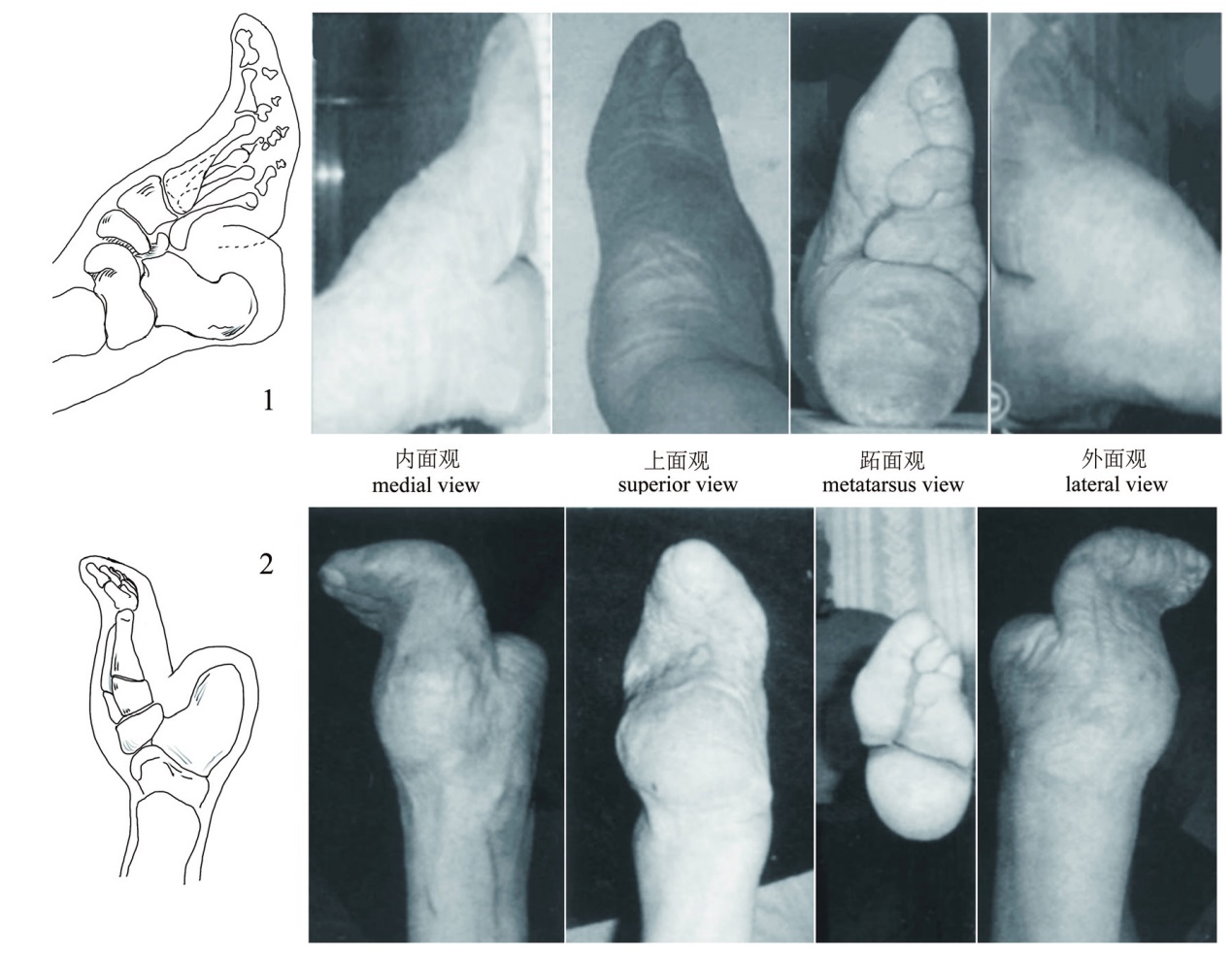
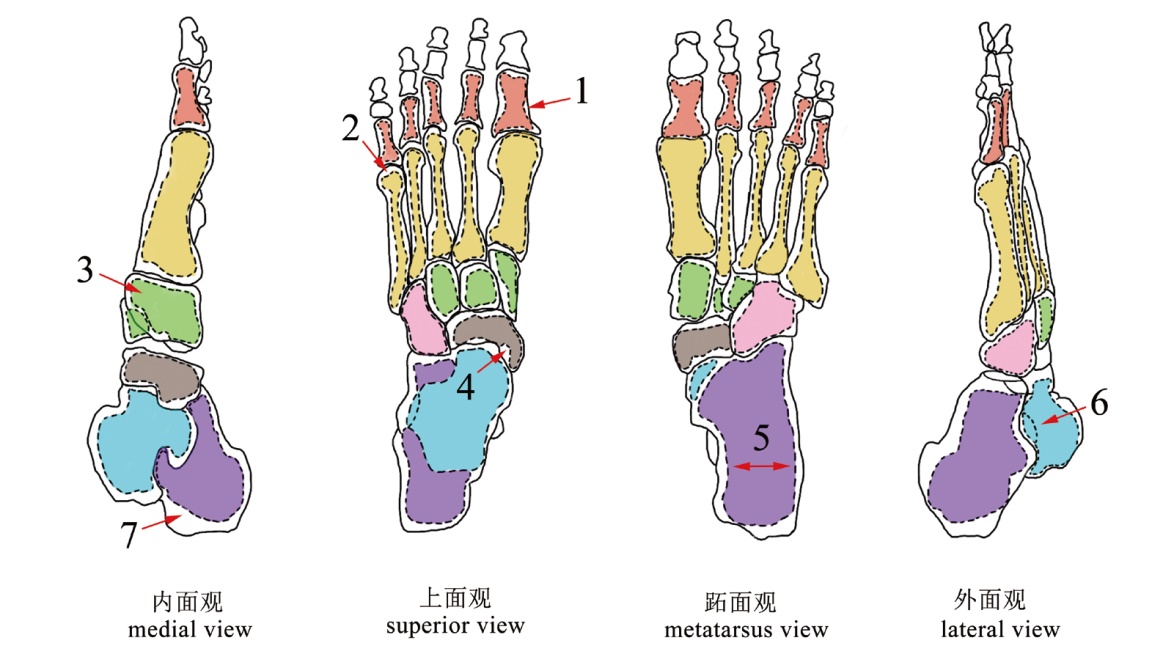
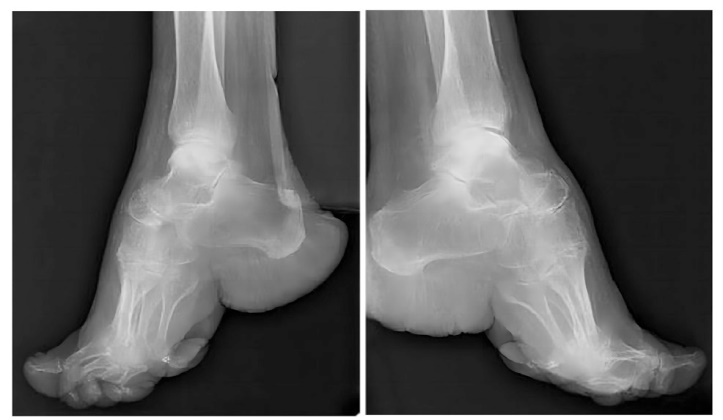
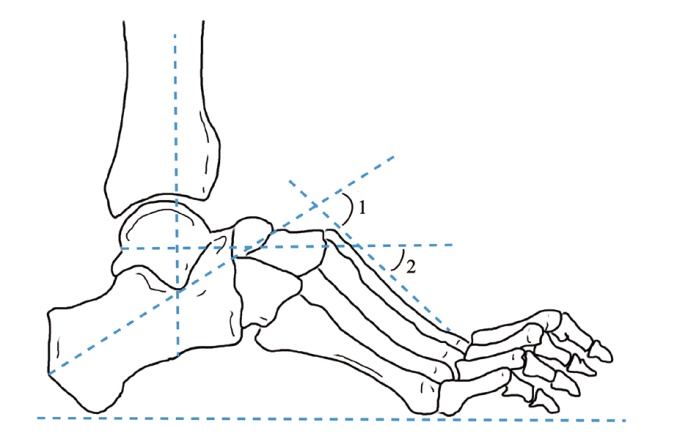
| [1] |
秦为径, 雷伟, 吴子祥, 等. 缠足畸形的形态学特征[J]. 第四军医大学学报, 2008, 14: 1328-1330
|
| [2] |
孙晓璠, 张全超, 牟萍媛, 等. 山西洪洞西冯堡清代墓地缠足女性的骨骼损伤和关节疾病[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(2): 1-13
|
| [3] |
王美玲. 从缠足习俗看中国古代的女性角色[D]. 硕士研究生学位论文, 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2013, 1-44
|
| [4] |
朱泓, 侯侃, 王晓毅. 从生物考古学角度看山西榆次明清时期平民的两性差异[J]. 吉林大学社会科学学报, 2017, 57(4): 117-124+206
|
| [5] |
Michael LR. Chinese foot binding: Radiographic findings and case report.[J]. Radiology Case Reports, 2009, 4(1): 270
|
| [6] |
郭祥. 云南缠足畸形形态及影像学特征及与骨质疏松相关性研究[D]. 硕士研究生学位论文, 昆明: 昆明医学院, 2011, 1-52
|
| [7] |
Stone PK. Binding women: Ethnology, skeletal deformations, and violence against women[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2012, 2(2-3): 53-60
doi: S1879-9817(12)00055-1
pmid: 29539382
|
| [8] |
秦为径. 中国四省部分地区现存缠足畸形抽样调查[D]. 硕士研究生学位论文, 西安: 第四军医大学, 2008, 1-50
|
| [9] |
赵永生, 郭林, 郝导华, 等. 山东地区清墓中女性居民的缠足现象[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(3): 344-358
|
| [10] |
李法军, 邱林欢, 赵晨, 等. 天津蓟州区桃花园墓地明清时期缠足女性的足骨形变[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(4): 674-685
|
| [11] |
邱林欢, 李法军. 天津蓟县桃花园墓地明清时期缠足女性足骨的形态观察[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(5): 787-800
|
| [12] |
Scheuer L, Black S, Christie A. The juvenile skeleton[M]. Academic Press, 2004, 1-485
|
| [13] |
Berger E, Yang L, Ye W. Foot binding in a Ming dynasty cemetery near Xi'an, China[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2019, 24: 79-88
doi: S1879-9817(18)30072-X
pmid: 30300764
|
| [14] |
Berg EE. Chinese foot binding[J]. National Association of Orthopaedic Nurses, 1995, 14(5): 66-68
|
| [15] |
Ma JB, Song YQ, Rong M, et al. Bound foot metatarsals skeletal rays kinematics information through inverse modelling[J]. International Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, 2013, 13(2): 147-153
|
| [16] |
Zhang Y, Li FL, Shen WW, et al. Characteristics of the skeletal system of bound foot: A case study[J]. Biomimetics Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering, 2014, 19: 120
|
| [17] |
孙晓璠. 山西洪洞西冯堡墓地清代女性居民的缠足研究[D]. 硕士研究生学位论文, 长春: 吉林大学, 2021
|
| [18] |
Broe KE, Hannan MT, Kiely DK, et al. Predicting fracture using bone mineral density: A prospective study of long-term care residents[J]. Osteoporos International, 2000, 11: 765
|
| [19] |
Holick MF, Chen TC. Vitamin D deficiency: a worldwide problem with health consequences[J]. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2008, 87(4): 10805-10865
|
| [20] |
Cummings SR, Ling X, Stone K. Consequences of foot binding among older women in Beijing, China[J]. American Journal of Public Health, 1997, 87(10): 1167-1679
|
| [21] |
Sun XF, Man XY, Liao XZ, et al. Footbinding and non-footbinding Han Chinese females in the Qing Dynasty (1644-1912 CE) Xifengbu cemetery: A skeletal and mortuary analysis[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2021, 13(18): 1-40
|
| [22] |
彭华. 中国缠足史考辨[J]. 江苏科技大学学报(社会科学版), 2013, 13(3): 6-16+24
|
| [23] |
黄时鉴. 元代缠足问题新探[J]. 东方博物, 2006, 1: 6-12
|
| [24] |
高洪兴. 缠足史[M]. 上海: 上海文艺出版社, 2007, 1-245
|
| [25] |
孙彦贞. 缠足风习与满族马蹄底鞋源起考述[J]. 中国历史文物, 2005, 3: 53-60+97
|
| [26] |
邱志诚. 国家、身体、社会:宋代身体史研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018, 333-352
|
| [27] |
柯基生. 三寸金莲[M]. 产业情报杂志社,1995
|
| [28] |
高世瑜. 缠足再议[J]. 史学月刊, 1999, 2: 20-24+111
|
| [29] |
姚灵犀. 采菲录[M]. 上海: 上海书店, 1997, 10-24
|
| [30] |
王晶可. 中国女性缠足习俗与整容文化的比较研究[J]. 现代商贸工业, 2020, 41(9): 190-192
|
| [31] |
Lee C. A bioarchaeological and biocultural investigation of Chinese footbinding at the Xuecun archaeological site, Henan Province, China[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2019, 25: 9-19
doi: S1879-9817(18)30091-3
pmid: 30927655
|
| [32] |
Zhao YS, Guo L, Xiao YN, et al. Osteological characteristics of Chinese foot-binding in archaeological remains[J]. International Journal of Paleopathology, 2020, 28: 48-58
doi: S1879-9817(19)30150-0
pmid: 31945597
|
| [33] |
张峰. 古代社会“三寸金莲”习俗长久存在的因素浅析[J]. 文化产业, 2020, 3: 26-27
|
| [34] |
杨幼梅. 三寸金莲与闽南男性审美的表征[J]. 大众文艺, 2016, 3: 261-263
|
| [35] |
丁梅. 缠足文化的“兴”与“衰”[J]. 大众文艺, 2020, 15: 222-223
|
| [36] |
Dorothy Y Ko. Cinderella’s Sisters: A revisionist history of foot binding[M]. University of California Press, 2005, 305-311
|
| [37] |
张五常. 中国旧家庭的礼教与国家的盛衰[J]. 紫光阁文摘, 2016, 12
|
| [38] |
姚遂. 耕织经济与中国灰姑娘:中国缠足兴衰的经济学解释[J]. 经济学报, 2017, 4(2): 96-130
|
| [39] |
[清] 赵翼. 陔余丛考[M]. 北京: 中华书局, 1963, 540
|
| [40] |
[加]宝森(Laurel Bossen)著. 中国妇女与农村发展:云南禄村六十年的变迁[M]. 译者:胡宝坤. 南京: 江苏人民出版社, 2005, 40-92
|
| [41] |
Bossen L, Wang XR, Brown MJ, et al. Feet and fabrication: footbinding and early twentieth-century rural women’s labor in Shaanxi[J]. Modern China, 2011, 37(4): 347-383
|
| [42] |
邵象清. 人体测量手册[M]. 上海: 上海辞书出版社, 1985, 191-192
|
| [43] |
罗卓荆, 唐农轩. 国人足弓指数的测定[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 1994, 1: 16-17
|
| [44] |
Schwend RM, Drennan JC. Cavus foot deformity in children[J]. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2003, 11(3): 201-211
pmid: 12828450
|
| [45] |
刘国忠, 王伯雄, 史辉, 等. 激光线扫描足部三维测量方法及其应用[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 5: 820-823
|
| [46] |
何晓宇, 王朝强, 周之平, 等. 三维有限元方法构建足部健康骨骼与常见疾病模型及生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(9): 1410-1415
|
| [47] |
石敏, 姚瀚钦, 李淳芃, 等. 基于深度Alignment网络的足部测量[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2020, 32(7): 1267-1278
doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.19-VR0467
|
| [48] |
黎刚, 周忠和. 物理之光助力古生物学前行[CP/OL]. URL: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_Qe4qppizQL6Xhq_tzoLQQ. Released on: 2021-09-27
|
| [49] |
邓涛. 当古生物遇到新科技[N]. 光明日报,2023-03-02(016)
|
| [50] |
Qutbi M, Soltanshahi M, Shiravand Y, et al. Technical and patient-related sources of error and artifacts in bone mineral densitometry using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry: A pictorial review[J]. Indian Journal of Radiology & Imaging. 2020, 30(3): 362-371
|
| [51] |
Li N, Li XM, Xu L, et al. Comparison of QCT and DXA: osteoporosis detection rates in postmenopausal women[J]. International Journal Endocrinology, 2013, 895474
|
| [52] |
[美]高彦颐, 刘东. 缠足:“金莲崇拜”盛极而衰的演变[M]. 南京: 江苏人民出版社, 2022
|
| [53] |
陈东原. 中国妇女生活史[M]. 北京: 商务印书馆, 1937, 98
|
| [54] |
刘妍. 宋代女子缠足的特点及其成因探析[J]. 学理论, 2016, 11: 142-143
|
| [55] |
湖北省文物考古研究所, 襄阳市文物考古研究所, 枣阳市文物考古队. 湖北枣阳九连墩M2发掘简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2018, 6: 3-55+2
|
| [56] |
湖南省博物馆, 中国科学院考古研究所. 长沙马王堆一号汉墓[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2008, 70
|
| [57] |
湖北省荆州地区博物馆. 江陵马山一号楚墓[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1985, 24-25
|
| [58] |
益阳市文物管理处, 益阳市博物馆. 益阳楚墓[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2008, 206
|
| [59] |
凤凰山一六七号汉墓发掘整理小组. 江陵凤凰山一六七号汉墓发掘简报[J]. 文物, 1976, 10: 31-35, 50, 36-37, 96
|
| [60] |
新疆维吾尔自治区博物馆. 新疆吐鲁番阿斯塔那北区墓葬发掘简报[J]. 文物, 1960, 6: 13-21+2+1-4
|
| [61] |
新疆维吾尔自治区博物馆考古部, 吐鲁番地区文物局阿斯塔那文物管理所. 新疆吐鲁番阿斯塔那古墓群西区考古发掘报告[J]. 考古与文物, 2016, 5: 31-50
|
| [62] |
崔成实. 浙江衢州市南宋墓出土器物[J]. 考古, 1983, 11: 1004-1011+1018+1061-1063
|
| [63] |
俞立军. 浙江兰溪市南宋墓[J]. 考古, 1991, 7: 670-672+680
|
| [64] |
李科友, 周迪人, 于少先. 江西德安南宋周氏墓清理简报[J]. 文物, 1990, 9: 1-13+97-101
|
| [65] |
李庚善. 从考古发现的人骨架谈古代女性的裹足问题[J]. 长江文化论丛, 2009, 99-105
|
| [66] |
李海军, 刘力铭, 张一丹, 等. 中国古代先民遗骸人工改形的发现与研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(4): 540-553
|