

收稿日期: 2020-09-10
网络出版日期: 2021-04-12
基金资助
国家社科基金(18BKG009);河南省文物局南水北调文物保护项目
Report of the stone artifacts from the Liangjiagang Locality 2 and the Donggang Paleolithic site in Danjiangkou reservoir region
Received date: 2020-09-10
Online published: 2021-04-12
李京亚 , 赵静芳 , 宋国定 . 丹江口库区梁家岗2号和东岗旧石器地点的调查与发掘[J]. 人类学学报, 2022 , 41(01) : 108 -120 . DOI: 10.16359/j.cnki.cn11-1963/q.2020.0052
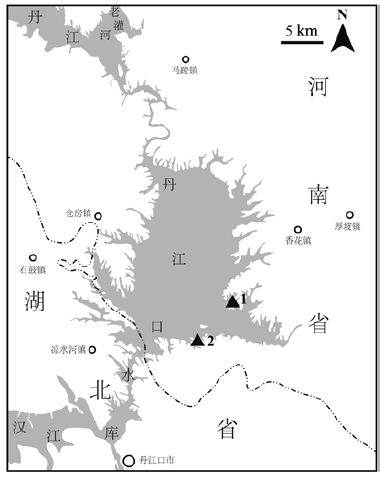
Danjingkou reservoir is the source of water for the Middle Route Project of the South to-North Water Diversion in China. Liangjiagang locality 2 and Donggang Paleolithic site are located on the 3rd terrace of left bank of Danjiang River, originally discovered in 1994 and excavated in 2009. The excavation was conducted in an area of 1425 m2where 193 stone artifacts were found. The typology and technological analyses of these stone artifacts reveal that: 1) Lithic raw materials exploited at the two sites were locally available from ancient river gravels in which quartz is dominant. 2) The excavated lithic assemblage includes core, flake, chunk, and stone tool. Stone tool mainly includes scraper that makes up the largest proportion of all the stone tools, point, chopper, handaxe. 3) The flaking technique contains direct hard hammer freehand percussion and bipolar percussion. Freehand cores percussion is dominated by the double-platform and the multi-platform core reduction strategies. 4) Flake blanks were main raw material to make stone tool, other than few chunks or pebbles. Based on the geomorphology and the dating of the sediments from other sites in the Danjiangkou reservoir region, we suggest that the age of the sites is around the late stage of Middle Pleistocene to upper Pleistocene.
| [1] | 李超荣, 冯兴无, 李浩. 1994年丹江口库区调查发现的石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(4): 337-354 |
| [2] | 李浩, 李超荣, 冯兴无. 2004 年丹江口库区调查发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(2): 113-126 |
| [3] | 牛东伟, 马宁, 裴树文, 等. 丹江口库区宋湾旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(1): 11-23 |
| [4] | 卫奇. 《西侯度》石制品之浅见[J]. 人类学学报, 2000, 19(2): 85-96 |
| [5] | Toth N. The Oldowan reassessed: a close look at early stone artifacts[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1985, 12: 101-120 |
| [6] | 李英华. 湖北郧县后房遗址石器工业的年代、操作链及其意义[J]. 江汉考古, 2018, 155(2): 36-47 |
| [7] | 北京联合大学应用文理学院,湖北省文物局,郧阳区文物局. 湖北省郧县滴水岩旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 华夏考古, 2018(6): 43-57 |
| [8] | 黄学诗, 郑绍华, 李超荣, 等. 丹江库区脊椎动物化石和旧石器的发现与意义[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 1996, 34(3): 228-233 |
| [9] | Li H, Li CR, Kuman K. Rethinking the “Acheulean” in East Asia: Evidence from Recent Investigations in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, Central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 347: 163-175 |
| [10] | 张森水. 管窥新中国旧石器考古学的重大发展[J]. 人类学学报, 1998, 18(3): 193-214 |
| [11] | 张森水. 近20年来中国旧石器考古学的进展与思考[J]. 第四纪研究, 2002, 22(1): 11-19 |
| [12] | 牛东伟, 彭菲, 裴树文, 等. 丹江口水库淹没区白渡滩旧石器地点[A].见:中国古生物学会古脊椎动物学分会、第四纪古人类-旧石器专业委员会.第十三届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012: 171-178 |
| [13] | 牛东伟, 裴树文, 仪明洁, 等. 丹江口库区贾湾1号地点发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(2): 97-112 |
| [14] | Pei SW, Niu DW, Guan Y, et al. Middle pleistocene hominin occupation in the danjiangkou reservoir region, central china: studies of formation processes and stone technology of maling 2A site[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 53: 391-407 |
| [15] | 中国科学院大学考古学与人类学系,河南省文物考古研究院. 河南淅川坑南遗址北区2016-2017年度发掘简报[J]. 华夏考古, 2019(3): 3-13 |
| [16] | 中国科学院大学考古学与人类学系,河南省文物考古研究院. 河南淅川坑南旧石器时代遗址TG05发掘简报[J]. 中原文物, 2020(3): 4-14 |
| [17] | 李英华, 孙雪峰. 湖北郧县后房旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2013, 126(1): 6-15 |
| [18] | 陈全家, 陈晓颖, 方启. 丹江口库区水牛洼旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 27-38 |
| [19] | 裴树文, 关莹, 高星. 丹江口库区彭家河旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(2): 95-109 |
| [20] | 周振宇, 王春雪, 高星. 丹江口北泰山庙旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 29(3): 246-261 |
| [21] | 李浩, 李超荣, Kuman K. 丹江口库区果茶场II 旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(2): 144-154 |
| [22] | 李意愿, 高成林, 向开旺. 丹江口库区舒家岭旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(2): 149-165 |
| [23] | 陈胜前, 陈慧, 董哲, 等. 湖北郧县余嘴2号旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 39-50 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |