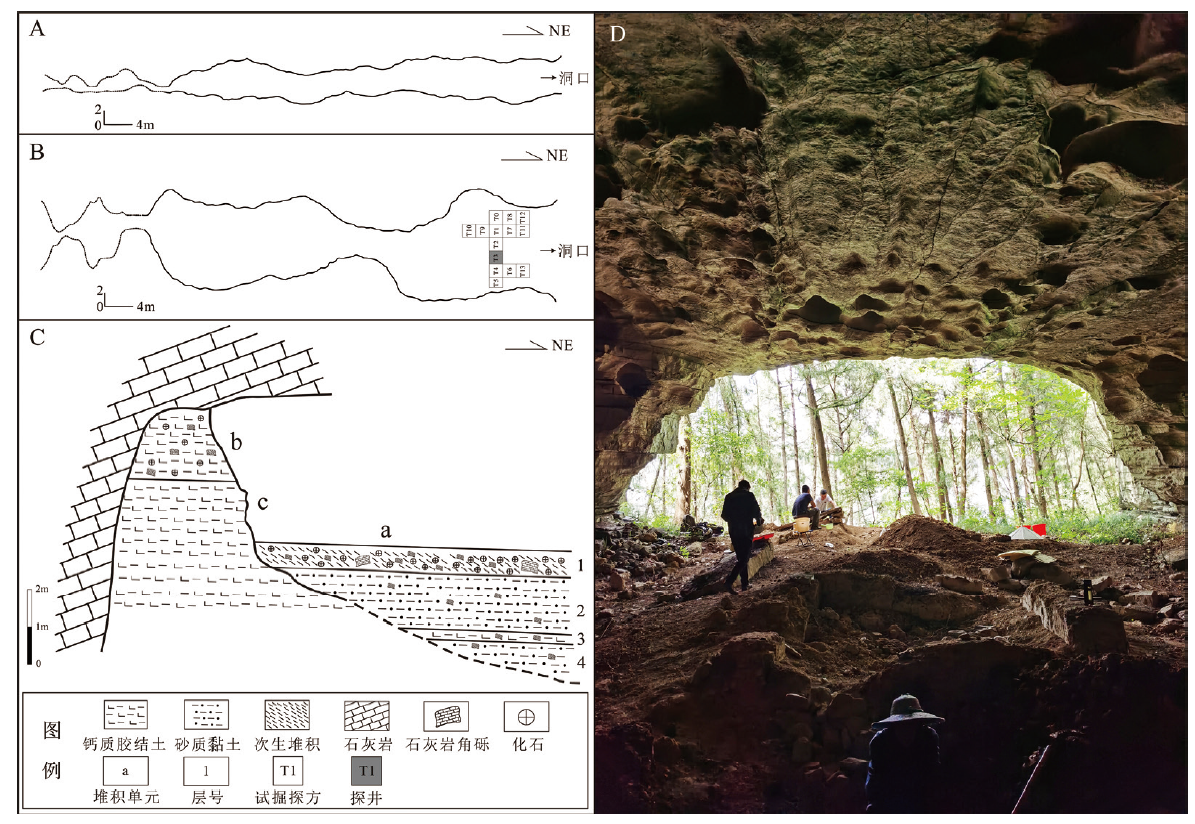
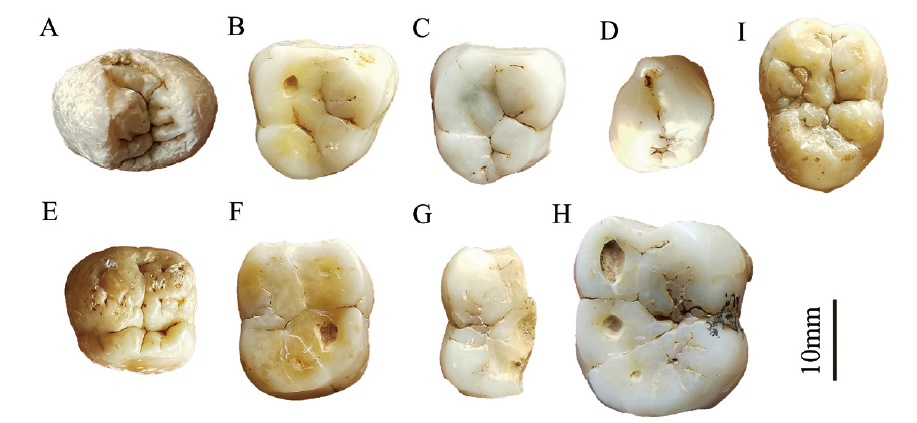
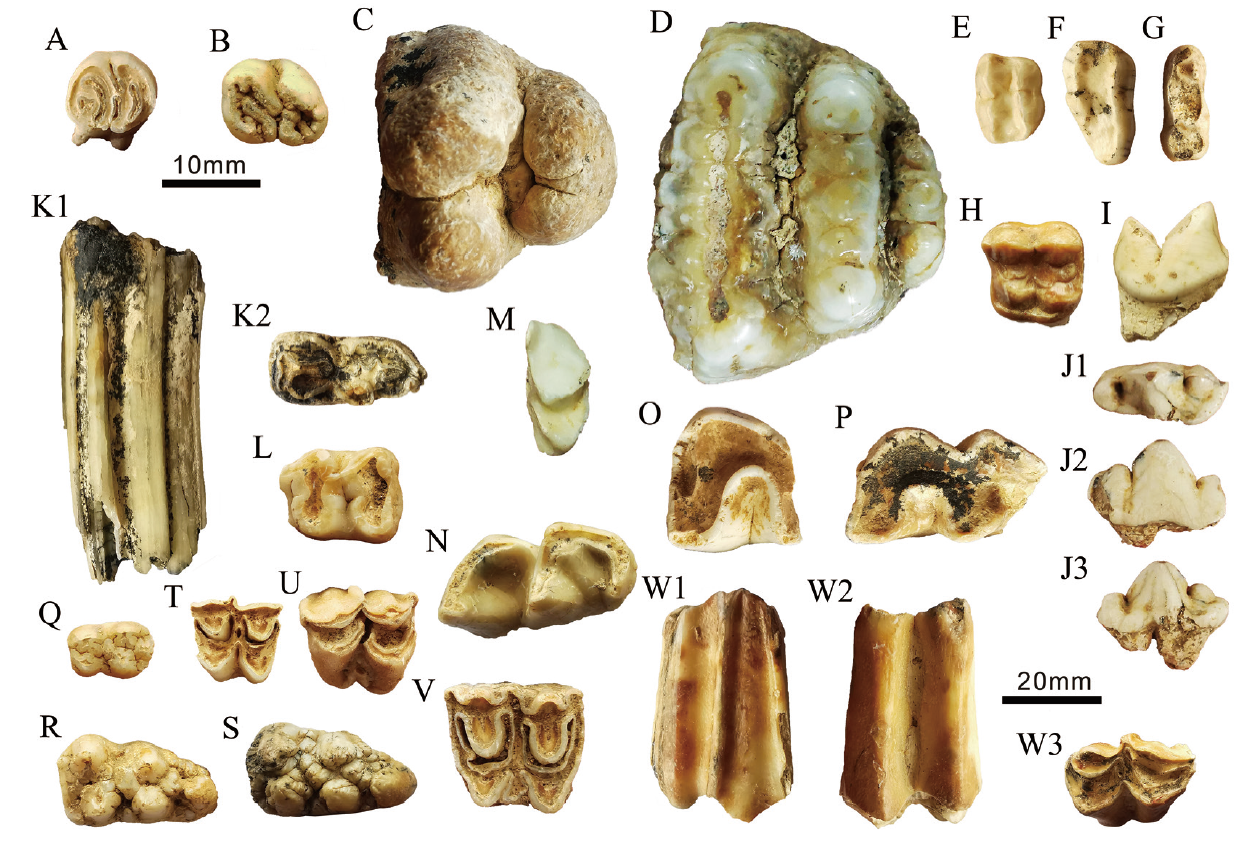
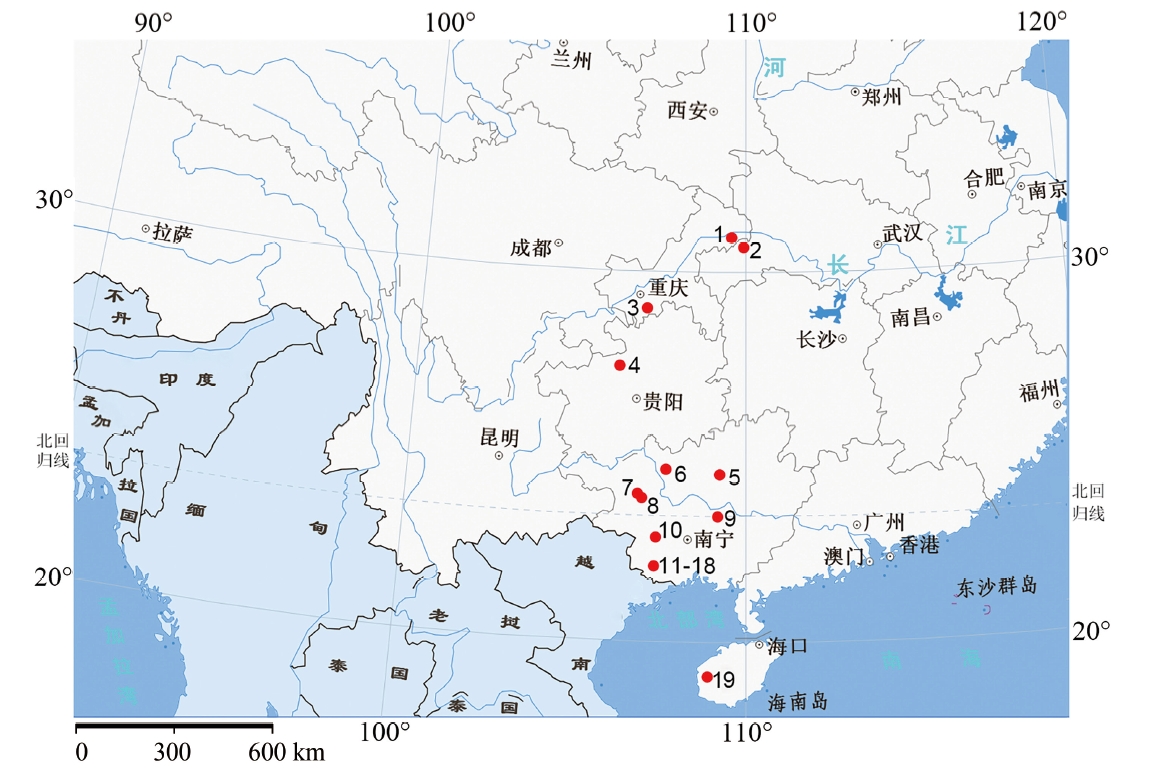
| [1] |
von Koenigswald GHR. Eine fossile Säugetierfauna mit Simia aus Südchina[J]. Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, Series B, 38(2): 872-879
|
| [2] |
吴汝康. 巨猿下颌骨和牙齿研究. 中国古生物志(新丁种)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1962, 11, 1-94
|
| [3] |
黄万波, 方其仁. 巫山猿人遗址[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991, 1-230
|
| [4] |
张银运, 王令红, 董兴仁, 等. 广西巴马发现的巨猿牙齿化石[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1975, 13(3): 148-154
|
| [5] |
张银运, 吴茂霖, 刘金荣. 广西武鸣新发现的巨猿牙齿化石[J]. 科学通报, 1973, 3: 130-133
|
| [6] |
Zhang YQ, Harrison T. Gigantopithecus blacki: A giant ape from the Pleistocene of Asia revisited[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2017, 162, 153-177
|
| [7] |
赵凌霞, 同号文, 计春华, 等. 贵州毕节发现的巨猿牙齿化石及其意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(4): 548-554.
|
| [8] |
Cameron DW. The taxonomic siatus of the Siwalik late Miocene hominid indopithecus (Gigantopithecus)[J]. Himalayan geology, 2001, 22(2): 29-34
|
| [9] |
韩康信, 赵凌霞. 湖北巨猿牙齿龋病观察[J]. 人类学学报, 2002, 21(3): 191-198
|
| [10] |
张银运, 潘悦容. 灵长目[C]. 见:郑绍华(主编).建始人遗址 北京: 科学出版社, 2004, 67-80
|
| [11] |
裴文中, 李有恒. 第三个“巨猿”下颚骨的发现[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1958, 2(4): 193-200
|
| [12] |
Jin CZ, Wang Y, Deng CL, et al. Chronological sequence of the early Pleistocene Gigantopithecus faunas from cave sites in the Chongzuo, Zuojiang River area, South China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 354: 4-14
|
| [13] |
Jin CZ, Qin DG, Pan WS, et al. A newly discovered Gigantopithecus fauna from Sanhe Cave, Chongzuo, Guangxi, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 54(5): 788-797
|
| [14] |
Wang Y, Jin CZ, Pan WS, et al. The Early Pleistocene Gigantopithecus-Sinomastodon fauna from Juyuan karst cave in Boyue Mountain, Guangxi, South China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 434: 4-16
|
| [15] |
Wang W. New discoveries of Gigantopithecus blacki teeth from Chuifeng Cave in the Bubing Basin, Guangxi, south China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2009, 57(3): 229-240
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2009.05.004
pmid: 19656551
|
| [16] |
Liao W, Liang H, Li JY, et al. Early Pleistocene large-mammal assemblage associated with Gigantopithecus at Chuifeng Cave, Bubing Basin, South China[J]. Historical Biology, 2023, 1-18
|
| [17] |
Welker F, Ramos-Madrigal J, Kuhlwilm M, et al. Enamel proteome shows that Gigantopithecus was an early diverging pongine[J]. Nature, 2019, 576: 262-265
|
| [18] |
Zhang YQ, Jin CZ, Kono RT, et al. A fourth mandible and associated dental remains of Gigantopithecus blacki from the Early Pleistocene Yanliang Cave, Fusui, Guangxi, South China[J]. Historical Biology, 2015, 28(1-2): 95-104
|
| [19] |
Zhang YQ, Westaway KE, Haberle, et al. The demise of the giant ape Gigantopithecus blacki[J]. Nature, 2024, 625(7995): 1-5
|
| [20] |
Zhang YQ, Jin CZ, Cai YJ, et al. New 400-320 ka Gigantopithecus blacki remains from Hejiang Cave, Chongzuo City, Guangxi, South China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 354: 35-45
|
| [21] |
Pan Y, Zhang YQ, Yang LY, et al. Preliminary description of a late Middle Pleistocene mammalian fauna prior to the extinction of Gigantopithecus blacki from the Yixiantian Cave, Guangxi ZAR, South China[J]. The Anatomical Record Advances in Integrative Anatomy and Evolutionary Biology, 2023, 1-26
|
| [22] |
Zhang YQ, Kono RT, Wang W, et al. Evolutionary trend in dental size in Gigantopithecus blacki revisited[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2015, 83: 91-100
|
| [23] |
韩德芬. 广西大新黑洞哺乳动物化石[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1982, 20(1): 58-64
|
| [24] |
王頠. 广西田东么会洞早更新世遗址[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013, 1-152
|
| [25] |
郑绍华. 建始人遗址[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004, 1-412
|
| [26] |
裴文中. 广西柳城巨猿洞及其他山洞之食肉目、长鼻目和偶蹄目化石[M]. 中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所集刊, 1987,18: 5-134
|
| [27] |
金昌柱, 郑家坚, 王元, 等. 中国南方早更新世主要哺乳动物群层序对比和动物地理[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(4): 304-317
|
| [28] |
Han F, Bahain JJ, Deng CL, et al. The earliest evidence of hominid settlement in China: Combined electron spin resonance and uranium series (ESR/U-series) dating of mammalian fossil teeth from Longgupo cave[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 434: 75-83
|
| [29] |
李钊, 李超荣, 王大新. 海南的旧石器考古[A].见:董为(主编).第十一届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008, 167-172
|
| [30] |
Jin CZ, Ciochon R, Ciochon R, et al. The first skull of the earliest giant panda[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2007, 104 (26): 10932-10937
|
| [31] |
Hu HQ, Tong HW, Shao QF et al. New remains of Ailuropoda melanoleuca baconi from Yanjinggou, China: Throwing light on the evolution of giant pandas during the Pleistocene[J]. Journal of Mammalian Evolution, 2023, 30: 137-154
|
| [32] |
Tong HW. Dental characters of the Quaternary tapirs in China, their significance in classification and phylogenetic assessment[J]. Geobios, 2005, 38: 139-150
|
| [33] |
刘金毅, 赵凌霞, 陈津, 等. 贵州毕节扒耳岩巨猿动物群的年代与环境:来自食肉类化石的分析和研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(4): 654-666
|
| [34] |
Hu HQ, Tong HW, Yu HD, et al. New study sheds light on the impressive intraspecific variation of Quaternary Asiatic black bears in China[J]. Quaternary International, 2023, 646(10): 22-33
|
| [35] |
Head M, Gibbard P. Early-Middle Pleistocene transitions: linking terrestrial and marine realms[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 389: 7-46
|
| [36] |
Yang SX, Yue JP, Zhou XY, et al. Hominin site distributions and behaviours across the Mid-Pleistocene climate transition in China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 248: 106614
|
| [37] |
Bergmann C. Über die verhältnisse der wärmeökonomie der thiere zu ihrer grösse[J]. Gottinger Studien, 1847, 2: 595-708
|
| [38] |
Weidenrich F. Giant early man from Java and South China[J]. Anthropology Papers of American Museum Natural History, 1945, 40: 1-134
|
| [39] |
王令红, 吴茂霖, 张银运. 论巨猿与人类的关系[A].见:古脊椎动物与古人类研究所(编).古人类论文集[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978, 67-76
|
| [40] |
Begun DR. How to identify (as opposed to define) a homoplasy: examples from fossil and living great apes[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2007, 52(5): 559-572
pmid: 17434574
|
| [41] |
Stanford CB, Allen JS, Anton SC. Biological Anthropology: the natural history of humankind (3rd edition) [M]. Boston, Ma: Pearson, 2013, 285-305
|