

Mogera robusta fossils from the Listvenka site, Siberia
Received date: 2020-11-16
Revised date: 2020-12-22
Online published: 2021-12-17
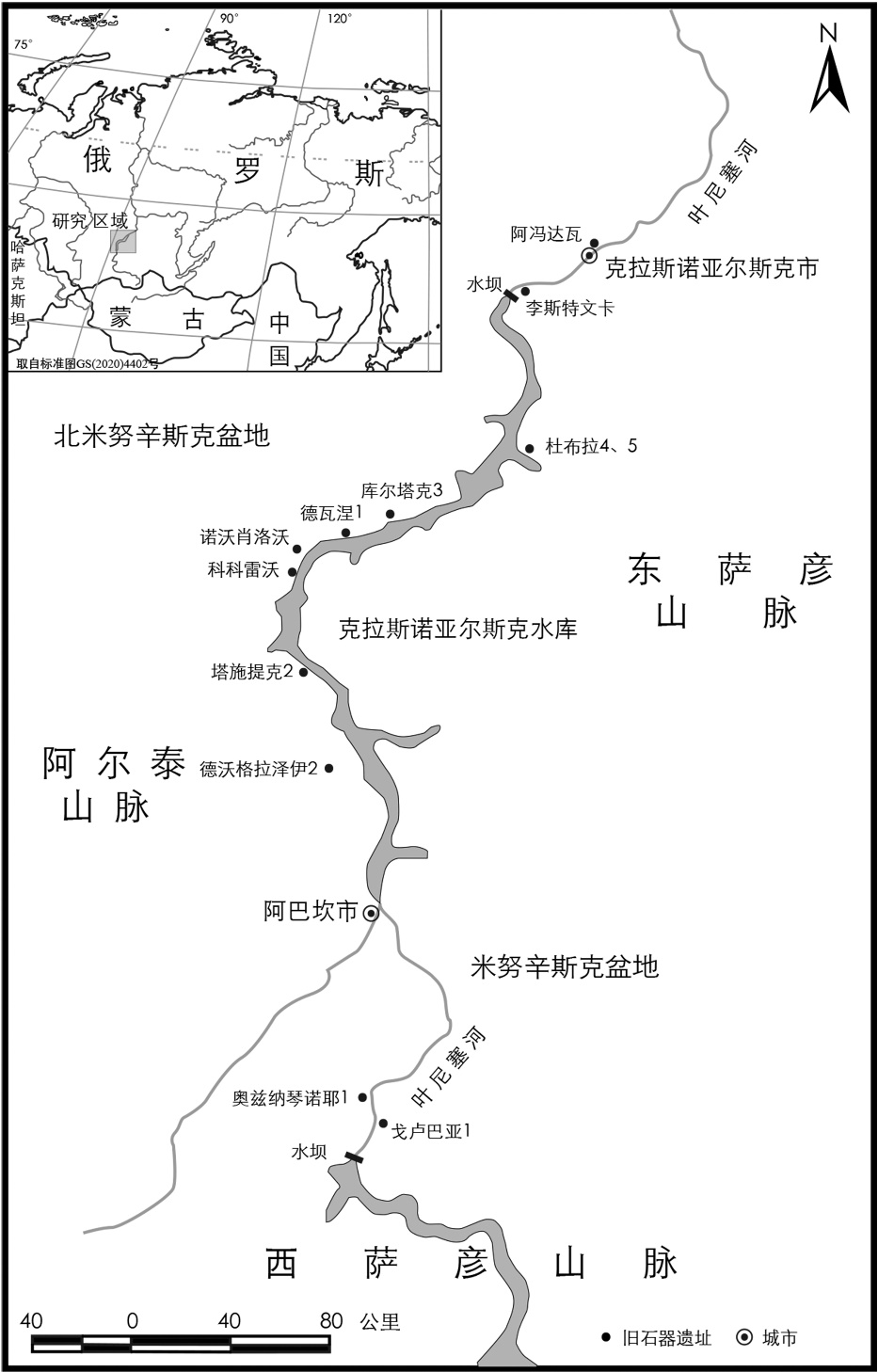
The Listvenka site is located in the Upper Yenisei, Siberia, Russia, on the right bank (the second terrace) of this largest river in the Arctic Ocean system. Its geographical coordinates measure 55°35′22″N, 85°46′24″E. It is an important Upper Palaeolithic site in Siberia with numerous unearthed cultural remains including microlithic assemblages and bone artefacts. Layer 7 of the site dates back to ca. 13.59-15.00 kaBP. There has identified 3 Mogera robusta individuals fossil material for study through MNI calculation. This discovery suggests its paleoenvironment was under continental monsoon climate with comparative abundant precipitation and distribution of woodland mixed with taiga forest and broad-leaf forest, rather than occupied by tundra-forest and cold tundra-steppe as that had presumed. It provided a good ecological environment and supported a diversity of fauna species, including mollusc, small mammal and large mammal. The study on Mogera robusta specimens of Listvenka site indicates the possibility for the hominin capturing large moles as an important food supplement during the harsh and long Siberian winter. It plays a vital role in the in-depth analysis of hominin cultural exchange, physical evolution and adaption to the cold environment in Asia. It provides significant research material for the study of the Talpidae family’s origin and evolution as well.
Key words: Mogera robusta; Listvenka site; Zooarchaeology; Siberia
Xianzhu WU , Yuzhi CHEN , NI Drozdov . Mogera robusta fossils from the Listvenka site, Siberia[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2021 , 40(06) : 1032 -1040 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0027
| [1] | 吴新智, 崔娅铭. 人种及其演变[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(34):3630-3637 |
| [2] | 武仙竹, 哈连维奇·弗拉基米尔,阿给莫娃·伊莲娜.西伯利亚特罗伊茨卡亚季节性古营地遗址研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(4):805-812 |
| [3] | Vasil’ev S, Semenov V. Prehistory of the Upper Yenisei Area (Southern Siberia)[J]. Journal of World Prehistory, 1993, 7(2) : 213-242 |
| [4] | 冯恩学. 人类向北美洲迁徙的考古观察[J]. 社会科学战线, 2005, (3):129-133 |
| [5] | 德诺兹诺夫 NI. 俄罗斯图瓦南部的旧石器考古研究[A].译者: 杨光,严思.见:武仙竹(主编).科技考古与文物保护技术(第一辑)[C]. 北京: 科学出版社. 2018, 285-289 |
| [6] | 巴浦洛夫 VV, 武仙竹. 论西伯利亚南部三种青铜时代文化[A].见:武仙竹(主编).科技考古与文物保护技术(第二辑)[C]. 北京: 科学出版社. 2018, 293-301 |
| [7] | 武仙竹, 冯玲. 南西伯利亚发现的“驾牌”与明土木堡之变[J]. 中国边疆史地研究, 2018, 28(4):61-64 |
| [8] | Kuzmin Y. Mammalian Fauna From Palaeolithic Sites in the Upper Yenisei River Basin (Southern Siberia): Review of the Current Zooarchaeological Evidence[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2011, 21:218-228 |
| [9] | 权乾坤, 阿尔杰米耶夫·叶甫盖尼, 武仙竹. 中西伯利亚旧石器晚期的细石器文化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(4):797-804 |
| [10] | 张森水. 丁村54: 100地点石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1993, 12(3):195-213 |
| [11] | 王应祥. 中国哺乳动物种和亚种分类名录与分布大全[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2003, 8-9 |
| [12] | 肖宁, 何芳, 邓怀庆. 梵净山缺齿鼹的分类学讨论[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 36(1):40-44 |
| [13] | 雷博宇, 崔继法, 岳阳, 等. 湖北兴山发现霍氏缺齿鼩[J]. 动物学杂志, 2019, 54(6):820-824 |
| [14] | 潘清华, 王应祥, 岩崑. 中国哺乳动物彩色图鉴[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2007, 35 |
| [15] | 王文, 王秀辉, 高中信, 等. 呼伦贝尔草原的兽类[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 1997, 25(6):20-25 |
| [16] | Davis R. The Enisei River of Central Siberia in the Late Pleistocene[J]. Journal of Archaeological Research, 1998, 6(2):169-194 |
| [17] | Chlachula J. Pleistocene climate change, natural environments and palaeolithic occupation of the Altai area, west-central Siberia[J]. Quaternary International, 2001, 80(1) : 101-130 |
| [18] | 阿芙洛娃HA. 克拉斯诺亚尔斯克地区考古学和第四纪沉积地层[M]. 克拉斯诺亚尔斯克: 白金出版社, 2007, 84-117(俄文) |
| [19] | 尹文英. 中国土壤动物[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000, 237-242 |
| [20] | 王宁. 鼢鼠、鼹鼠的本草考证[J]. 中药通报, 1987, 12(1):3-5 |
| [21] | 大卫·麦克唐纳. 世界动物大百科全书[M]. 译者: 程高龄. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江科学技术出版社, 2000, 877-883 |
| [22] | 黄万波, 方其仁. 巫山猿人遗址[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991, 43-45 |
| [23] | 金昌柱, 刘金毅. 安徽繁昌人字洞-早期人类活动遗址[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009, 93-101 |
| [24] | 同号文, 吴秀杰, 董哲, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞古人类遗址哺乳动物化石的初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(2):284-305 |
| [25] | 郑少华. 建始人遗址[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004, 83-87 |
| [26] | 张森水. 北京志·周口店遗址志[M]. 北京: 北京出版社, 2004, 175-192 |
| [27] | 武仙竹, 马江波. 三峡地区古代居住环境中的食虫目动物伴栖现象[J]. 三峡生态环境监测, 2016, 1(2):44-51 |
| [28] | Hisashi ABE. Revision of the Asian moles of the genus Mogera[J]. Journal of the Ma mmalogical Society of Japan, 1995, 20:51-68 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |