

丹江口库区旧石器遗址的年代与石器技术的演进
收稿日期: 2022-02-16
修回日期: 2022-07-03
网络出版日期: 2023-04-03
基金资助
国家社科基金冷门绝学研究专项“丹江下游地区史前打制石器研究”(21VJXG025);河南省南水北调中线工程考古钻探发掘项目“河南省南阳市淅川县坑南遗址群(勘探)发掘”(201807);河南省文物局南水北调文物保护专项经费“丹江库区旧石器时代晚期石器加工技术研究”;郑州大学“中华文明根系研究”(XKZDJC202006)
Chronology and lithic technological progresses of those Paleolithic sites in Danjiangkou Reservoir Region
Received date: 2022-02-16
Revised date: 2022-07-03
Online published: 2023-04-03
丹江口库区位于东秦岭南麓,是连接我国南北文化的重要地带,本文全面梳理了该地区目前已发掘的旧石器遗址,重新厘定了遗址的年代。结合年代和石制品特征,本文得到以下几点认识:1)该地区文化发展可以被划分为三个阶段:阶段1(相当于MIS 27~MIS 8)石器工业为石核-石片类型,阶段2(相当于MIS 7~MIS 3c)出现了大型切割石器组合,阶段3(约晚于MIS 3b)以小型石片石器为特征;2)在文化阶段性发展的同时,石核-石片技术一直贯穿于本地区的更新世期间,体现了区域文化发展的连续性;3)丹江下游石器技术在形成过程中受到了来自华北和秦岭地区的文化辐射,显示出融合性的技术特征;4)100~50 ka BP期间,丹江口库区汉水上游的现代人石器工业中可能包含了大型切割石器组合。
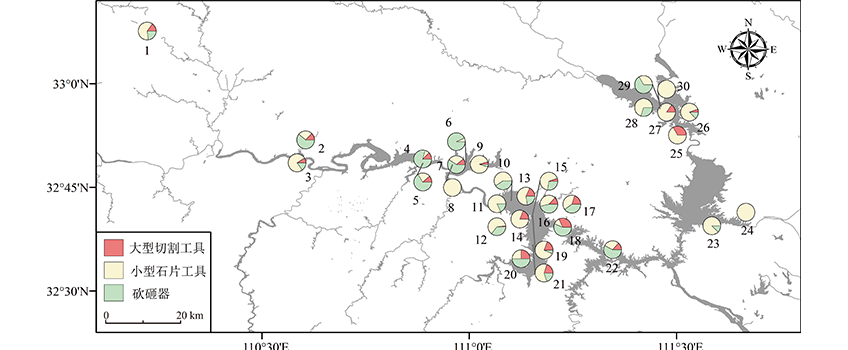
李文成 , 宋国定 . 丹江口库区旧石器遗址的年代与石器技术的演进[J]. 人类学学报, 2023 , 42(02) : 277 -287 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2023.0004
Situated at the southern piedmont of Qinling Mountains, the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region (DRR) is served as the critical area for human migration and cultural interaction between Southern and Northern China. Many Paleolithic sites have been discovered during the South-to-North Water Diversion Project conducted by the Chinese government, and some of them have been systematically excavated, which demonstrates the DRR is an essential zone for the adaption and evolution of hominins during the Pleistocene. However, given the limitation of chronological data, the cultural and technological development trajectory in the DRR is still unclear.
This paper has scrutinized all the excavated sites published so far, with a special focus on their geomorphological location, lithic artifacts and dates. The DRR with a total of 38 sites can be divided into two sub-areas when considering their locations, including the upstream of the Hanshui River region (n=25) and the downstream of the Danjiang River region (n=13).
In this paper, we reevaluate the chronology of excavated sites in DRR and further proposes the following opinions:
1) Regional cultural development can be divided into three stages: a) Phase 1 is dated from MIS 27-MIS 8, represented by the simple core-and-flake industry, including sites located on the fourth terrace of the Hanshui River, the lower layers of sites on the third terrace of the Hanshui and Danjiang river, as well as Bailongdong and Longgudong caves. b) Phase 2 with a chronology ranging from MIS 7-MIS 3c is characterized by the emergence of Large Cutting Tool (LCT) assemblages. This stage consists of the open-air sites buried in the upper layers on the third terrace of the DRR, all the sites on the second terrace of Hanshui River, and one cave site, the Huanglong Cave. c) Phase 3 is estimated to be dated from MIS 3b to the end of Pleistocene which includes the upper cultural layer of Shuiniuwa and Longkou site on the third terrace of the Hanshui Branch. Small-sized flake tools dominate the lithic assemblage during this stage, and no LCT factors are found.
2) Although well-organized technological stages can be observed in the DRR, the core-and-flake assemblages still dominate at all sites throughout the Pleistocene, even when LCT factors appeared, which indicates a technological and cultural continuity in this area.
3) Considering the two sub-areas in the DRR, the lithic technology in downstream of the Danjiang River is slightly different from that in the Hanshui Branch. The former is characterized by more flake tool components and fewer LCT factors during 250-50 kaBP, indicating technological influence from northern China and the Qinling Mountains (or Southern China) and further implying the potential cultural transmission with both regions.
4) We further propose that the LCT complex in Hanshui branch of the DRR during 100-50 ka BP is coinstantaneous with the presence of Homo sapiens in this area, which is represented by fossils discovered at Huanglongdong Cave. Their coexistence suggests that the LCT complex is likely part of the tool kit made by Homo sapiens.

Key words: Danjiangkou; Paleolithic; Chronology; Culture
| [1] | 李超荣, 冯兴无, 李浩. 1994年丹江口库区调查发现的石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(4): 337-354 |
| [2] | 李浩, 李超荣, 冯兴无. 2004年丹江口库区调查发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(2): 113-126 |
| [3] | 李浩, 李超荣, 周兴明, 等. 丹江口库区第四级阶地旧石器遗址调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(2): 145-153 |
| [4] | Li H, Li CR, Kuman K. Rethinking the “Acheulean” in East Asia: evidence from recent investigations in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 347: 163-175 |
| [5] | Kuman K, Li CR, Li H. Large cutting tools in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, central China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2014, 76: 129-153 |
| [6] | 李浩, 李超荣, Kathleen KUMAN. 丹江口库区的薄刃斧[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(2): 162-176 |
| [7] | Li H, Kuman K, Li CR. The symmetry of handaxes from the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region (central China): A methodological consideration[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 400: 65-72 |
| [8] | Li H, Li CR, Sherwood NL, et al. Experimental flaking in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region (central China): A rare case of bipolar blanks in the Acheulean[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2017, 13: 26-35 |
| [9] | Li H, Li CR, Kuman K, et al. The Middle Pleistocene handaxe site of Shuangshu in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, central China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2014, 52: 391-409 |
| [10] | Pei SW, Niu DW, Guan Y, et al. Middle Pleistocene hominin occupation in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Region, Central China: studies of formation processes and stone technology of Maling 2A site[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 53: 391-407 |
| [11] | Sun XF, Li YH, Feng XB, et al. Pedostratigraphy of aeolian deposition near the Yunxian Man site on the Hanjiang River terraces, Yunxian Basin, central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 400: 187-194 |
| [12] | Sun XF, Lu HY, Wang SJ, et al. Hominin distribution in glacial-interglacial environmental changes in the Qinling Mountains range, central China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 198: 37-55 |
| [13] | 中国科学院大学考古学与人类学系,河南省文物考古研究院. 河南淅川坑南旧石器时代遗址TG05发掘简报[J]. 中原文物, 2020 (3): 4-14 |
| [14] | 中国科学院大学考古学与人类学系,河南省文物考古研究院. 河南淅川坑南遗址北区2016-2017年度发掘简报[J]. 华夏考古, 2019, 3: 3-13 |
| [15] | 武汉大学历史学院,南京大学地理与海洋科学学院. 湖北郧县后房旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2013, 1: 6-15 |
| [16] | Li YH, Zhou YD, Sun XF, et al. New evidence of a lithic assemblage containing in situ Late Pleistocene bifaces from the Houfang site in the Hanshui River Valley, Central China[J]. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 2018, 17(1-2): 131-142 |
| [17] | 李英华, 周玉端, 孙雪峰, 等. 湖北郧县后房遗址石器工业的年代, 操作链及其意义[J]. 江汉考古, 2018, 2: 36-47 |
| [18] | 仪明洁, 裴树文, 牛东伟, 等. 丹江口库区三处地点发现的石制品[J/OL]. 人类学学报, doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0083. |
| [19] | 李京亚, 赵静芳, 宋国定. 丹江口库区梁家岗2号和东岗旧石器地点的调查与发掘[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(1): 108-120 |
| [20] | 陈昌富, 张居中, 杨晓勇. 丹江口库区双河一号旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(3): 359-370 |
| [21] | 中国科学技术大学科技史与科技考古系,河南省文物局南水北调文物保护办公室. 丹江口库区双河二号旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2016(5): 3-12+69 |
| [22] | 牛东伟, 裴树文, 仪明洁, 等. 丹江口库区贾湾1号地点发现的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(2): 149-161 |
| [23] | 牛东伟, 彭菲, 裴树文, 等. 丹江口水库淹没区白渡滩旧石器地点[A].见:董为(主编).第十三届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C].北京:海洋出版社, 2012: 179-186 |
| [24] | 牛东伟, 马宁, 裴树文, 等. 丹江口库区宋湾旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(1): 11-23 |
| [25] | 李浩, 李超荣, 雷蕾. 丹江口库区大土包子旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(3): 349-356 |
| [26] | 北京联合大学应用文理学院,郧阳区文化和旅游局. 湖北省郧县周家坡旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2020, 3: 3-11 |
| [27] | 周天媛, 祁钰, 贾汉清, 等. 湖北省丹江口市雷陂旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[A].见:董为(主编).第十六届中国古脊椎动物学学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2018, 292-305 |
| [28] | 北京联合大学应用文理学院,湖北省文物局,郧阳区文物局. 湖北省郧县滴水岩旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 华夏考古, 2018(06): 43-55+2+129 |
| [29] | 赵海龙, 徐廷, 王利, 等. 湖北郧县肖沟旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(1): 27-37 |
| [30] | 吉林大学边疆考古研究中心. 湖北郧县余嘴遗址旧石器时代遗存发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2016, 8: 3-11 |
| [31] | 杜杰, 冯小波, 王凤竹, 等. 湖北省郧县肖家河发现的石制品[J]. 华夏考古, 2015, 1: 26-33 |
| [32] | 李意愿, 高成林, 向开旺. 丹江口库区舒家岭旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(2): 149-165 |
| [33] | 陈全家, 陈晓颖, 方启. 丹江口库区水牛洼旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 27-38 |
| [34] | 陈胜前, 陈慧, 董哲, 等. 湖北郧县余2嘴号旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 39-50 |
| [35] | 北京联合大学应用文理学院,中国科学院大学,武汉市文物考古研究所. 湖北省郧县黄家窝旧石器时代遗址石制品初步研究[J]. 中原文物, 2014(5): 16-23 |
| [36] | 李超荣, 李锋, 李浩. 丹江口库区红石坎Ⅰ旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(1): 17-26 |
| [37] | 吉林大学边疆考古研究中心,湖北省文物事业管理局. 湖北丹江口市杜店旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2013, 11: 7-21 |
| [38] | 李浩, 李超荣, Kathleen KUMAN. 丹江口库区果茶场Ⅱ旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(2): 144-155 |
| [39] | 北京联合大学应用文理学院历史文博系, 中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所. 湖北郧县刘湾旧石器时代遗址发掘简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2012(2): 3-11+133-134 |
| [40] | 方启, 陈全家, 卢悦. 湖北丹江口北泰山庙2号旧石器地点发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(4): 344-354 |
| [41] | 王欢. 丹江库区龙口旧石器遗址的石器研究与讨论[D]. 吉林大学, 2011 |
| [42] | 方启, 陈全家, 高霄旭. 黄家湾旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 考古与文物, 2011, 1: 29-35+113-115 |
| [43] | 周振宇, 王春雪, 高星. 丹江口北泰山庙旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(3): 246-261 |
| [44] | 裴树文, 关莹, 高星. 丹江口库区彭家河旧石器遗址发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(2): 95-110 |
| [45] | 冯小波, 陆成秋, 王昊. 湖北郧县直立人遗址研究新进展[J]. 江汉考古, 2011, 3: 57-64 |
| [46] | 武仙竹, 裴树文, 吴秀杰, 等. 湖北郧西白龙洞古人类遗址初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(1): 1-15 |
| [47] | 武仙竹, 吴秀杰, 陈明惠, 等. 湖北郧西黄龙洞古人类遗址2006年发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2007, 26(3): 193-205 |
| [48] | Xing S, Martinón-Torres M, Deng CL, et al. Early Pleistocene hominin teeth from Meipu, southern China[J]. Journal of human evolution, 2021, 151: 102924 |
| [49] | 郭永强, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 汉江上游郧县人遗址地层沉积学研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(2): 149-158 |
| [50] | 王社江, 鹿化煜. 秦岭地区更新世黄土地层中的旧石器埋藏与环境[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2016, 46(7): 881-890 |
| [51] | 郭小奇, 孙雪峰, 王社江, 等. 秦岭汉江流域新发现旧石器遗址的地层与释光年代[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(2): 319-333 |
| [52] | Han F, Shao QF, Bahain J J, et al. Coupled ESR and U-series dating of Middle Pleistocene hominin site Bailongdong cave, China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2019, 49: 291-296 |
| [53] | Kong YF, Deng CL, Liu W, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the hominin occupation of Bailong Cave, central China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-12 |
| [54] | Liu XB, Shen GJ, Tu H, et al. Initial 26Al/10Be burial dating of the hominin site Bailong Cave in Hubei Province, central China[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 389: 235-240 |
| [55] | 同号文, 张贝, 武仙竹, 等. 湖北郧西白龙洞中更新世古人类遗址的哺乳动物化石[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(4): 613-640 |
| [56] | Liu W, Wu XJ, Pei SW, et al. Huanglong cave: a Late Pleistocene human fossil site in Hubei Province, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2010, 211(1-2): 29-41 |
| [57] | 裴树文, 武仙竹, 吴秀杰. 湖北郧西黄龙洞古人类石器技术与生存行为探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 6: 1007-1013 |
| [58] | 武仙竹, 刘武, 高星, 等. 湖北郧西黄龙洞更新世晚期古人类遗址[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 16: 1929-1935 |
| [59] | 涂华, 沈冠军, 武仙竹. 古人类遗址湖北郧西黄龙洞的铀系年代[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(3): 327-333 |
| [60] | 任文勋, 李京亚, 宋国定. 河南南水北调水源地旧石器时代遗址的发现与研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(5): 917-928 |
| [61] | Wang YP. Late Pleistocene human migrations in China[J]. Current Anthropology, 2017, 58(S17): 504-513 |
| [62] | 王幼平. 华北晚更新世的石片石器[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(4): 525-535 |
| [63] | 中国科学院大学考古学与人类学系,河南省文物局南水北调文物保护办公室. 丹江口库区燧石遗存调查简报[J]. 江汉考古, 2018, 2: 3-16 |
| [64] | 张弛. 中国新石器时代的石叶技术——汉水中游仰韶文化石叶石镞[J]. 江汉考古, 2021, 6: 71-78 |
| [65] | 刘武, 吴秀杰, 邢松. 现代人的出现与扩散——中国的化石证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(2): 161-171 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |