

Diagnostic criteria of ancient ankylosing spondylitis and a research review in China
Received date: 2022-05-10
Revised date: 2022-08-29
Online published: 2023-06-13
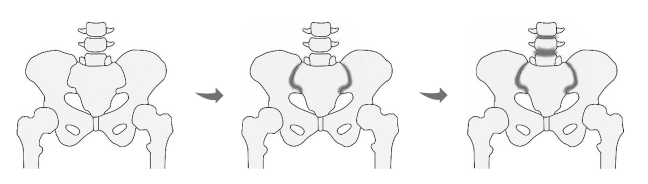
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a rheumatic disease mainly affecting the axial skeleton that is characterized by sacroiliitis in earlier disease stages (a major diagnostic criteria). In the field of paleopathology, inappropriate identification of AS usually results in missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis, and thus we have established new criteria for diagnosing AS in ancient human remains employing advances in clinical medicine and medical imagery. The criteria were as follows: 1) sacroiliitis grade G≥1 (minimum lesion) bilaterally or G≥2 (moderate lesion) unilaterally; 2) without large or deep erosions(d≥1cm) in neither iliac nor sacral side; 3) if the spine is involved, the syndesmophytes are thin and smooth on consecutive vertebrae. We also discussed differential diagnosis with other easily confused diseases, such as psoriatic arthritis, and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. As part for this work, we summarized detailed points of skeletal pathological manifestations to be recorded in the diagnostic process.
Reviewing 30 paleopathological or archaeological studies in China we found that since the Holocene, 128 human skeletons have been identified as AS. However, only 25.8% (n=33) met our new diagnostic criteria after being reanalyzed. The remaining 74.2% of cases were diagnosed with AS based on “spinal fusion” on only two vertebrae or lacking pathological information of the sacroiliac joint, which could not be well distinguished from other diseases. These suspected cases need further investigation.
Among these 33 confirmed cases, 63.6% (n=21) were males. There were 27 individuals with definite age range of death, mainly middle-aged individuals (n=17). The earliest cases dated back to the Neolithic Age (n=4), then the Xia, Shang and Zhou dynasties (n=5), the Warring States, Qin and Han dynasties (n=13), the Wei, Jin, Southern and Northern dynasties (n=8), the Sui and Song dynasties (n=1), and the Yuan and Qing dynasties (n=2). Almost all cases were located north of the Yangtze River, possibly an influence of bone preservation.
The aim of this study is to create a process for recording and diagnosing ancient AS more standardized and normalized, leading to more accurate and persuasive identification results. This work established a solid foundation in study of the developmental and evolutionary history of AS. In addition to morphological diagnosis, the HLA-B27 test is another important means to diagnose AS. The advent of ancient DNA techniques has brought forth potential molecular means of diagnosis and investigation of this hereditary disease especially for mutilated skeletal remains.
Key words: Biological anthropology; Ankylosing spondylitis; Paleopathology
Bangyan WANG , Jiucun WANG , Shaoqing WEN . Diagnostic criteria of ancient ankylosing spondylitis and a research review in China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023 , 42(03) : 422 -434 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2023.0017
| [1] | Braun J, Sieper J. Ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Lancet, 2007, 369(9570): 1379-1390 |
| [2] | Firestein GS. 凯利风湿病学(第10版)[M].译者:栗占国,等. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2020, 1362-1454 |
| [3] | 梁慧英. 古代医家对强直性脊柱炎的认识[J]. 吉林中医药, 2011, 31(6): 594-596 |
| [4] | Bywaters EG. Historical aspects of ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Rheumatology and Rehabilitation, 1979, 18(4): 197-203 |
| [5] | Zeidler H, Calin A, Amor B. A historical perspective of the spondyloarthritis[J]. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 2011, 23(4): 327-333 |
| [6] | Waldron T. Paleopathology (2nd edition)[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2020, 107-111 |
| [7] | Waldron T. Chapter 20 - Joint disease[A]. In: Buikstra JE. Ortner’s Identification of Pathological Conditions in Human Skeletal Remains (3rd edition)[C]. San Diego: Academic Press, 2019: 734 |
| [8] | Leden I, G?therstr?m A, Drenzel L, et al. HLA-B27 sequences identified in a mediaeval skeleton with ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2009, 68(5): 757-758 |
| [9] | Slaus M, Novak M, Cavka M. Four cases of ankylosing spondylitis in medieval skeletal series from Croatia[J]. Rheumatology International, 2012, 32(12): 3985-3992 |
| [10] | Duyar I. A case of ankylosing spondylitis from the excavations at Klcl Necropolis (Sinope, northern Turkey) and its implications on the antiquity of the disease in Anatolia[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2019, 29(6): 1100-1108 |
| [11] | Dean LE, Jones GT, MacDonald AG, et al. Global prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Rheumatology, 2014, 53(4): 650-657 |
| [12] | Raychaudhuri SP, Deodhar A. The classification and diagnostic criteria of ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Journal of Autoimmunity, 2014, 48-49: 128-133 |
| [13] | Navarro-Compán V, Sepriano A, El-Zorkany B, et al. Axial spondyloarthritis[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2021, 80(12): 1511-1521 |
| [14] | Taurog JD, Chhabra A, Colbert RA. Ankylosing spondylitis and axial spondyloarthritis[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2016, 374(26): 2563-2574 |
| [15] | Sieper J, Poddubnyy D. Axial spondyloarthritis[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390(10089): 73-84 |
| [16] | Dougados M, Baeten D. Spondyloarthritis[J]. Lancet, 2011, 377(9783): 2127-2137 |
| [17] | Rashid T, Ebringer A. Ankylosing spondylitis is linked to Klebsiella--the evidence[J]. Clinical Rheumatology, 2007, 26(6): 858-864 |
| [18] | Tam LS, Gu J, Yu D. Pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2010, 6(7): 399-405 |
| [19] | 徐文坚, 袁慧书. 中华影像医学骨肌系统卷(第3版)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019, 356-534 |
| [20] | Sieper J, Braun J, Rudwaleit M, et al. Ankylosing spondylitis: An overview[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2002, 61(S3): iii8-18 |
| [21] | Sieper J, Braun J, Dougados M, et al. Axial spondyloarthritis[J]. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 2015, 1:15013 |
| [22] | Ward MM, Tan S. Better quantification of syndesmophyte growth in axial spondyloarthritis[J]. Current Rheumatology Reports, 2018, 20(46) |
| [23] | 中国医师协会风湿免疫科医师分会影像学组. 影像学技术在脊柱关节炎中应用的中国专家共识 (2021年版)[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2021, 25(9): 577-583 |
| [24] | Robinson PC, van der Linden S, Khan MA, et al. Axial spondyloarthritis: Concept, construct, classification and implications for therapy[J]. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2021, 17(2): 109-118 |
| [25] | Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2009, 68(6): 777-783 |
| [26] | Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, et al. The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) handbook: A guide to assess spondyloarthritis[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2009, 68(S2): ii1-44 |
| [27] | van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 1984, 27(4): 361-368 |
| [28] | Roberts C, Manchester K. 疾病考古学[M].译者:张桦. 济南: 山东画报出版社, 2011, 145-239 |
| [29] | Grauer AL. A Companion to Paleopathology[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2011, 513-530 |
| [30] | Mann RW. 骨骼疾病图谱(第3版)[M].译者:张全超,等. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020, 19-128 |
| [31] | Helliwell PS, Hickling P, Wright V. Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing spondylitis differ from the changes found in the spondylitis associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive arthritis?[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1998, 57(3): 135-140 |
| [32] | Ritchlin CT, Colbert RA, Gladman DD. Psoriatic arthritis[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2017, 376(10): 957-970 |
| [33] | Villani AP, Rouzaud M, Sevrain M, et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed psoriatic arthritis among psoriasis patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 2015, 73(2): 242-248 |
| [34] | Gottlieb AB, Merola JF. Axial psoriatic arthritis: An update for dermatologists[J]. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 2021, 84(1): 92-101 |
| [35] | Feld J, Chandran V, Haroon N, et al. Axial disease in psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: a critical comparison[J]. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2018, 14(6): 363-371 |
| [36] | Helliwell PS. Axial disease in psoriatic arthritis[J]. Rheumatology, 2020, 59(6): 1193-1195 |
| [37] | Ory PA, Gladman DD, Mease PJ. Psoriatic arthritis and imaging[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2005, 64(S2): ii55-57 |
| [38] | Winchester R, FitzGerald O. The many faces of psoriatic arthritis: their genetic determinism[J]. Rheumatology, 2020, 59(S1): i4-i9 |
| [39] | Veale DJ, Fearon U. The pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10136): 2273-2284 |
| [40] | Olivieri I, Cantini F, Castiglione F, et al. Italian Expert Panel on the management of patients with coexisting spondyloarthritis and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews, 2014, 13(8): 822-830 |
| [41] | Fragoulis GE, Liava C, Daoussis D, et al. Inflammatory bowel diseases and spondyloarthropathies: From pathogenesis to treatment[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2019, 25(18): 2162-2176 |
| [42] | Karreman MC, Luime JJ, Hazes JMW, et al. The prevalence and incidence of axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis, 2017, 11(5): 631-642 |
| [43] | Selmi C, Gershwin ME. Diagnosis and classification of reactive arthritis[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews, 2014, 13(4-5): 546-549 |
| [44] | Stavropoulos PG, Soura E, Kanelleas A, et al. Reactive arthritis[J]. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 2015, 29(3): 415-424 |
| [45] | Jacobson JA, Girish G, Jiang Y, et al. Radiographic evaluation of arthritis: Inflammatory conditions[J]. Radiology, 2008, 248(2): 378-389 |
| [46] | Mader R, Verlaan JJ, Buskila D. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: Clinical features and pathogenic mechanisms[J]. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2013, 9(12): 741-750 |
| [47] | Kuperus JS, Waalwijk JF, Regan EA, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of ankylosing spondylitis and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: A systematic review[J]. Rheumatology, 2018, 57(12): 2120-2128 |
| [48] | Bieber A, Masala IF, Mader R, et al. Differences between diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and spondyloarthritis[J]. Immunotherapy, 2020, 12(10): 749-756 |
| [49] | Ramlakan RJ, Govender S. Sacroiliac joint tuberculosis[J]. International Orthopaedics, 2007, 31(1): 121-124 |
| [50] | Littleton J. Paleopathology of skeletal fluorosis[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1999, 109(4): 465-483 |
| [51] | 张振标. 中国古代人类强直性脊椎炎的骨骼例证[J]. 人类学学报, 1995, 14(2): 110-117+193-194 |
| [52] | Rogers J, Watt I, Dieppe P. Palaeopathology of spinal osteophytosis, vertebral ankylosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and vertebral hyperostosis[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44(2): 113-120 |
| [53] | Samsel M, Kacki S, Villotte S. Palaeopathological diagnosis of spondyloarthropathies: Insights from the biomedical literature[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2014, 7: 70-75 |
| [54] | Ventades NG, Laza IM, Hervella M, et al. A recording form for differential diagnosis of arthropathies[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2018, 20: 45-49 |
| [55] | Feldtkeller E, Lemmel EM, Russell AS. Ankylosing spondylitis in the pharaohs of ancient Egypt[J]. Rheumatology International, 2003, 23(1): 1-5 |
| [56] | Saleem SN, Hawass Z. Ankylosing spondylitis or diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in royal Egyptian mummies of 18th -20th Dynasties? CT and archaeology studies[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2014, 66(12): 3311-3316 |
| [57] | Chhem RK, Schmit P, Faure C. Did Ramesses II really have ankylosing spondylitis? A reappraisal[J]. Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal-Journal De L Association Canadienne Des Radiologistes, 2004, 55(4): 211-217 |
| [58] | MA WH, Gruber P, MD FJR, et al. Molecular evidence of HLA-B27 in a historical case of ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2005, 52(10): 3318-3319 |
| [59] | Laza IM, Hervella M, de la Rúa C. Genetic markers in a medieval case of ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Journal of Rheumatology, 2016, 43(3): 679-681 |
| [60] | Laza IM, Ventades NG, Hervella M, et al. Contribution of ancient human remains analysis to the understanding of the variability in HLA-B gene variants in relation to the diagnosis of spondyloarthropathies[J]. Journal of Autoimmunity, 2018, 94: 70-82 |
| [61] | Spyrou MA, Bos KI, Herbig A, et al. Ancient pathogen genomics as an emerging tool for infectious disease research[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019, 20(6): 323-340 |
| [62] | Wu X, Ning C, Key FM, et al. A 3,000-year-old, basal S. enterica lineage from Bronze Age Xinjiang suggests spread along the Proto-Silk Road[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2021, 17(9): e1009886 |
| [63] | Wanders AJ, Landewé RB, Spoorenberg A, et al. What is the most appropriate radiologic scoring method for ankylosing spondylitis? A comparison of the available methods based on the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials filter[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2004, 50(8): 2622-2632 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |