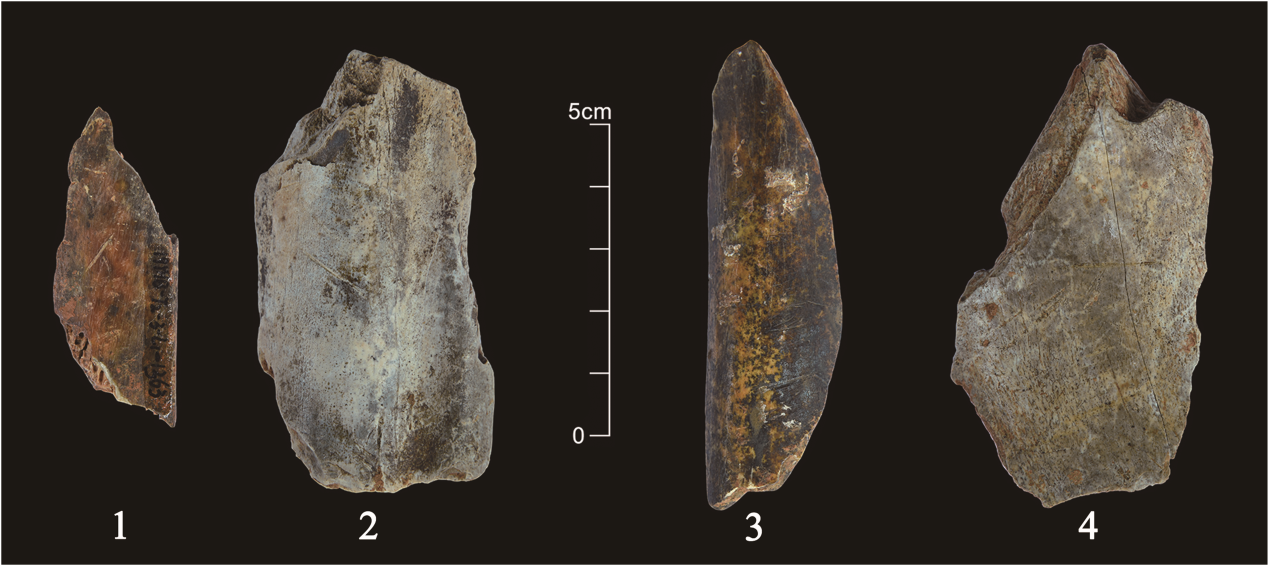
| [1] |
HU Haiqian, HUANG Wanbo, WEI Guangbiao, DAI Hui, XIONG Can, HE Shuxing, JIANG Tao.
Gigantopithecus blacki discovered in the Early Pleistocene strata of Wulong, Chongqing
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(05): 701-711.
|
| [2] |
REN Jincheng, LI Feng, CHEN Fuyou, GAO Xing.
Core reduction technology of stone artifacts unearthed in 2015 from the Banjingzi site in Nihewan Basin
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(05): 712-726.
|
| [3] |
CUI Zuowen, WANG Chunxue, CHEN Quanjia, ZENG Qingshuo, ZHANG Nan.
New paleolithic discoveries in Nanzhao, Henan in 2021
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(05): 853-864.
|
| [4] |
WANG Jiaqi, ZHANG Xuewei, WANG Chunxue, SHENG Lishuang.
A preliminary report of the 2021 excavation at the Taiziling locality in Jizhou County, Tianjin City
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(03): 440-447.
|
| [5] |
LIAO Wei.
Progress in the study of fossil orangutans in South China
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(02): 199-213.
|
| [6] |
CHEN Yuzhi, WU Xianzhu.
Paleoenvironment and survival behaviour of early hominin in the Three Gorges area and its surrounding regions
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(02): 287-297.
|
| [7] |
AI Lan, TIAN Chun, LI Dawei, LI Jinyan, WANG Wei.
An excavation report of the Dingmo site in Tiandong of Guangxi
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(02): 298-313.
|
| [8] |
WEI Tianxu, WANG Chunxue, ZHANG Xuewei, WANG Jiaqi, SHENG Lishuang.
A preliminary report of the excavation of Chaoyang Cave 2 in Jizhou County, Tianjin City
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(02): 314-320.
|
| [9] |
ZHAO Yunxiao, TONG Guang, TU Hua, ZHAO Hailong.
Excavation report of the Shigou site C area in the Nihewan Basin, Hebei Province
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(01): 122-131.
|
| [10] |
ZHANG Zhen, WANG Ying, LI Yuecong.
Research progress on the relationship between Paleolithic hominid activities and environmental changes in the Nihewan Basin
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(01): 184-198.
|
| [11] |
PEI Shuwen, XU Zhe, YE Zhi, MA Dongdong, JIA Zhenxiu.
Human adaptive behaviors during the Middle Pleistocene Climatic Transition in the Nihewan Basin
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(01): 19-39.
|
| [12] |
LIU Lianqiang, PU Yuxiao, HOU Jiaqi, WANG Fagang.
Stone artifacts from the Yuzuigou Locality 1 of the Majuangou Paleolithic site excavated in 2017 and 2018
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(01): 40-54.
|
| [13] |
WU Xiujie.
Research progress on human fossils from the Xujiayao site in late Middle Pleistocene
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(01): 5-18.
|
| [14] |
WANG Xiaomin, LIU Lianqiang, CHEN Guopeng, LI Feng, XIE Fei, GAO Xing.
Behavior of the ancient humans as reflected by the broken long bones of mammals from the Majuangou site, Nihewan Basin
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024, 43(01): 91-105.
|
| [15] |
ZHAO Qinpo, ZHANG Shuimu, SU Kai, MA Huanhuan, CHEN Jun, XU Yonghua.
Discovery and preliminary study of the Wenquan Paleolithic site in Ruzhou, Henan
[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2023, 42(05): 616-625.
|