

A preliminary report on the excavation of Nanshangen Paleolithic Locality in the Nihewan Basin
Received date: 2021-10-20
Revised date: 2022-05-12
Online published: 2023-04-03
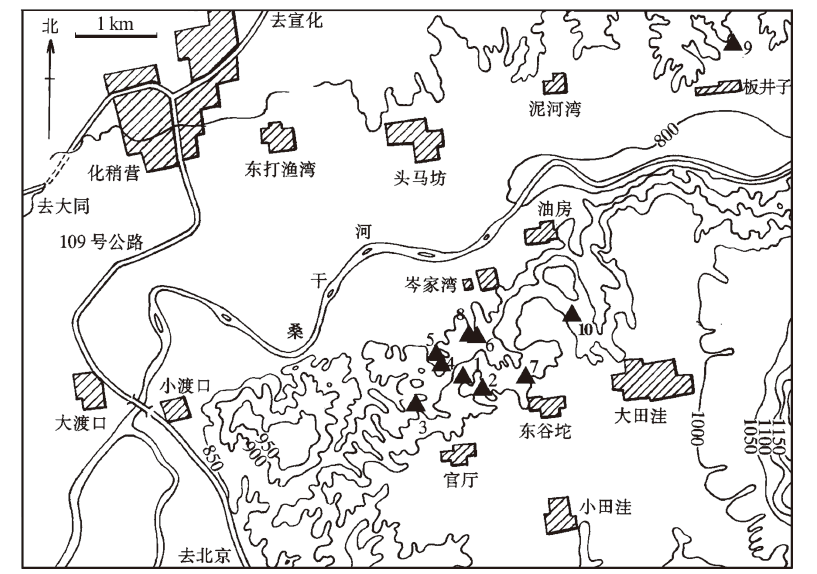
The scientific research in the Nihewan Basin has experienced a long history of nearly 100 years, involving a variety of fields such as geology, paleontology, paleoanthropology, chronology, etc. With abundant scientific research achievements, the Nihewan Basin draws the attention of the world. Located in the southwest of Cenjiawan village, Yangyuan County, Hebei Province, the Nanshangen Paleolithic locality is the early Paleolithic site. The archaeological culture layer is buried in the lake facies layer of Nihewan, with the geological age being early Pleistocene.
From May to July of 2017, the archaeological team of Hebei Normal University carried out excavations at this site, within an area of about 22 m2. A cultural layer was discovered as the excavation of the Nanshangen locality proceeded. A total of 519 pieces of numbered relics were unearthed, most of which were stone artifacts whose main types were stone cores, flakes, tools,fragments, etc. The minority of 17 fossils were broken. The direct percussion was the dominate debitage technique. The raw materials of stone artifacts were breccia, flint, siliceous limestone, quartz sandstone and so on, among which brown-red breccia accounted for the vast majority. The bedrock exposed in the south and east of Nanshangen Paleolithic Locality was visible, so the raw materials of stone artifacts could be drawn near. Overall, stone artifacts were small, belonging to the small stone tradition of North China.
According to the analysis of the preservation and distribution of stone artifacts, there was little displacement of the relic position in the plane and vertical direction caused by the fault and stratum tilt as well as the impact of water transportation. The stone products were less disturbed by later factors. A total of 25 splicing groups were found at the site, including 57 pieces of spliceable stone products. The fossils buried in situ were broken and poorly preserved, which might be caused by weathering after exposure in the wilderness for a period of time. It can be inferred that the Nanshangen site is a temporary activity place for humans to make stone tools.
The Nanshangen Paleolithic Locality lied in the northwest wall of the Brown fault. The strata were declining and adjacent to the sites of Cenjiawan, Shigou, and Donggutuo. The Nanshangen and Cenjiawan’s cultural layers are in the same natural accumulation layer, but the cultural layer of this site is slightly higher than that of Cenjiawan site. Therefore the age is slightly close to and later than that of Cenjiawan site(1.1Ma). It is of great significance to study the survival strategies of early Paleolithic humans in the Datianwa area of the Nihewan Basin.
Wentian FAN , Xiaodong YANG . A preliminary report on the excavation of Nanshangen Paleolithic Locality in the Nihewan Basin[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023 , 42(02) : 260 -271 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2023.0015
| [1] | 袁宝印, 夏正楷, 牛平山. 泥河湾裂谷与古人类[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 1-12 |
| [2] | 裴树文, 马宁, 李潇丽. 泥河湾盆地东端2007年新发现的旧石器地点[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(1): 33-43 |
| [3] | 贾真秀, 裴树文, 马宁, 等. 泥河湾盆地麻地沟E6和E7旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(3): 343-358 |
| [4] | Wang HQ, Deng CL, Zhu RX, et al. Paleomagnetic dating of the Cenjiawan Paleolithic site in the Nihewan Basin, northern China[J]. Science in China, Series D, 2006, 49 (3): 295-303 |
| [5] | 卫奇. <西侯度>石制品之浅见[J]. 人类学学报, 2000, 19(2): 85-96 |
| [6] | 陈宥成, 曲彤丽. 盘状石核相关问题探讨[J]. 考古, 2016, 2: 88-94 |
| [7] | 李英华. 旧石器技术:理论与实践[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2017, 55 |
| [8] | Toth N. The Oldowan reassessed: A close look at early stone artifacts[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1985, 12(2): 101-120 |
| [9] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 方启, 等. 安图沙金沟旧石器遗址发现的石器研究[J]. 华夏考古, 2008, 2: 51-58 |
| [10] | 陈全家, 李霞, 石晶, 等. 本溪王家威子西山旧石器地点发现的石器研究[A].见:董为(主编).第十三届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C].北京:海洋出版社, 2012: 147-156 |
| [11] | 陈全家, 付永平, 赵宇超, 等. 法库五里山旧石器地点发现的石器研究[J]. 文物春秋, 2013, 4: 21-31 |
| [12] | 陈全家, 赵海龙, 王欢. 浑江流域(2007年)发现的石器研究[J]. 北方文物, 2012, 1: 1-8 |
| [13] | 马东东, 赵海龙, 等. 泥河湾盆地板井子遗址锯齿刃器实验研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(3): 319-330 |
| [14] | 王社江. 洛南盆地旷野旧石器地点群石制品的拼合观察[J]. 考古与文物, 2007, 5: 57-64 |
| [15] | 谢飞. 泥河湾[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2006, 69-78 |
| [16] | 冯小波. 郧县人遗址石制品的拼合研究[A].见:北京大学考古文博学院(编).考古学研究(七)[C].北京:科学出版社, 2008, 77-85 |
| [17] | 王红强, 邓成龙, 朱日祥, 等. 泥河湾盆地岑家湾旧石器遗址的古地磁定年[C]. 北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 2007 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |