

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (04): 594-605.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0003cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0003
郭小奇1( ), 孙雪峰1(
), 孙雪峰1( ), 弋双文1, 王社江2, 李英华3, 汪英华4, 周玉端3
), 弋双文1, 王社江2, 李英华3, 汪英华4, 周玉端3
收稿日期:2024-04-07
接受日期:2024-07-19
出版日期:2025-08-15
发布日期:2025-08-07
通讯作者:
孙雪峰
作者简介:郭小奇,博士,主要从事旧石器遗址点释光测年研究。E-mail: 602022270012@smail.nju.edu.cn
基金资助:
GUO Xiaoqi1( ), SUN Xuefeng1(
), SUN Xuefeng1( ), YI Shuangwen1, WANG Shejiang2, LI Yinghua3, WANG Yinghua4, ZHOU Yuduan3
), YI Shuangwen1, WANG Shejiang2, LI Yinghua3, WANG Yinghua4, ZHOU Yuduan3
Received:2024-04-07
Accepted:2024-07-19
Online:2025-08-15
Published:2025-08-07
Contact:
SUN Xuefeng
摘要: 我国西北戈壁和沙漠地区的自然条件相对恶劣、资源匮乏,但野外调查表明这里也有一些史前人类活动遗存,是研究晚更新世以来人类扩散的重要资料。然而这些人类活动痕迹多发现于地表,缺乏明确的地层,很难进行包括年代学在内的精细研究。2020年以来,我们在巴丹吉林沙漠东缘曼德拉山新发现7个石器地点和收集113件石制品,并使用释光测年法测定了石制品下伏地层的年代作为人类活动的参考年代。结果显示,史前人群在巴丹吉林沙漠东缘曼德拉山地区的活动年代可能晚于7.3 kaBP;温度和降雨量模拟结果表明,该时段巴丹吉林沙漠部分地区气候相对湿润,地下水和地表植被覆盖度相对较高,为打制石器使用者狩猎采集人群的生存提供了有利条件。本研究对于认识全新世早、中期我国西北戈壁和沙漠的人类活动具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
郭小奇, 孙雪峰, 弋双文, 王社江, 李英华, 汪英华, 周玉端. 内蒙古中部曼德拉山石器遗址的年代与环境[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(04): 594-605.
GUO Xiaoqi, SUN Xuefeng, YI Shuangwen, WANG Shejiang, LI Yinghua, WANG Yinghua, ZHOU Yuduan. Age and environment of the Mandelashan lithic site in central Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2025, 44(04): 594-605.
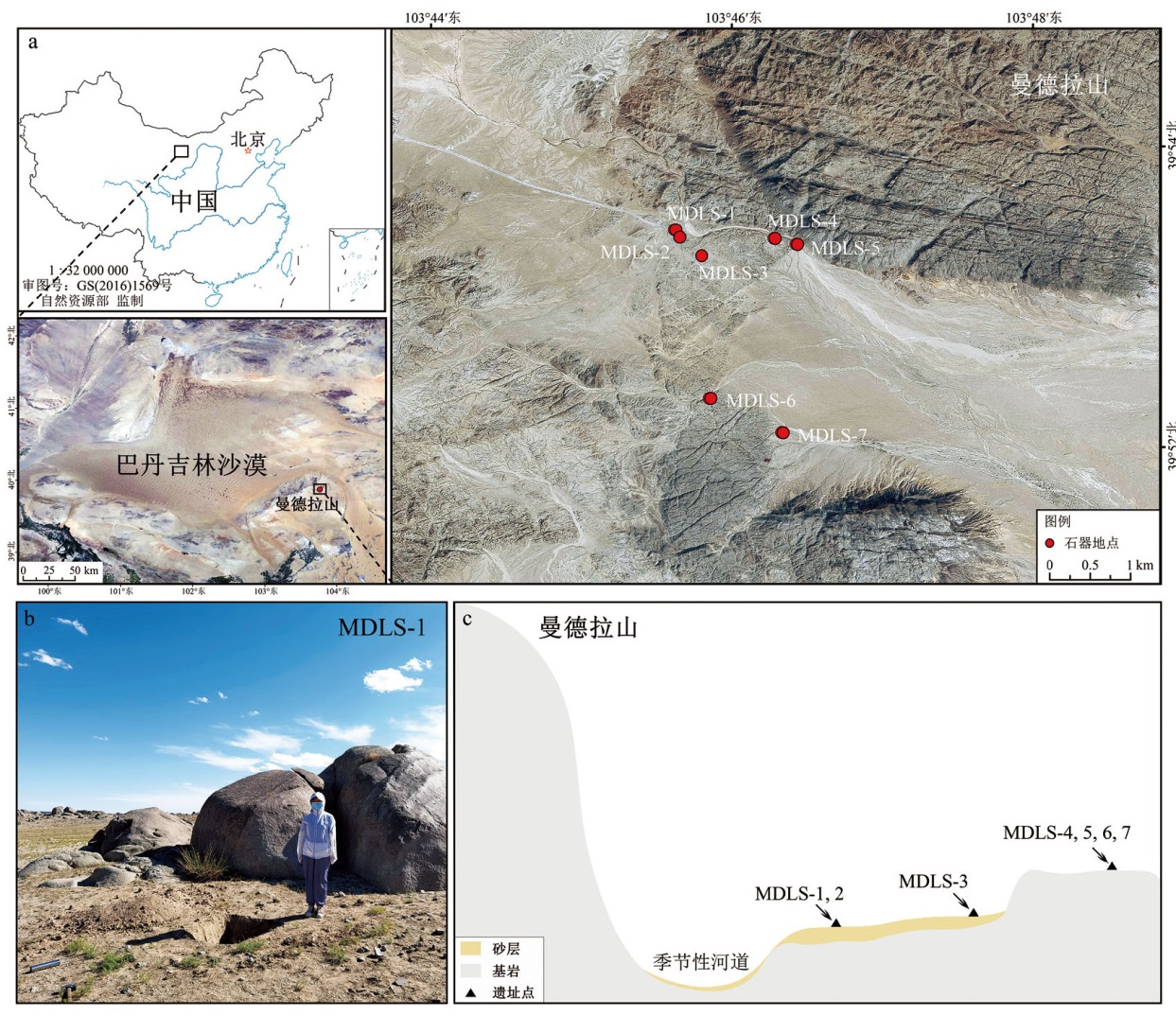
图1 曼德拉山地区的石器地点位置及地貌特征 a.巴丹吉林沙漠东缘曼德拉山地区新发现的石器地点New discovered stone artifact sites of Mandela Mountain area in the eastern margin of the Badain Jaran Desert;b.曼德拉山第1地点的野外采样照片Photograph of field sampling at MDLS-1 site;c.该区域的地貌特征geomorphologic features of the area
Fig.1 Stone artifact sites and geomorphologic features of Mandela Mountain area
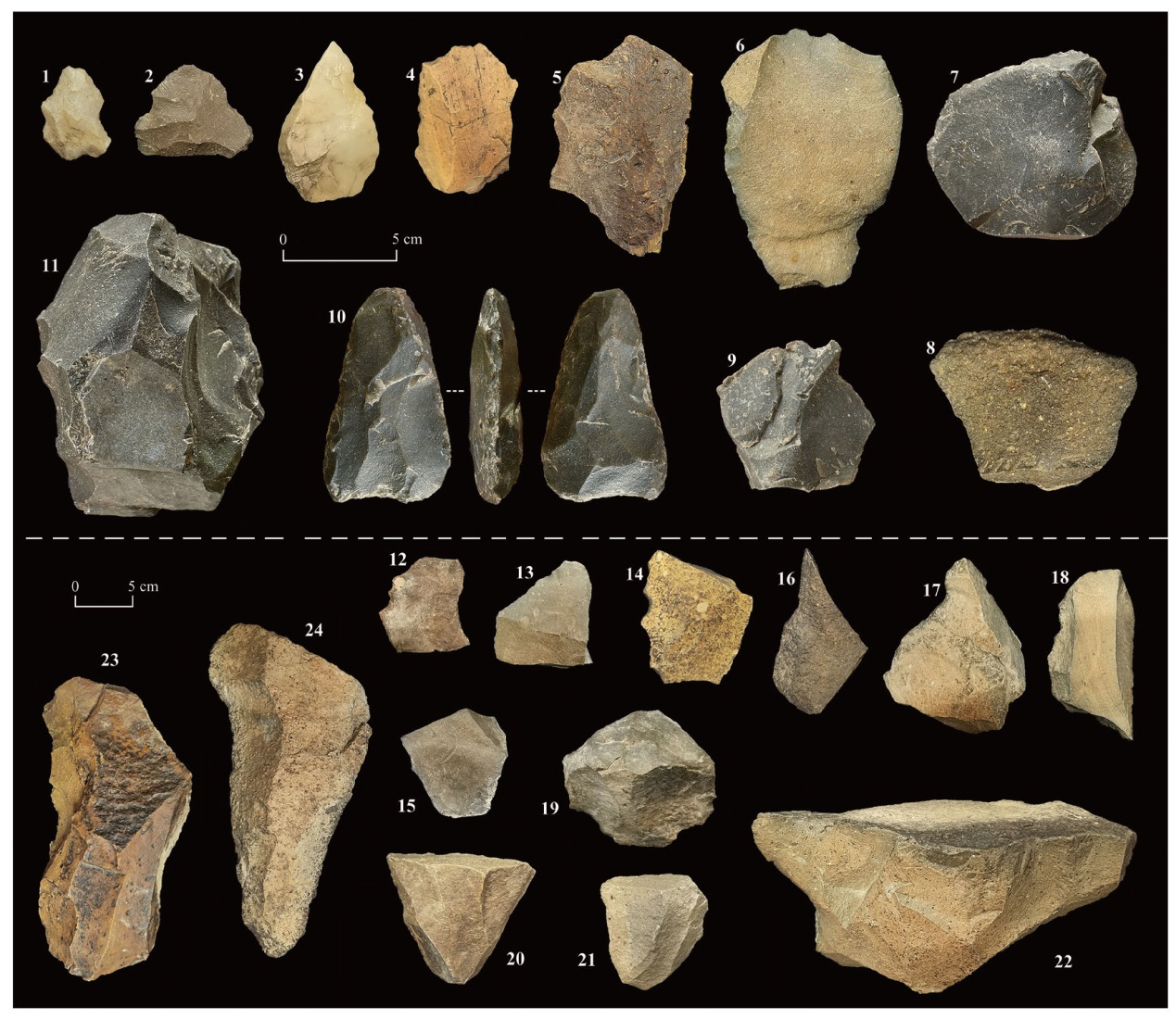

图2 MDLS遗址的石制品组合 1. MDLS-4:01, 刮削器 scrapers; 2. MDLS-4:02, 刮削器 scrapers; 3. MDLS-6:01, 刮削器 scrapers; 4. MDLS-4:03, 刮削器 scrapers; 5. MDLS-3:01, 刮削器 scrapers; 6. MDLS-3:02, 刮削器 scrapers; 7. MDLS-1:01, 刮削器 scrapers; 8. MDLS-3:03, 石片flakes; 9. MDLS-1:02, 石片flakes; 10. MDLS-1:03, 两面器biface; 11. MDLS-1:04, 砍砸器choppers; 12. MDLS-7:01, 刮削器 scrapers; 13. MDLS-7:02, 刮削器 scrapers; 14. MDLS-7:03, 刮削器 scrapers; 15. MDLS-5:01, 石片flakes; 16. MDLS-3:04, 使用石片used flakes; 17. MDLS-7:04, 使用石片used flakes; 18. MDLS-7:05, 砍砸器choppers; 19. MDLS-3:05, 石核cores; 20. MDLS-6:02, 石核cores; 21. MDLS-7:06, 石核cores; 22. MDLS-2:01, 石核cores; 23. MDLS-4:04, 大型砍砸器large choppers;24. MDLS-3:06, 大型刮削器large scrapers.
Fig.2 Stone artifacts from the MDLS sites
| 地点Site | 石核Cores | 大石片Large flakes | 石片 Flakes | 使用石片Used flakes | 石器Tools | 合计 Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两面器Bifaces | 尖状器Points | 刮削器Scrapers | 雕刻器Burins | 砍砸器Choppers | ||||||
| MDLS-1 | 2 | 1 | 28 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 4 | 47 | ||
| MDLS-2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 14 | ||||
| MDLS-3 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 23 | ||
| MDLS-4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6 | ||||
| MDLS-5 | 4 | 2 | 6 | |||||||
| MDLS-6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | ||||||
| MDLS-7 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 13 | ||||||
| 合计Total | 10 | 3 | 54 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 30 | 1 | 6 | 113 |
表1 MDLS遗址的石器分类统计(n)
Tab.1 Classification statistics of stone artifacts from the MDLS sites
| 地点Site | 石核Cores | 大石片Large flakes | 石片 Flakes | 使用石片Used flakes | 石器Tools | 合计 Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两面器Bifaces | 尖状器Points | 刮削器Scrapers | 雕刻器Burins | 砍砸器Choppers | ||||||
| MDLS-1 | 2 | 1 | 28 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 4 | 47 | ||
| MDLS-2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 14 | ||||
| MDLS-3 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 23 | ||
| MDLS-4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6 | ||||
| MDLS-5 | 4 | 2 | 6 | |||||||
| MDLS-6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | ||||||
| MDLS-7 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 13 | ||||||
| 合计Total | 10 | 3 | 54 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 30 | 1 | 6 | 113 |
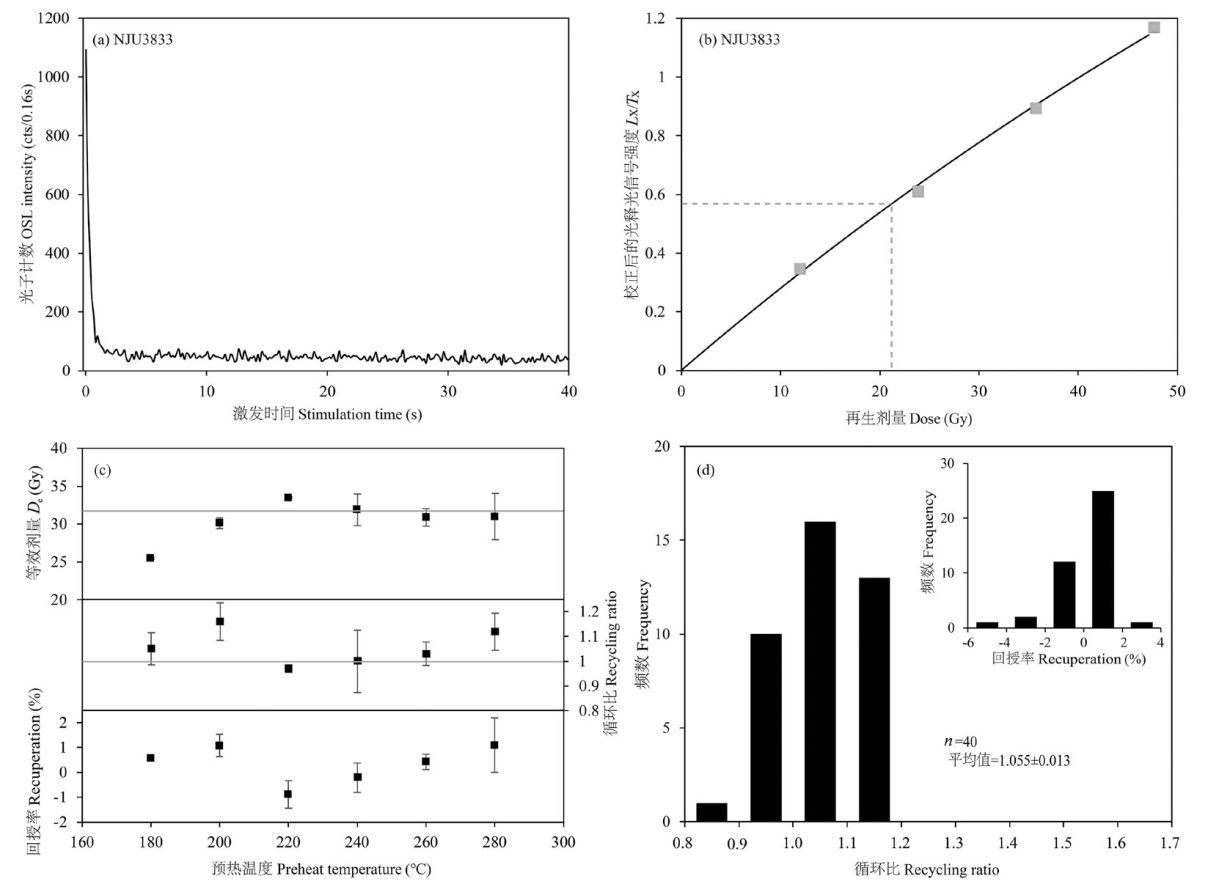
图3 样品NJU3833的自然释光信号衰退曲线(a)、生长曲线(b)、预热坪实验(c)以及所有样品的循环比和回授率(d)
Fig.3 Typical natural decay curve (a), DRC (b) and preheat plateau test (c) for the sample NJU3833, (d) recycling ratios and recuperation values for all aliquots
| 实验编号 Lab No. | 样品Sample No. | 深Depth (cm) | 含水量Water content(%) | U (μg/g) | Th (μg/g) | K(%) | 年剂量Dose rate (Gy/ka) | 数量Quantity(n) | 等效剂量De(Gy) | 年代Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NJU3833 | MDLS-1 | 15 | 5%±2.5% | 1.60±0.03 | 5.47±0.09 | 1.71%±0.01% | 2.66±0.06 | 16 | 19.3±0.5 | 7.3±0.3 |
| NJU3835 | MDLS-1 | 30 | 5%±2.5% | 1.16±0.02 | 3.65±0.02 | 2.30%±0.02% | 2.98±0.07 | 12 | 24.7±1.2 | 8.3±0.5 |
| NJU3836 | MDLS-3 | 20 | 5%±2.5% | 1.29±0.02 | 5.03±0.03 | 1.99%±0.01% | 2.82±0.07 | 12 | 26.4±1.9 | 9.4±0.4 |
表2 曼德拉山遗址的光释光测年结果
Tab.2 OSL dating results for the MDLS sites
| 实验编号 Lab No. | 样品Sample No. | 深Depth (cm) | 含水量Water content(%) | U (μg/g) | Th (μg/g) | K(%) | 年剂量Dose rate (Gy/ka) | 数量Quantity(n) | 等效剂量De(Gy) | 年代Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NJU3833 | MDLS-1 | 15 | 5%±2.5% | 1.60±0.03 | 5.47±0.09 | 1.71%±0.01% | 2.66±0.06 | 16 | 19.3±0.5 | 7.3±0.3 |
| NJU3835 | MDLS-1 | 30 | 5%±2.5% | 1.16±0.02 | 3.65±0.02 | 2.30%±0.02% | 2.98±0.07 | 12 | 24.7±1.2 | 8.3±0.5 |
| NJU3836 | MDLS-3 | 20 | 5%±2.5% | 1.29±0.02 | 5.03±0.03 | 1.99%±0.01% | 2.82±0.07 | 12 | 26.4±1.9 | 9.4±0.4 |
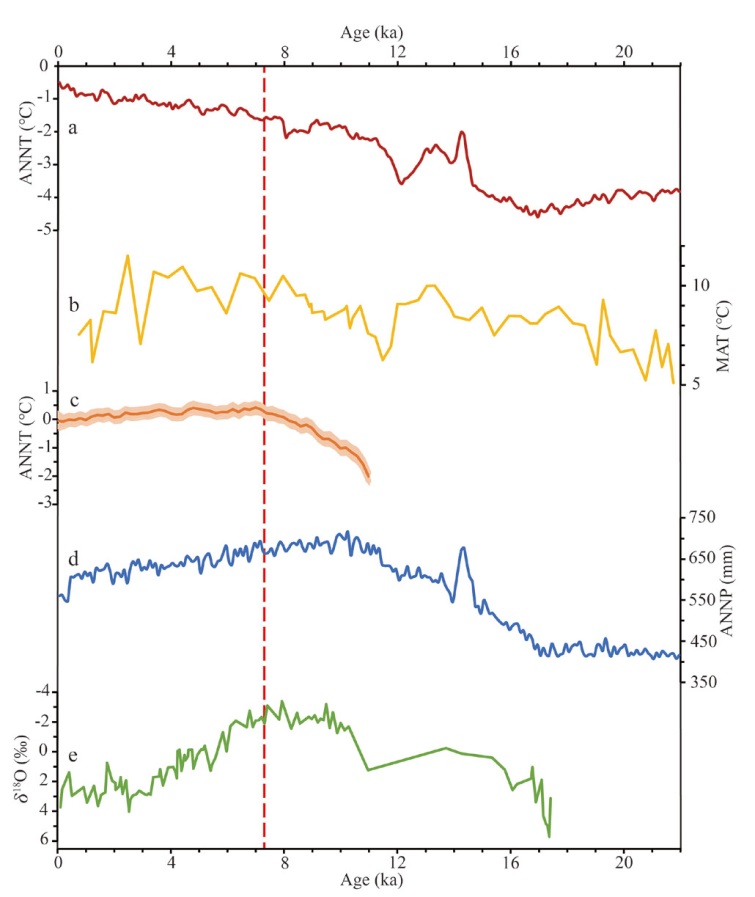
图5 巴丹吉林沙漠温度和降水的气候模拟(TraCE-21 ka)和地质记录 a.巴丹吉林沙漠22 kaBP以来的年温度变化[45] / Annual temperature of the Badain Jaran Desert since 22 kaBP, 99-point filtered[45];b.泾川的年平均温度变化[48] / Mean annual temperature at Jingchuan[48];c.基于花粉和CCSM3模拟的北半球年温度变化重建[49] / Pollen-based and CCSM3-simulated changes of annual temperature in Northern Hemisphere. Shading indicates 95% uncertainty bands of reconstructions[49];d.巴丹吉林沙漠22 kaBP以来的年降水变化[45] / Annual precipitation of the Badain Jaran Desert since 22 kaBP, 99-point filtered[45];e.晚冰期以来青海湖QH-2000岩芯中介形虫壳的δ18O记录[50] / δ18O records of ostracode shells in Lake Qinghai core QH-2000 since the late Glacial[50];红色虚线代表人类可能出现的最早时间阶段(7.3 kaBP)Red dashed line represents the earliest possible stage (7.3 kaBP) of human occurrence
Fig.5 Climate simulation (TraCE-21 ka) and geological records of the temperature and precipitation in the Badain Jaran Desert
| [1] |
Pitulko V, Nikolsky PA, Girya EY, et al. The Yana RHS Site: Humans in the Arctic Before the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Science, 2004, 303(5654): 52-56
pmid: 14704419 |
| [2] | Petraglia MD, Alsharekh AM, Crassard R, et al. Middle paleolithic occupation on a marine isotope stage 5 lakeshore in the Nefud Desert, Saudi Arabia[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(13-14): 1555-1559 |
| [3] |
Matthew RB, David B, Jeffrey SP, et al. Evidence of humans in North America during the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6562): 1528-1531
doi: 10.1126/science.abg7586 pmid: 34554787 |
| [4] |
Zhang XL, Ha BB, Wang SJ, et al. The earliest human occupation of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau 40 thousand to 30 thousand years ago[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6418): 1049-1051
doi: 10.1126/science.aat8824 pmid: 30498126 |
| [5] | Mafessoni F, Grote S, Filippo CD, et al. A high-coverage Neandertal genome from Chagyrskaya Cave[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2020, 117(26): 202004944 |
| [6] | Rybin E, Khatsenovich A. Middle and Upper Paleolithic Levallois technology in eastern Central Asia[J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 535: 117-138 |
| [7] | Chen FH, Welker F, Shen CC, et al. A late Middle Pleistocene Denisovan mandible from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Nature, 2019, 569: 409-412 |
| [8] | 高星, 裴树文, 彭菲, 等. 2004年新疆旧石器考古调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(4): 499-509. |
| [9] | 于建军, 王幼平, 何嘉宁, 等. 新疆吉木乃县通天洞遗址[J]. 考古, 2018, 7: 3-14+2 |
| [10] | Gladyshev SA, Olsen JW, Tabarev AV, et al. Chronology and periodization of upper paleolithic sites in Mongolia[J]. Archaeology, Ethnology and Anthropology of Eurasia, 2010, 38(3): 33-40 |
| [11] | Kolobova KA, Roberts RG, Chabai VP, et al. Archaeological evidence for two separate dispersals of Neanderthals into southern Siberia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2020, 117(6): 201918047 |
| [12] | Ge JY, Wang YH, Shan MC, et al. Evidence from the Dayao Paleolithic site, Inner Mongolia for human migration into arid northwest China during mid-Pleistocene interglacials[J]. Quaternary Research, 2021, 103: 1-17 |
| [13] | 戴尔俭, 盖培, 黄慰文. 阿拉善沙漠中的打制石器[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1964, 8(4): 414-416 |
| [14] | 李壮伟. 内蒙古阿拉善左旗发现原始文化遗存[J]. 考古, 1992, 5: 385-388 |
| [15] | 李壮伟. 内蒙古腾格里沙漠中的一处原始文化遗存[J]. 考古, 1993, 11: 981-984 |
| [16] | Sun XF, Lu HY, Yi SW, et al. Age and paleoenvironment of Paleolithic stone artifact remains discovered in the Tengger Desert, northern China[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2013, 91: 129-137 |
| [17] | Madsen DB, Oviatt CG, Zhu Y, et al. The early appearance of Shuidonggou core-and-blade technology in north China: Implications for the spread of Anatomically Modern Humans in northeast Asia?[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 347: 21-28 |
| [18] | 彭菲, 铁卫冬, 秦彬, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善南寺峡谷旧石器遗址再调查[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(4): 531-539 |
| [19] | 景学义, 边文利, 胡杨, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善左旗苏宏图遗址调查简报[J]. 考古与文物, 2016, 1: 3-8 |
| [20] | Wang NA, Ning K, Li ZL, et al. Holocene high lake-levels and pan-lake period on Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59: 1633-1641 |
| [21] | 袁建民. 简述阿拉善旧新石器的演变[J]. 理论研究, 2020, 2: 198 |
| [22] | 贾兰坡, 盖培, 李炎贤. 水洞沟旧石器时代遗址的新材料[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1964, 8(1): 75-83 |
| [23] | 高星, 王惠民, 关莹. 水洞沟旧石器考古研究的新进展与新认识[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(2): 121-132 |
| [24] | Peng F, Lin SC, Patania I, et al. A chronological model for the Late Paleolithic at Shuidonggou Locality 2, North China[J]. Plos One, 2020, 15(5): e0232682 |
| [25] | Li F, Kuhn SL, Bar-Yosef O, et al. History, Chronology and Techno-Typology of the Upper Paleolithic Sequence in the Shuidonggou Area, Northern China[J]. Journal of World Prehistory, 2019, 32(2): 111-141 |
| [26] | 王惠民, 郭家龙, 张艳玲, 等. 生态视角下宁夏鸽子山遗址尖状器的形态与功能[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(4): 575-583 |
| [27] | 郭家龙, 姚乐音, 王惠民, 等. 宁夏青铜峡鸽子山第15地点发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(2): 182-190 |
| [28] | Yang HY, Zhao H, Wang XF, et al. Optical dating of Yardang sediments and its implications for past flood events on the border of the Badain Jaran Desert, Northern China[J]. Catena, 2021, 207: 105614 |
| [29] | Zhao H, Wang X, Yang H, et al. Luminescence dating of late Pleistocene lacustrine deposits in Badain Jaran Desert, north China[J]. Geochronometria, 2021, 48(1): 000010247820200032 |
| [30] | Fan YX, Li ZJ, Cai QS, et al. Dating of the late Quaternary high lake levels in the Jilantai area, northwestern China, using optical luminescence of quartz and K-feldspar[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 224: 105024 |
| [31] | Peng J, Wang X, Yin G, et al. Accumulation of aeolian sediments around the Tengger Desert during the late Quaternary and its implications on interpreting chronostratigraphic records from drylands in north China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2022, 275: 107288 |
| [32] | Guo YJ, Li B, Zhang JF, et al. Luminescence-based chronologies for palaeolithic sites in the Nihewan basin, northern China: first tests using newly developed optical dating procedures for potassium feldspar grains[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2015, 3: 31-40 |
| [33] | Zhang JF, Hou YM, Guo YJ, et al. Radiocarbon and luminescence dating of the Wulanmulun site in Ordos, and its implication for the chronology of Paleolithic sites in China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2022, 72(1): 101371 |
| [34] | Dong ZB, Qian GQ, Lv P, et al. Investigation of the sand sea with the tallest dunes on Earth: China’s Badain Jaran Sand Sea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 120: 20-39 |
| [35] | Yang XP, Ma NN, Dong JF, et al. Recharge to the Inter-Dune Lakes and Holocene Climatic Changes in the Badain Jaran Desert, Western China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 73(1): 10-19 |
| [36] | 陆晨遨. 基于孢粉的巴丹吉林沙漠腹地湖泊早中全新世环境重建[D]. 硕士研究生毕业论文, 兰州: 兰州大学, 2023 |
| [37] | 文茜. 阿拉善岩画研究[D]. 硕士研究生毕业论文, 大连: 辽宁师范大学, 2019 |
| [38] | Yang XP. Chemistry and late Quaternary evolution of ground and surface waters in the area of Yabulai Mountains, western Inner Mongolia, China[J]. CATENA, 2006, 66(1-2): 135-144 |
| [39] | Duller GA. Distinguishing quartz and feldspar in single grain luminescence measurements[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2003, 37(2): 161-165 |
| [40] | Murray AS, Wintle AG. Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32(1): 57-73 |
| [41] | Murray AS, Wintle AG. The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol: potential for improvements in reliability[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2003, 37(4-5): 377-381 |
| [42] | Wallinga J, Ma S, Btter-Jensen L. Measurement of the dose in quartz in the presence of feldspar contamination[J]. Radiat Prot Dosimetry, 2002, (1-4): 367-370 |
| [43] | Prescott JR, Hutton JT. Cosmic ray contributions to dose rates for luminescence and ESR dating: Large depths and long-term time variations[J]. Radiation Measurements, 1994, 23(2-3): 497-500 |
| [44] | Durcan JA, King GE. Duller GA. DRAC: Dose rate and age Calculator for trapped charge dating[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 28: 54-61 |
| [45] |
Liu Z, Otto-Bliesner BL, He F, et al. Transient Simulation of Last Deglaciation with a New Mechanism for Bolling-CAllerod Warming[J]. Science, 2009, 325: 310-C314
doi: 10.1126/science.1171041 pmid: 19608916 |
| [46] | He F. Simulating Transient Climate Evolution of the Last Deglaciation with CCSM3[D]. The Ph.D Thesis, Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin-Madison, 2011: 1-185 |
| [47] | Timmermann A, Yun K, Raia P, et al. Climate effects on archaic human habitats and species successions[J]. Nature, 2022, 604: 495-501 |
| [48] |
Dong Y, Wu N, Li F. et al. The Holocene temperature conundrum answered by mollusk records from East Asia[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 5153
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32506-7 pmid: 36055986 |
| [49] |
Zhang W, Wu H, Cheng J, et al. Holocene seasonal temperature evolution and spatial variability over the Northern Hemisphere landmass[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 5334
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33107-0 pmid: 36088463 |
| [50] | Liu XQ, Shen J, Wang SM, et al. Southwest monsoon changes indicated by oxygen isotope of ostracode shells from sediments in Lake Qinghai since the late Glacial[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52: 539-544 |
| [51] | Li ZL, Wang NA, Li RL, et al. Indication of Millennial-scale Moisture Changes by the Temporal Distribution of Holocene Calcareous Root Tubes in the Deserts of the Alashan Plateau, Northwest China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2015, 440: 496-505 |
| [52] | 杨小平. 巴丹吉林沙漠地区钙质胶结层的发现及其古气候意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(3): 295 |
| [53] | 刘子亭, 杨小平, 朱秉启. 巴丹吉林沙漠全新世环境记录的年代校正与古气候重建[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(5): 925-933 |
| [54] | Gao QZ, Tao Z, Li BS, et al. Palaeomonsoon variability in the southern fringe of the Badain Jaran Desert, China, since 130 ka BP[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2006, 31: 265-283 |
| [55] | Ning K, Wang N, Lu X, et al. A grain size and n-alkanes record of Holocene environmental evolution from a groundwater recharge lake in Badain Jaran Desert, Northwestern China[J]. The Holocene, 2019, 29(6): 1045-1058 |
| [56] | Ning K, Wang N, Yang Z, et al. Holocene vegetation history and environmental changes inferred from pollen records of a groundwater recharge lake, Badain Jaran Desert, northwestern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 577: 110538 |
| [57] | Gao Y, Li Z, Zhu R, et al. Quantitative reconstruction of Holocene millennial-scale precipitation in the Asian monsoon margin of northwest China, revealed by phytolith assemblages from calcareous root tubes in the Tengger Desert[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2020, 55: 755-770 |
| [58] | Li ZL, Li X, Dong S, et al. Holocene climate background for lake evolution in the Badain Jaran Desert of northwestern China revealed by proxies from calcareous root tubes[J]. Quaternary Research, 2022, 110: 1-12 |
| [1] | 邓婉文, 闵锐. 云南元谋丙弄丙洪遗址的石器工业[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(04): 568-582. |
| [2] | 郭小奇, 孙雪峰, 王社江, 徐行华, 曾琼萱, 鹿艺鸣, 鹿化煜. 秦岭汉江流域新发现旧石器遗址的地层与释光年代[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 319-333. |
| [3] | 赵海龙, 仝广, 闫晓蒙. 基于Agisoft PhotoScan的石器三维建模与应用[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 40-48. |
| [4] | 汪英华, 孙祖栋, 单明超, 何佳, 刘望, 陈福友. 内蒙古扎赉诺尔蘑菇山北遗址2019年调查报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(02): 173-182. |
| [5] | 任海云, 王晓毅, 王小娟, 张光辉. 山西兴县碧村遗址石器研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(01): 52-63. |
| [6] | 王建;周新郢;隆浩;陈福友;李锋;陈宇鹏;葛俊逸;李小强. 山东青岛大珠山遗址晚更新世人类活动的环境背景[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(04): 640-652. |
| [7] | 张晓凌;王社江;陈祖军. 西藏旧石器考古调查取得丰硕成果[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(01): 86-86. |
| [8] | 汪英华;刘家旭;单明超;李锋;陈福友. 内蒙古大窑遗址27号洞石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(01): 51-59. |
| [9] | 長友恒人; 下冈順直; 波冈久惠; 佐川正敏; 卫奇. 泥河湾盆地几处旧石器时代文化遗址光释光测年[J]. 人类学学报, 2009, 28(03): 276-284. |
| [10] | 彭菲;刘德成;王春雪. 光释光技术的新应用[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(04): 386-386. |
| [11] | 蓝玫瑰. 动物考古学与石器制作技术专题讲习班[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(01): 44-44. |
| [12] | 陈福友;冯兴无;高星;姚炯;吴永健. 三峡洋安渡遗址石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(04): 309-322. |
| [13] | 张晓凌;于汇历;高星. 黑龙江十八站遗址的新材料与年代[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(02): 115-128. |
| [14] | 吴伟鸿;王宏;谭惠忠;张镇洪. 香港深涌黄地峒遗址试掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2006, 25(01): 56-67. |
| [15] | 韩志勇,沈冠军,张家富. 光释光单片技术及其在澳大利亚旧石器遗址上的应用[J]. 人类学学报, 2004, 23(03): 248-253. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3