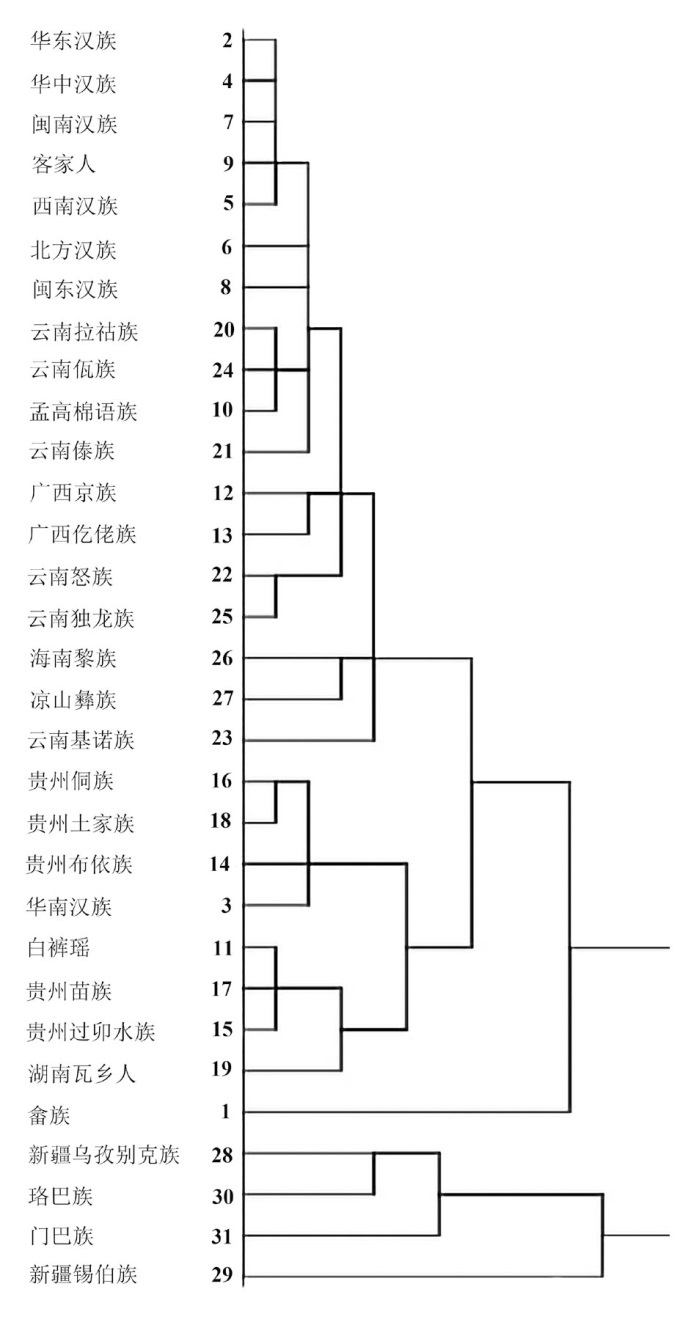
| [1] |
徐规. 畬族的名称、来源和迁徙[J]. 杭州大学学报(人文科学版), 1962, 1: 57-62
|
| [2] |
施联朱. 关于畲族来源与迁徙[J]. 中央民族学院学报, 1983, 2: 34-42+33
|
| [3] |
禄佳妮, 王传超. 分子人类学视域中畲族族源新探[J]. 北方民族大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2019, 1: 98-107
|
| [4] |
Cai XY, Qin ZD, Wen B, et al. Human Migration through Bottlenecks from Southeast Asia into East Asia during Last Glacial Maximum Revealed by Y Chromosomes[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(8): e24282
|
| [5] |
Liu SH, Chen GC, Huang HH, et al. Patrilineal background of the She minority population from Chaoshan Fenghuang Mountain, an isolated mountain region, in China[J]. Genomics, 2017, 109(3-4): 284-289
doi: S0888-7543(17)30033-2
pmid: 28487173
|
| [6] |
胡荣. 福建畲族人群体型特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(5): 824-833
|
| [7] |
张振标. 现代中国人体质特征及其类型的分析[J]. 人类学学报, 1988, 7(4): 314-323
|
| [8] |
徐杰舜. 雪球:汉民族的人类学分析[M]. 上海: 上海人民出版社, 1999
|
| [9] |
曾宪智, 戴福珍, 史习舜, 等. 福建省福安市畲族成人体质调查报告[J]. 福建医药杂志, 1996, 18(5): 211-216
|
| [10] |
孙思, 何学华, 曹显明, 等. 贵州南部地区苗族、畲族和汉族头面部形态特征调查[J]. 黔南民族医专学报, 2006, 19(3): 211-216
|
| [11] |
席焕久, 陈昭. 人体测量方法(第二版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010
|
| [12] |
李咏兰, 宇克莉, 陆舜华, 等. 中国南方汉族群体的头面部特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 101-108
|
| [13] |
宇克莉, 郑连斌, 李咏兰, 等. 中国北方、南方汉族头面部形态学特征的差异[J]. 解剖学报, 2016, 47(3): 404-408
|
| [14] |
张兴华, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 等. 闽南人的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(4): 516-527
|
| [15] |
郑连斌, 李咏兰, 陆舜华, 等. 中国客家人体质特征[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2013, 43(3): 213-222
|
| [16] |
孙泽阳, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 等. 孟高棉语族未识别民族的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(5): 811-823
|
| [17] |
罗载刚, 杨家力, 余跃生, 等. 白裤瑶体质人类学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2003, 22(2): 150-160
|
| [18] |
郑连斌, 陆舜华, 丁博. 仫佬族体质特征研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(3): 242-250
|
| [19] |
余跃生, 任光祥, 戎聚全, 等. 贵州布依族体质人类学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2005, 24(3): 204-214
|
| [20] |
余跃生, 王克松, 陆玉炯, 等. 贵州“过卯”水族的体质人类学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2007, 26(2): 155-164
|
| [21] |
杨秀海, 余跃生, 欧德灯, 等. 贵州侗族体质人类学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(1): 73-81
|
| [22] |
余跃生, 陆玉炯, 罗载刚, 等. 贵州王卡苗族体质人类学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2007, 26(1): 54-63
|
| [23] |
任光祥, 余跃生, 杨胜文, 等. 贵州土家族体质人类学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(3): 289-298
|
| [24] |
皮建辉, 黎杰, 李林, 等. 湖南瓦乡人体质特征研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(2): 218-226
|
| [25] |
李明, 李跃敏, 余发昌, 等. 云南拉祜族的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2001, 20(1): 39-44
|
| [26] |
宇克莉, 郑连斌, 李咏兰. 西双版纳傣族的人种学特点:来自人体测量学的数据[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(4): 553-560
|
| [27] |
郑连斌, 陆舜华, 罗东梅, 等. 怒族的体质调查[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(2): 158-166
|
| [28] |
包金萍, 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 等. 基诺族体质特征及35年来体质的变化[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(2): 261-271
|
| [29] |
李咏兰, 郑连斌, 金丹. 黎族的体成分与体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(1): 77-87
|
| [30] |
宇克莉, 董文静, 李咏兰. 四川凉山彝族的人体测量学[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(3): 478-483
|
| [31] |
郑连斌, 崔静, 陆舜华, 等. 乌孜别克族体质特征研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2004, 23(1): 35-45
|
| [32] |
徐国昌, 马长德, 裴林国, 等. 伊犁锡伯族成人头面部表型特征[J]. 南阳理工学院学报, 2021, 13(4): 113-117
|
| [33] |
郑连斌, 陆舜华, 张兴华, 等. 珞巴族与门巴族的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(4): 401-407
|
| [34] |
Reddy BM, Pferrer A, Crawford MH, et al. Population substructure and patterns of quantitative variation among the Gollas of southern Andhra Pradesh,India[J]. Human Biology, 2001, 291-306
|
| [35] |
Arya R, Duggirala R, Comuzzie AG. Heritability of anthropometric phenotypes in caste populations of Visakhapatnam, India[J]. Human Biology, 2002, 74(3): 325-344
pmid: 12180759
|
| [36] |
Karafet TM, Hallmark B, Cox MP, et al. Major East-west Division Underlies Y Chromosome Stratification Across Indonesia[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2010, 27(8): 1833-1844
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq063
pmid: 20207712
|