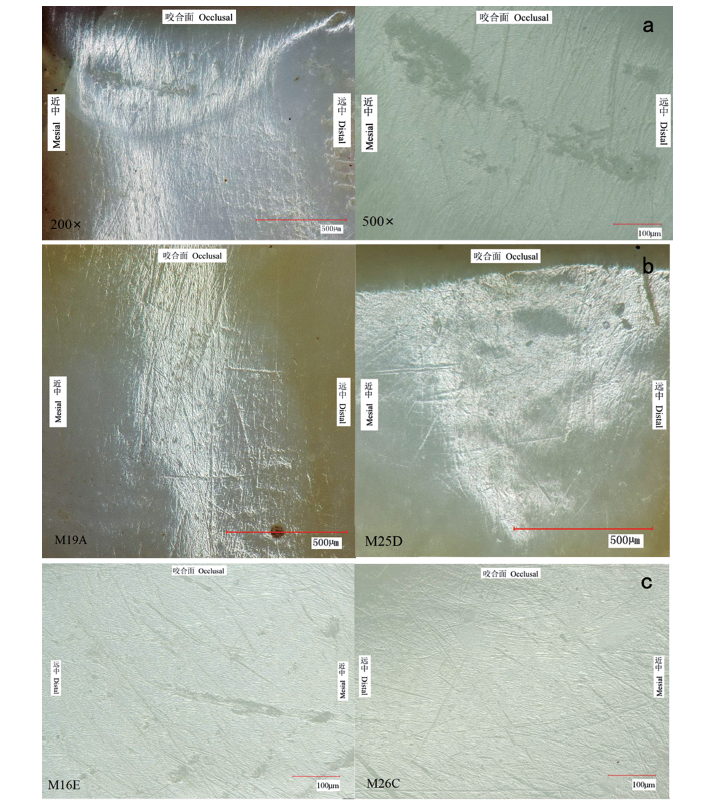
| [1] |
Ungar PS. Dental evidence for diet in primates[J]. Anthropologiai Közlemények, 1992, 34:141-155
|
| [2] |
Ungar PS, Spencer MA. Incisor microwear, diet, and tooth use in three Amerindian populations[J]. American journal of physical anthropology, 1999, 109(3):387-396
pmid: 10407466
|
| [3] |
Romero A, Juan JD. Intra- and interpopulation human buccal tooth surface microwear analysis: Inferences about diet and formation processes[J]. L Anthropologie, 2007, 45:61-70
|
| [4] |
El-Zaatari S. Occlusal molar microwear and the diets of the ipiutak and tigara populations (point hope) with comparisons to the aleut and arikara[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2008, 35(9):2517-2522
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2008.04.002
URL
|
| [5] |
Pérez-Pérez A, Lalueza C, Turbón D. Intraindividual and intragroup variability of buccal tooth striation pattern[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1994, 94(2):175-187
pmid: 8085610
|
| [6] |
张全超, 李墨岑, 张群, 等. 内蒙古哈民忙哈遗址史前居民牙齿微磨耗形态观察与研究[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2017(2):357-366
|
| [7] |
Homes Hogue S, Melsheimer R. Integrating dental microwear and isotopic analyses to understand dietary change in east-central Mississippi[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science. 2008, 35(2):228-238
doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2007.03.002
URL
|
| [8] |
Mahoney P. Dental microwear from natufian hunter-gatherers and early neolithic farmers: Comparisons within and between samples[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2006, 130(3):308-319
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-8644
URL
|
| [9] |
Puech P, Albertini H, Serratrice C. Tooth Microwear and Dietary Patterns in Early Hominids from Laetoli, Hadar and Olduvai[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 1983, 12:721-729
doi: 10.1016/S0047-2484(83)80127-4
URL
|
| [10] |
Lalueza C, Pérez-Pérez A, Turbon D. Dietary Inferences through Buccal Microwear Analysis of Middle and Upper Pleistocene Human Fossils[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1996, 100(3):367-387
pmid: 8798994
|
| [11] |
李肖, 张永兵, 祖力皮亚, 等. 新疆吐鲁番胜金店墓地2号墓发掘简报[J]. 文物, 2013(3):20-24
|
| [12] |
李志丹. 新疆吐鲁番胜金店墓地人骨研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2015
|
| [13] |
【东汉】 班固. 汉书·西域传[M]. 北京:中华书局, 1999: 2855-2857
|
| [14] |
吐鲁番学研究院. 新疆吐鲁番市胜金店墓地发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2013(02):29-55
|
| [15] |
张雯欣. 新疆吐鲁番加依墓地青铜——早期铁器时代居民牙齿磨耗研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2018
|
| [16] |
张全超, 韩涛, 张群. 新疆鄯善洋海墓地出土人骨的牙齿微磨耗痕迹研究[J]. 西域研究, 2018(3):83-88+145-146
|
| [17] |
蒋洪恩. 吐鲁番洋海墓地植物遗存与古洋海人及环境之间的关系[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学, 2006
|
| [18] |
支禄. 见证吐鲁番农业从游牧走向农耕[N]. 吐鲁番日报(汉), 2014-04-24 (004)
|
| [19] |
李亚, 李肖, 曹洪勇, 等. 新疆吐鲁番考古遗址中出土的粮食作物及其农业发展[J]. 科学通报, 2013(S1):40-45
|