [18] | Liu P, Deng CL, Li SH, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Huojiadi Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010,298(3-4):399-408 |
| [19] | Ao H, Deng CL, Dekkers MJ, et al. Astronomical dating of the Xiantai, Donggutuo and Maliang Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin (North China) and implications for early human evolution in East Asia[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010,297(1):129-137 |
| [20] | Ao H, An ZS, Dekkers MJ, et al. Pleistocene magnetochronology of the fauna and Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin: Significance for environmental and hominin evolution in North China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2013,18:78-92 |
| [21] | 左天文, 成洪江, 刘平, 等. 泥河湾盆地后沟旧石器遗址的磁性地层学定年[J]. 中国科学, 2012,42(1):94-102 |
| [22] | Guo YJ, Li B, Zhang JF, et al. Luminescence ages for three ‘Middle Palaeolithic’ sites in the Nihewan Basin, northern China, and their archaeological and palaeoenvironmental implications[J]. Quaternary Research, 2016,85(3):456-470 |
| [23] | 刘春茹, 尹功明, 高璐, 等. 泥河湾盆地东坡遗址ESR年代学初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2009,29(1):166-170 |
| [24] | Yang SX, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. The Paleolithic in the Nihewan Basin, China: Evolutionary history of an Early to Late Pleistocene record in Eastern Asia[J]. Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews, 2020,29(3):125-142 |
| [25] | Liu CR, Yin GM, Gao L, et al. ESR dating of Pleistocene archaeological localities of the Nihewan Basin, North China-Preliminary results[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2010,5(2-3):385-390 |
| [26] | Liu CR, Yin GM, Fang F, et al. ESR dating of the Donggutuo Palaeolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, northern China[J]. Geochronometria, 2013,40(4):348-354 |
| [27] | Liu CR, Yin GM, Deng CL, et al. ESR dating of the Majuangou and Banshan Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin, North China[J]. Journal of human evolution, 2014,73:58-63 |
| [28] | 侯亚梅, 刘扬, 李英华, 等. 泥河湾盆地三棵树旧石器遗址2008年试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2010,29(3):227-240 |
| [29] | 刘春茹, 尹功明, 高璐, 等. 第四纪沉积物ESR年代学研究进展[J]. 地震地质, 2011,33(2):490-494 |
| [30] | Toyoda S, Voinchet P, Falguères C, et al. Bleaching of ESR signals by the sunlight: A laboratory experiment for establishing the ESR dating of sediments[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2000,52(5):1357-1362 |
| [31] | Tissoux H, Falgurès C, Voinchet P, et al. Potential use of Ti center in ESR dating of fluvial sediment[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2007,2(1-4):367-372 |
| [32] | Walther R, Zilles D. ESR studies on bleached sedimentary quartz[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1994,13(5-7):611-614 |
| [33] | Voinchet P, Falguères C, Laurent M, et al. Artificial optical bleaching of the Aluminium center in quartz implications to ESR dating of sediments[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003,22(10-13):1335-1338 |
| [34] | Liu CR, Grün R. Fluvio-mechanical resetting of the Al and Ti centres in quartz[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2010,46(10), 1038-1042 |
| [35] | Toyoda S, Falguères C. The method to represent the ESR signal intensity of the aluminium hole center in quartz for the purpose of dating[J]. Advances in ESR applications, 2003,20:7-10 |
| [36] | Liu CR, Yin GM, Han F. Effects of grain size on quartz ESR dating of Ti-Li center in fluvial and lacustrine sediments[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015,30:513-518 |
| [37] | Aitken MJ. Introduction to optical dating: the dating of Quaternary sediments by the use of photon-stimulated luminescence[M]. Clarendon Press, 1998 |
| [38] | Duval M, Guilarte V. ESR dosimetry of optically bleached quartz grains extracted from Plio-Quaternary sediment: Evaluating some key aspects of the ESR signals associated to the Ti-centers[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2015,78:28-41 |
| [39] | Lisiecki LE, Raymo ME. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ 18O records [J]. Paleoceanography, 2005,20:1-17 |
| [40] | Sun YB, Yin QZ, Crucifix M, et al. Diverse manifestations of the mid-Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Nature communications, 2019,10(1):1-11 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |