

Received date: 2020-06-01
Online published: 2021-04-09
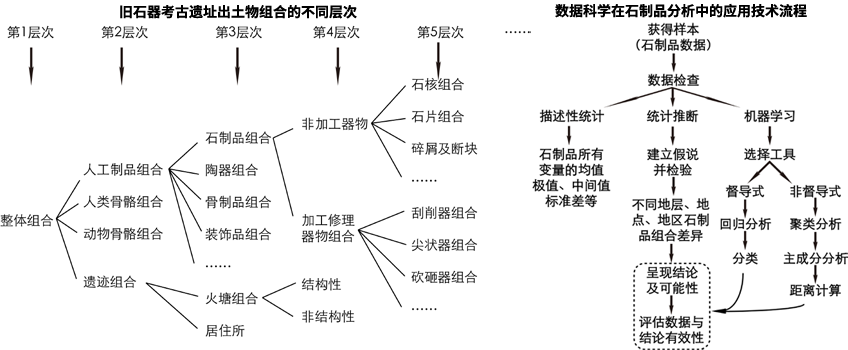
The examination and interpretation to the abstract data has been going since the born of Archaeology. In terms of Paleolithic Archaeology, artifact is considered as the main carrier to convey the prehistoric material and cultural information, and the scientific interpretation of the data extracted from the artifacts has become a key step in the restoration of ancient human history. Data science is the science of dealing with data, which was proposed since 1960s by computer scientist. This discipline has been applied in Archaeological studies within a context of rapid development of computer science and New Archaeology trend since later part of 20th century, especially in Paleolithic branch, which refers to natural science research avenues. According to the definition of data science, the application of this discipline in Paleolithic Archaeology could be summarized as a study of Archaeological data by statistic and mathematical method, with the help of computer program and language, and aiming at the interpretation and reconstruction of prehistoric human society. In this paper, we review the associated definitions and research history, and introduce the main areas of data science which have already engaged with Paleolithic Archaeology research.
Key words: Data Science; Paleolithic; Statistic; Human Behavior; Lithic Technology
Ying GUAN , Zhenyu ZHOU . Data science in Paleolithic Archaeology[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022 , 41(01) : 169 -179 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0009
| [1] | Naur P. Plan for et kursus I datalogi og datamatik (in Dannish, title in English: Outline of a course in data science and data processing)[M]. A/S Regneccentralen, Copenhagen, Denmark, 1966, 64 |
| [2] | Naur P. Concise survey of computer methods[M]. New York: Petrocelli/Charter, 1974, 30 |
| [3] | Cleveland WS. Data Science: An action plan for expanding the technical areas of the field of statistics[J]. International Statistical Review, 2001, 69(1): 21-26 |
| [4] | Ozdemir S. Principles of data science[M]. Birmingham: Packt, Publishing Ltd, 2016 |
| [5] | Clark DL. Analytical Archaeology (Second Edition)[M]. London: Methuen & Co Ltd, 1978 |
| [6] | VanPool TL, Leonard RD. Quantitative analysis in Archaeology[M]. West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell, 2011 |
| [7] | Carlson DL. Quantitative methods in Archaeology using R[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017 |
| [8] | Chorley RJ. Geography and analogue theory[J]. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 1964, 129 |
| [9] | Binford LR, Binford SR. A Preliminary Analysis of Functional Variability in the Mousterian of Levallois Facies[J]. American Anthropologiest, 1966, 68: 238-295 |
| [10] | Binford LR. Contemporary model building: paradigms and the current state of Paleolithic research[A]. In: Clark DL (Eds.). Models in Archaeology[M]. London: Methuen, 1972, 109-166 |
| [11] | Roe DA. A metrical analysis of selected sets of handaxes and cleavers from Olduvai Gorge[A]. In: Leakey MD, Roe DA (Eds.). Olduvai Gorge: excavations in beds III, IV and the masek deds 1968-1971[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994, 146-234 |
| [12] | Callow P. The Olduvai bifaces: Technology and raw materials[A]. In: Leakey MD, Roe DA (Eds.). Olduvai Gorge: excavations in beds III, IV and the masek deds 1968-1971[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994, 235-253 |
| [13] | Roe DA. The Kalambo Falls large cutting tools: a comparative metrical and statistical analysis[A]. In: Clark JD (Eds.). Kalambo Falls prehistoric site III—the early cultures: Middle and Earlier stone age[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001, 492-599 |
| [14] | Isaac GLL, Isaac B. Koobi Fora research project (Volume 5)[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997 |
| [15] | Isaac GLL. Early phases of human behavior: models in Lower Paleolithic archaeology[A]. In: Clark DL(Eds.). Models in Archaeology[M]. London: Methuen, 1972, 167-200 |
| [16] | Doran JE. Mathematics and computers in Archaeology[M]. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 1975 |
| [17] | Shennan S. Quantifying Archaeology[M]. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 1988 |
| [18] | Baxter MJ. Exploratory multivariate analysis in Archaeology[M]. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 1994 |
| [19] | Baxter MJ. Statistics in Archaeology[M]. London: Arnold, 2003 |
| [20] | Drennan RD. Statistics for Archaeologists[M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1996 |
| [21] | Binford LR. Constructing Frames of Reference: An Analytical Method for Archaeological Theory Building Using Ethnographic and Environmental Data Sets[M]. University of California Press, Berkeley, 2001 |
| [22] | 陈铁梅, 陈建立. 简明考古统计学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013 |
| [23] | 裴文中, 张森水. 中国猿人石器研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985 |
| [24] | 李珺, 谢飞. 马圈沟旧石器时代早期遗址发掘报告[A].见:河北省文物研究所.河北省文物考古文集[C]. 北京: 东方出版社, 1998, 30-45 |
| [25] | 中美泥河湾考古队. 飞梁遗址发掘报告[A].见:河北省文物研究所(主编).河北省文物考古文集[C]. 北京: 东方出版社, 1998, 1-30 |
| [26] | 谢飞, 于淑凤. 河北阳原西白马营晚期旧石器研究[J]. 文物春秋, 1989(3): 13-40 |
| [27] | 谢飞. 中国旧石器时代晚期锛状器之研究[A].见:韩国国立忠北大学先史文化研究所,中国辽宁省文物考古研究所.东北亚旧石器文化[C]. 首尔: 白山文化出版社, 1996 |
| [28] | 高星. 周口店第15 关于周口店第15 地点石器类型和加工技术的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2001, 20(1): 1-18 |
| [29] | 高星. 周口店第15 地点剥片技术研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2000, 19(3): 199-215 |
| [30] | 高星. 解析周口店第15地点古人类的技术与行为[A].见:邓涛,王元(主编).第八届中国古脊椎动物学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2001, 183-196 |
| [31] | 陈铁梅. 定量考古学[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2005 |
| [32] | Mendenhall WM, Sincich TL. Statistics for Engineering and the Sciences (Sixth Edition)[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2016 |
| [33] | Clark JS. Models for ecological data: An introduction; statistical computation for environmental sciences in R: lab manual for models for ecological data[M]. Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press, 2007 |
| [34] | 蔡莲珍, 仇士华. 贝叶斯统计应用于碳十四系列样品年代的树轮校正[J]. 考古, 1999(3): 85-91 |
| [35] | 龙腾文, Wagner M, Tarasov PE, 等. 海岱地区史前遗址~(14)C测年数据的贝叶斯分析——审视考古年代学[J]. 东方考古, 2019, 15: 92-112 |
| [36] | Bellot D. Learning probabilistic graphical models in R[M]. Birmingham: Packt Publishing, 2016 |
| [37] | Harrington P. Machine learning in action[M]. New York: Manning Publications Co., 2012 |
| [38] | Li H, Kuman K, Leader GM, Couzens R. Handaxes in South Africa: Two case studies in the early and later Acheulean[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 480: 29-42 |
| [39] | Kolobova KA, Roberts RG, Chabai VP, et al. Archaeological evidence for two separate dispersals of Neanderthals into southern Siberia[J]. PNAS, 117(6): 2879-2885 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |