

A comparison of head and facial characteristics between the Daur ethnic groups in Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang
Received date: 2024-04-26
Revised date: 2024-07-22
Online published: 2024-08-13
In this study, 629 healthy Daur adults (315 males and 314 females) from Molidavar Autonomous Banner (referred to as Moqi) of Hulunbuir, Inner Mongolia and Tacheng City of Xinjiang were selected as research objects. 40 head and face indexes were investigated, and 5 head and face indexes and their subtypes were calculated. The data were processed by SPSS20.0 statistical software and R software.Research has found that there is a significant difference in the head and facial features of adults between the Daur ethnic group in Inner Mongolia and the Daur ethnic group in Xinjiang. The average value of each index of Daur nationality in Xinjiang is higher than that of Daur nationality in Inner Mongolia. Inner Mongolia Daur adults have longer head, wider head, wider face, narrower nose and lower nose. The adults of Daur nationality in Xinjiang have the facial features of medium length and width of head, narrow nose and low nose,which may be related to the geographical environment and communication and integration between populations.This study provides a reference for exploring the reasons and rules of the evolution of phenotypic characteristics between Daur ethnic groups and exploring the origin relationship of Daur ethnic groups.
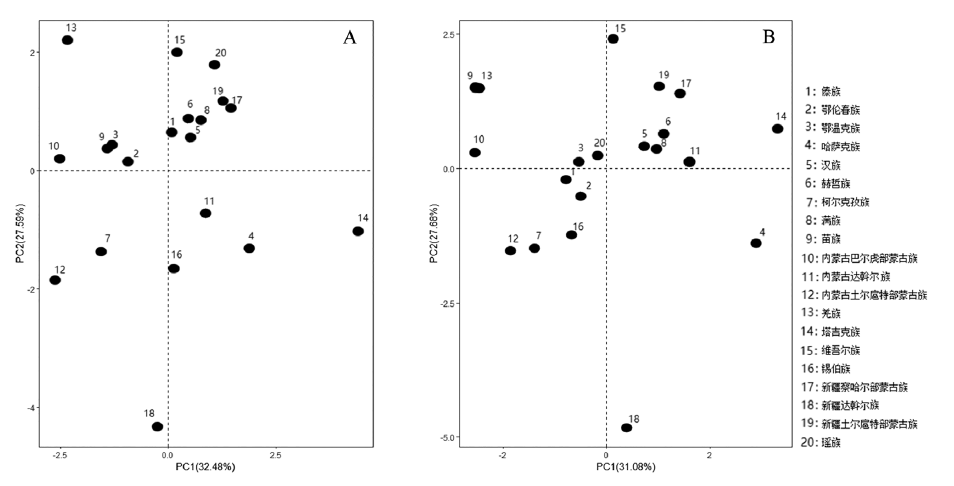
Key words: Daur; head and face; morphological features; Physical Anthropology
LI Xin , JIANG Shuai , HUANG Ting , ZHONG Hua , WEN Youfeng . A comparison of head and facial characteristics between the Daur ethnic groups in Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024 , 43(04) : 586 -596 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0061
| [1] | 杨圣敏. 中国民族志[M]. 北京: 中央民族大学出版社, 2003, 128-136 |
| [2] | 徐兴锐, 白絮飞, 苏福荣. 达斡尔族人迁徙至黑龙江流域的原因新探[J]. 边疆经济与文化, 2020, 4: 6-9 |
| [3] | 赵凤彩. 达斡尔族人口简析[J]. 人口学刊, 1991, 3: 50-53 |
| [4] | 类维顺, 王嘉昕. 达斡尔族“传统摇篮”的艺术特征与民俗文化研究[J]. 文艺争鸣, 2024, 2: 204-208 |
| [5] | 沙仁高娃, 程慧珍, 韦兰海. 达斡尔语分支早期在蒙古语族中的地位[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(6): 1037-1046 |
| [6] | 吕洋. 达斡尔族人类起源神话“天神抟土造人”与“洪水后生人神话”内涵探析[J]. 内蒙古学院学报, 2020, 28(1): 21-24 |
| [7] | 包羽, 伊乐泰. 达斡尔族历史上的萨满教疾病观[J]. 中国民族医药杂志, 2019, 25(3): 65-68 |
| [8] | 施全德, 胡俊清, 杨宏友. 黑龙江省达斡尔族体质特征调查[J]. 人类学学报, 1983, 2(1): 60-71 |
| [9] | 朱钦, 季晓君. 达斡尔族学生的体质发育与体型[J]. 人类学学报, 1993, 12(1): 71-79 |
| [10] | 朱钦, 富杰, 刘文忠, 等. 达斡尔族成人的体格、体型及半个多世纪来的变化[J]. 人类学学报, 1996, 15(2): 119-126 |
| [11] | 邓文涛, 姜东, 席焕久, 等. 辽宁锡伯族成人头面部体质特征[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2019, 42(2): 177-182 |
| [12] | 李强, 李欣, 买尔旦江·莫合塔尔, 等. 阿克陶县塔吉克族成人头面部表型特征[J]. 解剖学报, 2022, 53(3): 360-366 |
| [13] | 李欣, 李强, 张文虔, 等. 新疆不同地区柯尔克孜族成人容貌特征差异[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2020, 43(3): 220-225 |
| [14] | 李咏兰, 刘璐. 中国蒙古族头面部的体质人类学特征[J]. 解剖学报, 2019, 50(1): 98-106 |
| [15] | 张咸鹏. 辽宁满族人群体质特征及遗传结构研究[D].硕士学位毕业论文, 锦州: 锦州医科大学, 2022 |
| [16] | 孙思凡. 广西瑶族体质特征及遗传特征研究[D].硕士学位毕业论文, 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2021 |
| [17] | 珠娜. 水族体质特征及遗传特征研究[D].硕士学位毕业论文, 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2021 |
| [18] | 张咸鹏, 温有锋, 李文慧, 等. 中国阿尔泰语系人群头面部的表型特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(3): 342-358 |
| [19] | 刘小元, 温有锋, 叶丽平, 等. 满-通古斯语族人群头面部特征比较[J]. 解剖学报, 2018, 49(2): 251-257 |
| [20] | 席焕久, 陈昭(主编). 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010 |
| [21] | 刘学峰. 辽宁汉族成人头面部形态特征[D].硕士学位毕业论文, 锦州: 辽宁医学院, 2011 |
| [22] | 邵兴周, 崔静, 朱新安, 等. 新疆特克斯县柯尔克孜族表型特征[J]. 人类学学报, 1987, 6(4): 315-323 |
| [23] | 宇克莉, 李咏兰, 张兴华, 等. 维吾尔族体质类型:来自喀什的资料[J]. 中国科学(生命科学), 2020, 50(9): 983-995 |
| [24] | 李晶, 李珊, 宇克莉, 等. 羌族的表型特征[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2018, 41(4): 440-445, 486 |
| [25] | 廉祎. 中国苗族的体质类型和人种学特征[D].硕士学位毕业论文, 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2023 |
| [26] | 张兴华, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 等. 西双版纳傣族头面部形态特征的年龄变化[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2016, 39(1): 79-85 |
| [27] | 严明亮. 基于人体测量学的新疆蒙古族察哈尔部、土尔扈特部的人类生物学研究[D].硕士学位毕业论文, 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2020 |
| [28] | 廉伟. 土尔扈特人体质人类学与分子遗传学研究[D].硕士学位毕业论文, 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2017 |
| [29] | 张君瑞. 巴尔虎蒙古族体质人类学与人类群体遗传学研究[D].硕士学位毕业论文, 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师大学, 2016 |
| [30] | 刘海萍. 云南蒙古族表型特征与群体遗传学特征性研究[J]. 内蒙古师范大学, 2007, 18(3): 40-42 |
| [31] | 杜传书, 刘祖洞. 医学遗传学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1983, 755-756 |
| [32] | Steegmann AT Jr. Climate, racial category, and body proportions in the US[J]. American Journal of Human Biology, 2010, 17(4): 393-402 |
| [33] | Luojinsky YY, Levin MG. Anthropology[M]. Beijing: Police Education Press, 1993, 525-528 |
| [34] | Vernot B, Akey JM. Complex history of admixture between Modern Humans and Neandertal[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2015, 96(3): 448-453 |
| [35] | Cui W, Jin XY, Guo YX, et al. Forensic applicability of autosomal insertion/ deletion loci in Chinese Duar ethnic group and genetic affinity evaluations between Daur group and reference populations[J]. Leg Med (Tokyo), 2020, 47: 101741 |
| [36] | Chen LK. The compendium of ethnic history in China[M]. Beijing: Financial&Econo-mic press, 2008, 20(3): 3-8 |
| [37] | Wang CZ, Su MJ, Li Y, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of 27 Yfiler Plus loci in the Daur and Mongolian ehtnic minorities from Hulunbuir of Inner Mongolia Autonom- ous Region, China[J]. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2019, 40: 252-255 |
| [38] | 吴秀杰, 刘武, 张全超, 等. 中国北方全新世人群头面部形态特征的微观演化[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(2): 192-198 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |