

Stone artifacts from the Yuzuigou Locality 1 of the Majuangou Paleolithic site excavated in 2017 and 2018
Received date: 2023-07-22
Online published: 2024-02-06
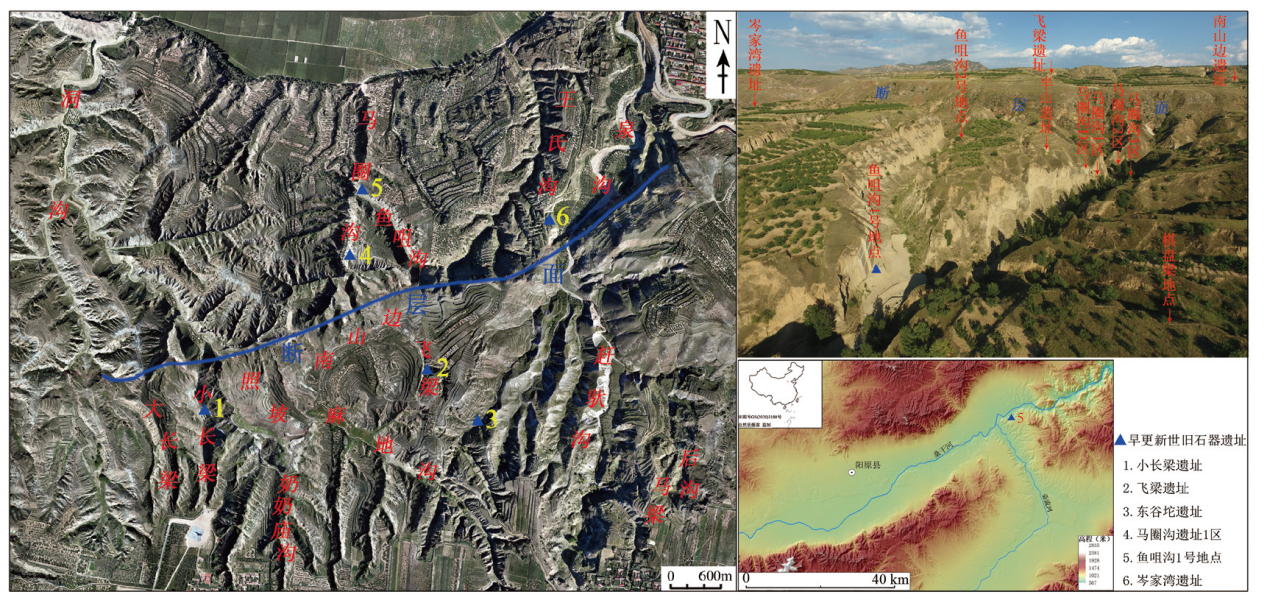
The Yuzuigou Paleolithic Locality 1 is located on the eastern edge of the Nihewan Basin along the north slope of the Datianwa platform and in the most northern part of the Majuangou Paleolithic site. In 2017 and 2018, an 80 m2 excavation was carried out at the site, during which 7 cultural layers, 4 fossil layers, 207 stone artifacts, and abundant fossils were discovered. There are 152 stone artifacts specifically from the Yuzuigou Locality 1. Chert, dolomite, siliceous limestone and basalt are the main raw materials. Artifacts are divided into general types, such as hammers, cores, flakes, tools, fragments, chunks, or specifically scrapers, notches, points, borers, burins, and choppers. These lithics belong to a tradition of core-flake technology, and are part of the core-flake industry in northern China. The cultural layers of the locality are unambiguous, and some of these layers can be directly compared with the Majuangou site. Layers 7 and 4 correspond directly to layers 3 and 1 at the Majuangou site; according to dating with absolute age determinations at 1.66 MaBP and 1.55 MaBP, respectively. Seven cultural layers in different stages were found in the same sections or beds, including three newly found cultural layers. Some of the cultural layers at the Yuzuigou Paleolithic Locality 1 are very rich while others are not, which can give an important clues to lithic technology, and patterns of human livelihood in the early Pleistocene. With accurate chronology for this locality, abundant cultural connotations, many cultural layers accompanied by large numbers of stone artifacts and fossils, the Yuzuigou Paleolithic Locality 1 is the earliest Early Pleistocene site at Majuangou at present. It provides important materials for the emergence and evolutionary patterns of early human beings in East Asia. More comprehensive and elaborate archaeological investigation and excavation can bring more insight about this location.
Lianqiang LIU , Yuxiao PU , Jiaqi HOU , Fagang WANG . Stone artifacts from the Yuzuigou Locality 1 of the Majuangou Paleolithic site excavated in 2017 and 2018[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024 , 43(01) : 40 -54 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0005
| [1] | Zhu RX, Potts R, Xie F, et al. New evidence on the earliest presence at high northern latitudes in northeast Asia[J]. Nature, 2004, 431: 559-562 |
| [2] | 王幼平. 石器技术与早期人类的迁徙扩散[M].见:北京大学考古文博学院,北京大学中国考古学研究中心(编).《考古学研究(十一)》[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020 |
| [3] | 河北省文物考古研究院. 河北阳原县马圈沟旧石器时代遗址2014年的发掘[J]. 考古, 2023, 11: 3-19 |
| [4] | 李珺, 谢飞. 马圈沟旧石器时代早期遗址发掘报告[M].见:河北省文物研究所(编).《河北省考古文集》[M]. 北京: 东方出版社,1998 |
| [5] | 陈淳, 沈辰, 陈万勇, 等. 小长梁石工业研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2002, 21(1): 23-40 |
| [6] | 张森水. 中国北方旧石器工业的区域渐进与文化交流[J]. 人类学学报, 1990, 9(4): 322-333 |
| [7] | 裴文中, 张森水. 中国猿人石器研究[M].见:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所,中国科学院南京地质古生物研究所(编).中国古生物志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1985 |
| [8] | 尤玉柱, 汤英俊, 李毅. 泥河湾组旧石器的发现[J]. 中国第四纪研究, 1980, 5(1): 11-13 |
| [9] | 贾兰坡, 卫奇. 阳高许家窑旧石器时代文化遗址[J]. 考古学报, 1976, 2: 97-114 |
| [10] | Wang FG, Yang SX, Ge JY, et al. Innovative ochre processing and tool use in China 40000 years ago[J]. Nature, 2022, 603: 284-289 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |