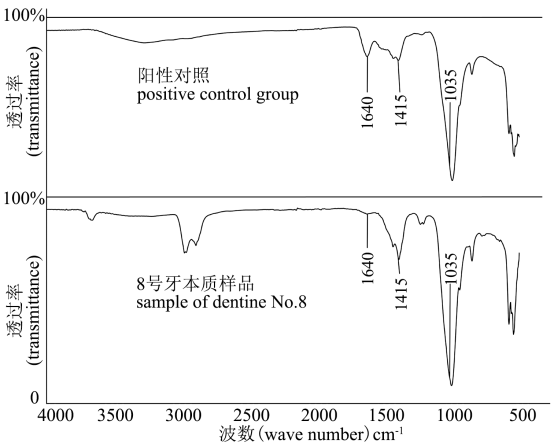
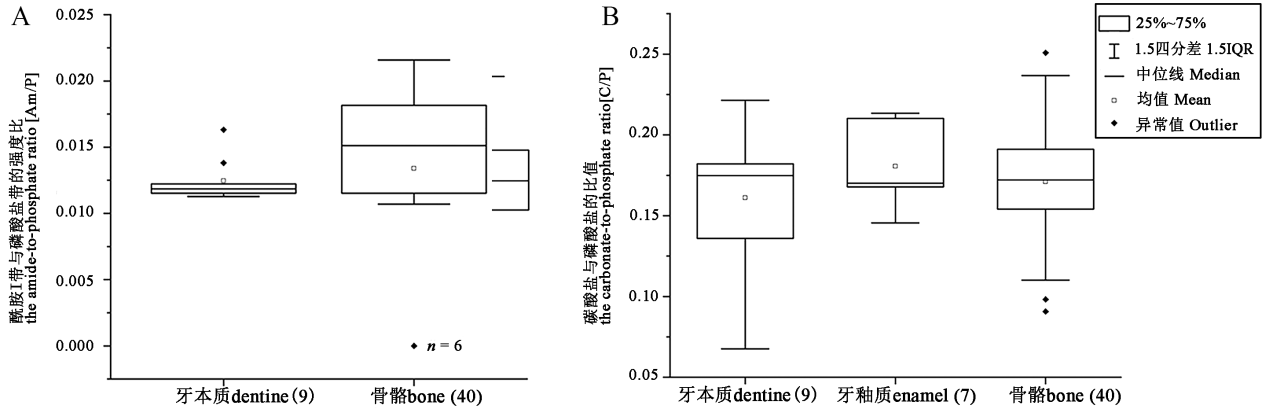
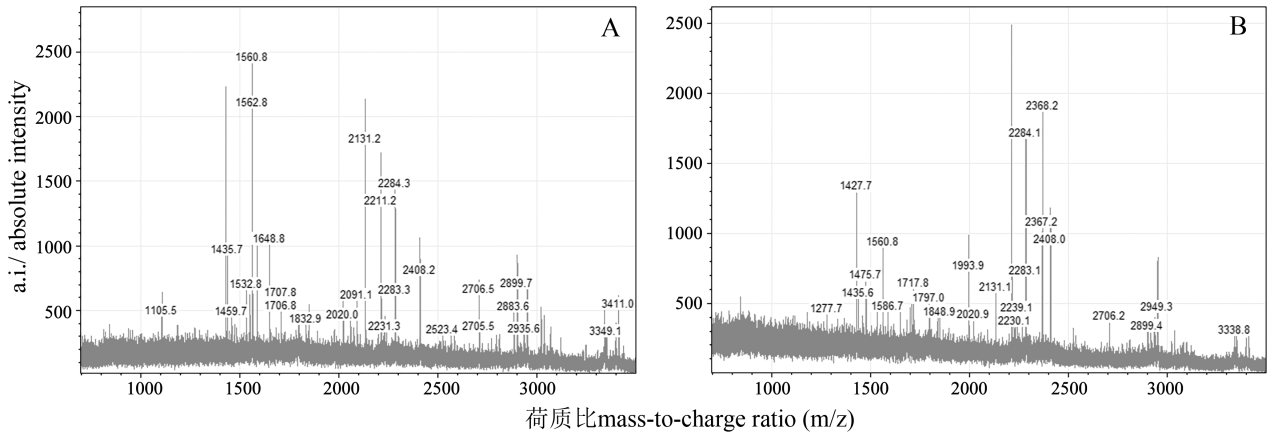
| [1] |
Wu XJ, Pei SW, Cai YJ, et al. Archaic human remains from Hualongdong, China, and Middle Pleistocene human continuity and variation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116: 9820-9824
|
| [2] |
宫希成, 郑龙亭, 邢松, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞出土的人类化石[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(4): 427-436
|
| [3] |
陈胜前, 罗虎. 安徽东至县华龙洞旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2012, 4: 7-13
|
| [4] |
同号文, 吴秀杰, 董哲, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞古人类遗址哺乳动物化石的初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(2): 284-305
|
| [5] |
裴树文, 蔡演军, 董哲, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞遗址洞穴演化与古人类活动[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(4): 593-607
|
| [6] |
董哲, 战世佳. 安徽东至县华龙洞旧石器时代遗址出土石制品研究[J]. 东南文化, 2015, 6: 63-71
|
| [7] |
董哲, 裴树文, 盛锦朝, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞古人类遗址2014-2016年出土的石制品[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(4): 778-788
|
| [8] |
李潇丽, 董哲, 裴树文, 等. 安徽东至华龙洞洞穴发育与古人类生存环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3): 169-179
|
| [9] |
刘武, 吴秀杰, 邢松. 更新世中期中国古人类演化区域连续性与多样性的化石证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(4): 473-490
|
| [10] |
Jiangzuo QG, Werdelin L, Zhang K, et al. Prionailurus kurteni (Felidae, Carnivora), a new species of small felid from the late Middle Pleistocene fossil hominin locality of Hualongdong, southern China[J]. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 2024, 61(1): 335-342
|
| [11] |
Wu XJ, Pei SW, Cai YJ, et al. Morphological description and evolutionary significance of 300 ka hominin facial bones from Hualongdong, China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2021, 161: 103052
|
| [12] |
Xing S, Wu XJ, Liu W, et al. Middle Pleistocene human femoral diaphyses from Hualongdong, Anhui Province, China[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2021, 174(2): 285-298
|
| [13] |
Wu XJ, Pei SW, Cai YJ, et al. Morphological and morphometric analyses of a late Middle Pleistocene hominin mandible from Hualongdong, China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2023, 182: 103411
|
| [14] |
吴秀杰, 张伟. 中国古人类颅容量的推算方法比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(4): 513-524
|
| [15] |
刘武, 惠家明, 何嘉宁, 等. 门齿孔位置在中国古人类化石与现代人群的表现及其演化意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(5): 739-750
|
| [16] |
刘武, 吴秀杰. 中更新世晚期中国古人类化石的形态多样性及其演化意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(4): 563-575
|
| [17] |
Liu W, Athreya S, Xing S, et al. Hominin evolution and diversity: A comparison of earlier-Middle and later-Middle Pleistocene hominin fossil variation in China[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 2022, 377(1849): 20210040
|
| [18] |
刘武. 二十一世纪中国人类演化研究的发现、认识与理论探索[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(6): 881-899
|
| [19] |
Chen FH, Welker F, Shen CC, et al. A late Middle Pleistocene Denisovan mandible from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Nature, 2019, 569: 409-412
|
| [20] |
Xia H, Zhang DJ, Wang J, et al. Middle and Late Pleistocene Denisovan subsistence at Baishiya Karst Cave[J]. Nature, 2024, 632: 108-113
|
| [21] |
Welker F, Hajdinjak M, Talamo S, et al. Palaeoproteomic evidence identifies archaic hominins associated with the Châtelperronian at the Grotte du Renne[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113: 201605834
|
| [22] |
Welker F, Ramos-Madrigal J, Gutenbrunner P, et al. The dental proteome of Homo antecessor[J]. Nature, 2020, 580: 235-238
|
| [23] |
Demeter F, Shackelford L, Zanolli C, et al. A Middle Pleistocene Denisovan molar from the Annamite Chain of northern Laos[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 2557
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29923-z
pmid: 35581187
|
| [24] |
Welker F, Ramos-Madrigal J, Kuhlwilm M, et al. Enamel proteome shows that Gigantopithecus was an early diverging pongine[J]. Nature, 2019, 576: 262-265
|
| [25] |
Paterson RS, Mackie M, Capobianco A, et al. A 20+ Ma Old Enamel Proteome from Canada's High Arctic Reveals Diversification of Rhinocerotidae in the Middle Eocene-Oligocene[CP/OL]. bioRxiv, 2024. 06.07.597871. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.07.597871
|
| [26] |
Demarchi B, Stiller j, Grealy A, et al. Ancient proteins resolve controversy over the identity of Genyornis eggshell[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2022, 119 (43): e2109326119
|
| [27] |
Demarchi B, Mackie M, Li ZH, et al. Survival of mineral-bound peptides into the Miocene[J]. eLife, 2022, 11: e82849
|
| [28] |
Demarchi B, Hall S, Roncal-Herrero T, et al. Protein sequences bound to mineral surfaces persist into deep time[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e17092
|
| [29] |
Stolarski J, Drake J, Coronado I, et al. First paleoproteome study of fossil fish otoliths and the pristine preservation of the biomineral crystal host[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13: 3822
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30537-8
pmid: 36882485
|
| [30] |
Cappellini E, Welker F, Pandolfi L, et al. Early Pleistocene enamel proteome from Dmanisi resolves Stephanorhinus phylogeny[J]. Nature, 2019, 574: 103-107
|
| [31] |
Cappellini E, Jensen LJ, Szklarczyk D, et al. Proteomic analysis of a Pleistocene mammoth femur reveals more than one hundred ancient bone proteins[J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2012, 11(2): 917-926
doi: 10.1021/pr200721u
pmid: 22103443
|
| [32] |
Rybczynski N, Gosse J C, Richard Harington C, et al. Mid-Pliocene warm-period deposits in the high arctic yield insight into camel evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1550
doi: 10.1038/ncomms2516
pmid: 23462993
|
| [33] |
Warinner C, Rodrigues JFM, Vyas R, et al. Pathogens and host immunity in the ancient human oral cavity[J]. Nature Genetics, 2013, 4(4): 336-344
|
| [34] |
Sawafuji R, Cappellini E, Nagaoka T, et al. Proteomic profiling of archaeological human bone[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2017, 4(6): 161004
|
| [35] |
Tsutaya T, Sawafuji R, Taurozzi AJ, et al. A male Denisovan mandible from Pleistocene Taiwan[J]. Science, 2025, 388(6743): 176-180
|
| [36] |
Presslee S, Penkman K, Fischer R, et al. Assessment of different screening methods for selecting palaeontological bone samples for peptide sequencing[J]. Journal of Proteomics, 2021, 230: 103986
|
| [37] |
Hollund HI, Ariese F, Fernandes R, et al. Testing an alternative High-throughput tool for investigating bone Diagenesis: FTIR in attenuated Total reflection (ATR) mode[J]. Archaeometry, 2013, 55: 507-532
|
| [38] |
Scaggion C, Marinato M, Dal Sasso G, et al. A fresh perspective on infrared spectroscopy as a prescreening method for molecular and stable isotopes analyses on ancient human bones[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14: 1028
|
| [39] |
Buckley M, Collins M, Thomas-Oates J, et al. Species identification by analysis of bone collagen using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrometr, 2009, 23(23): 3843-3854
|
| [40] |
Buckley M, Fraser S, Herman J, et al. Species identification of archaeological marine mammals using collagen fingerprinting[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2014, 41(Suppl. C): 631-641
|
| [41] |
Welker F, Soressi M, Rendu W, et al. Using ZooMS to identify fragmentary bone from the late middle / early upper Palaeolithic sequence of les Cottes, France[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 54: 279-286
|
| [42] |
Harvey VL, Daugnora L, Buckley M, et al. Species identification of ancient Lithuanian fish remains using collagen fingerprinting[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2018, 98: 102-111
|
| [43] |
Lacruz RS, Habelitz S, Wright JT, et al. Dental Enamel Formation and Implications for Oral Health and Disease[J]. Physiological Reviews, 2017, 97(3): 939-993
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2016
pmid: 28468833
|
| [44] |
Kontopoulos I, Penkman K, Mullin VE, et al. Screening archaeological bone for palaeogenetic and palaeoproteomic studies[J]. PLoS ONE, 2020, 15(6): e0235146
|
| [45] |
Pal Chowdhury M, Wogelius R, Manning PL, et al. Collagen deamidation in archaeological bone as an assessment for relative decay rates[J]. Archaeometry, 2019, 61(6): 1382-1398
doi: 10.1111/arcm.12492
|
| [46] |
Taurozzi AJ, Ruther PL, Patramanis I, et al. Deep-time phylogenetic inference by paleoproteomic analysis of dental enamel[J]. Nature Protocols, 2024, 19(5): 2085-2116
|
| [47] |
Porto IM, Laure HJ, Tykot RH, et al. Recovery and identification of mature enamel proteins in ancient teeth[J]. European Journal of Oral Sciences, 2011, 119: 83-87
|