

A preliminary report of the 2020 Paleolithic survey of the middle to lower reaches of the Jinghe River
Received date: 2023-03-13
Revised date: 2023-04-26
Online published: 2023-10-16
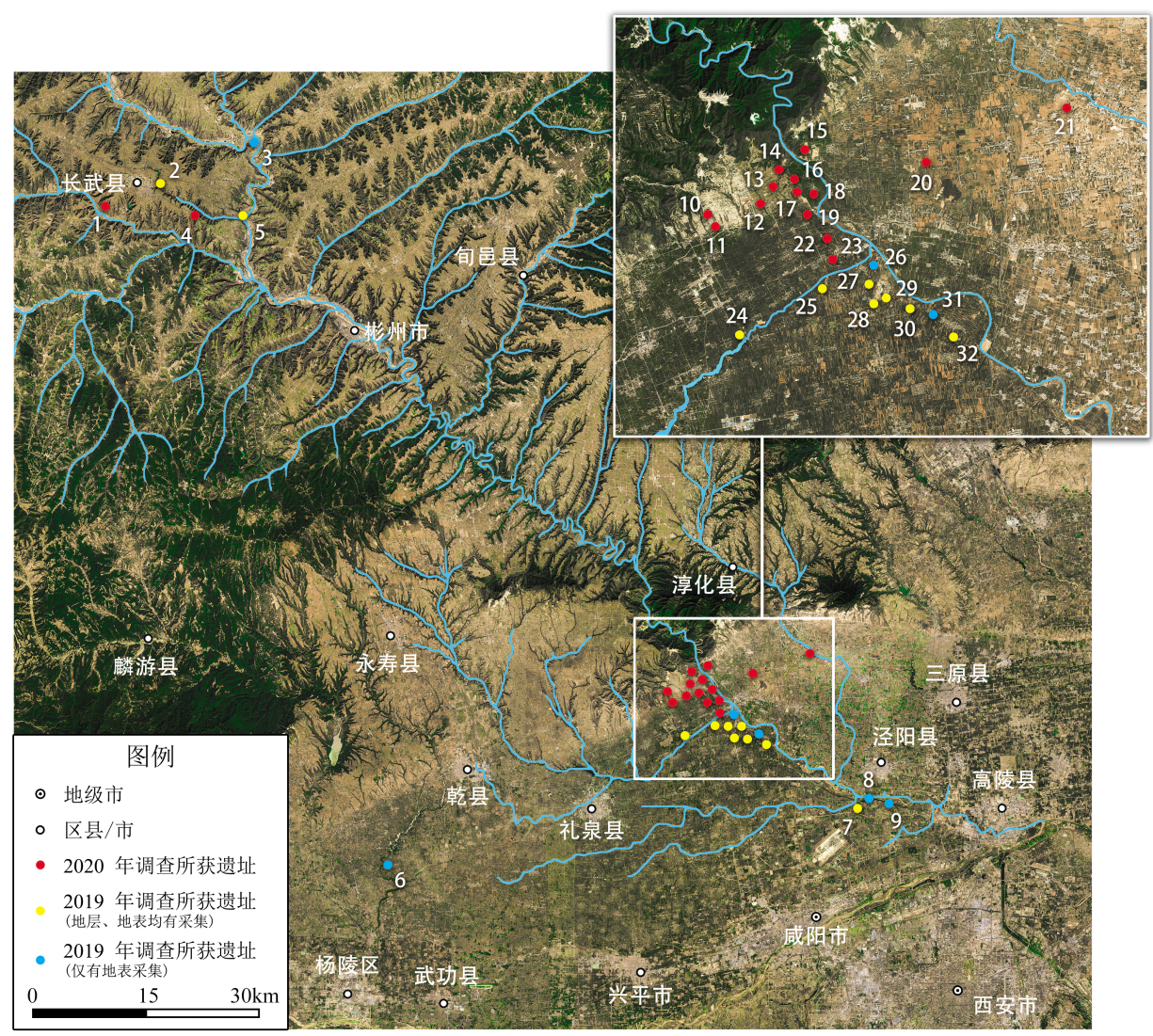
In October 2020, an investigation along the Jinghe River valley in Shaanxi Province was carried out by the School of Cultural Heritage at Northwest University. A total of 15 localities were newly discovered in Changwu, Liquan and Jingyang counties. Almost 300 stone artifacts were buried in the 4th terrace of the right bank of the Jinghe River with some artifacts also surface collected. Raw materials were procured from gravels at the bottom of this terrace. High quality quartzite dominates the raw material. Almost all surface lithics were covered by a thin calcareous concretion. Most stone artifacts were manufactured by free hand hammer percussion, followed by bipolar technique. Technologically, the stone artifacts can be classified into cores, flakes and scrapers, etc. The lithic assemblage is assigned to the flake tool industry of North China, while centripetal exploitation cores, deeply modified scrapers and a high degree symmetry discoid show obvious advanced flaking technique. Judging from the artifacts buried in the Malan Loess (corresponding to MIS 3), the age of this early human occupation from the middle to lower reaches of the Jinghe River is no later than Late Pleistocene.
Key words: Archaeology; Lithics; Late Pleistocene
Shijia ZHAN , Zhe DONG , Yaopeng QIAN . A preliminary report of the 2020 Paleolithic survey of the middle to lower reaches of the Jinghe River[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023 , 42(05) : 679 -686 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2023.0036
| [1] | 陕西师大地理系. 咸阳市地理志[D]. 西安: 陕西人民出版社, 1991: 35-86 |
| [2] | 刘玉林, 黄慰文, 林一璞. 甘肃泾川发现的人类化石和旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 1984, 3(1): 11-18 |
| [3] | 黄万波, 郑绍华. 记陕西长武晚更新世人牙及共生哺乳动物化石[J]. 人类学学报, 1982, 1(1): 14-17 |
| [4] | 陈恩志主编. 中国化石古人类和旧石器文化考古发现与研究(1901-1990) ·西北地区卷[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 1992, 477-482 |
| [5] | 薛祥煦. 甘肃环县楼房子晚更新世哺乳动物化石及古文化遗物[A]. 见:王永炎(主编).黄土与第四纪地质[M]. 西安: 陕西人民出版社, 1982, 108-137 |
| [6] | 谢骏义, 张鲁章. 甘肃庆阳地区的旧石器[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1977, 15(3): 211-222 |
| [7] | 杜水生, 杨宇霞, 王辉. 文化交流或适应趋同:甘肃环县楼房子遗址2011-2012年发掘的新材料[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(6): 1443-1456 |
| [8] | 慕占雄, 陈国科, 杜水生, 等. 甘肃环县楼房子遗址2018年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(1): 121-134 |
| [9] | 盖培, 黄万波. 陕西长武发现的旧石器时代中期文化遗物[J]. 人类学学报, 1982, 1(1): 18-29 |
| [10] | 裴文中. 陕西乾县发现的纳玛象化石[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1959, 1(4): 215-216 |
| [11] | 邱中郎. 陕西乾县的旧石器[J]. 人类学学报, 1984, 3(3): 212-214 |
| [12] | 战世佳, 董哲, 钱耀鹏. 陕西泾河流域2019年旧石器考古调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(1): 157-164 |
| [13] | Toth N. The stone technologies of early hominids at Koobi Fora: An experimental approach[D]. Berkeley: The PhD Dissertation of University of California, 1982, 48-101 |
| [14] | Cotterell B, Kamminga J. Finials on stone flakes[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1986, 13(5): 451-461 |
| [15] | 张森水. 管窥新中国旧石器考古学的重大发展[J]. 人类学学报, 1999, 18(3): 35-56 |
| [16] | 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985, 44-112 |
| [17] | 李玉梅, 刘东生, 吴文祥, 等. 黄土高原马兰黄土记录的MIS 3温湿气候[J]. 第四纪研究, 2003, 23(1): 69-76 |
| [18] | Li F, Vanwezer N, Boivin N, et al. Heading north: Late Pleistocene environments and human dispersals in central and eastern Asia[J]. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14(5): e0216433 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |