

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (06): 1060-1071.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0089cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0089
收稿日期:2025-01-06
接受日期:2025-06-06
出版日期:2025-12-15
发布日期:2025-12-15
作者简介:邓婉文,助理教授,主要研究方向为旧石器时代考古。E-mail: wwdeng@xmu.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2025-01-06
Accepted:2025-06-06
Online:2025-12-15
Published:2025-12-15
摘要:
本文关注的陡向加工技术产品包括两类。一类是对厚石片等剥坯产品进行深度加工,经持续单向剥片而使刃角逐渐增大,可见多层级阶状或合页状修疤特征。此类以厚石片为毛坯向背面多层级修理的刮削器类目前仅见于中国西南地区,年代大致为晚更新世中晚期。另一类是对宽厚砾石直接修型,以砾石较平一面为台面,经持续单向剥片而使加工面近陡直,加工面上通常可见层层叠叠的阶状修疤。此类陡向加工的砾石制品推测最早见于湘西山地中更新世晚期-晚更新世早期河流阶地堆积中,至晚更新世晚期-全新世早期则广泛分布在西南云贵至岭南地区,对砾石/块状毛坯的陡向加工偏好可能由北往南、往东逐渐扩散。对不同类型素材分别进行陡向加工的技术偏好,或与华南中-晚更新世古人类对不同环境的适应和多样化资源的开发利用策略相关。
中图分类号:
邓婉文, 刘锁强. 石器的陡向加工技术与华南中至晚更新世人群的适应及扩散[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 1060-1071.
DENG Wanwen, LIU Suoqiang. Steep-edged flaking technology of stone tools and adaptation and diffusion of populations in South China during the Middle to Late Pleistocene[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2025, 44(06): 1060-1071.
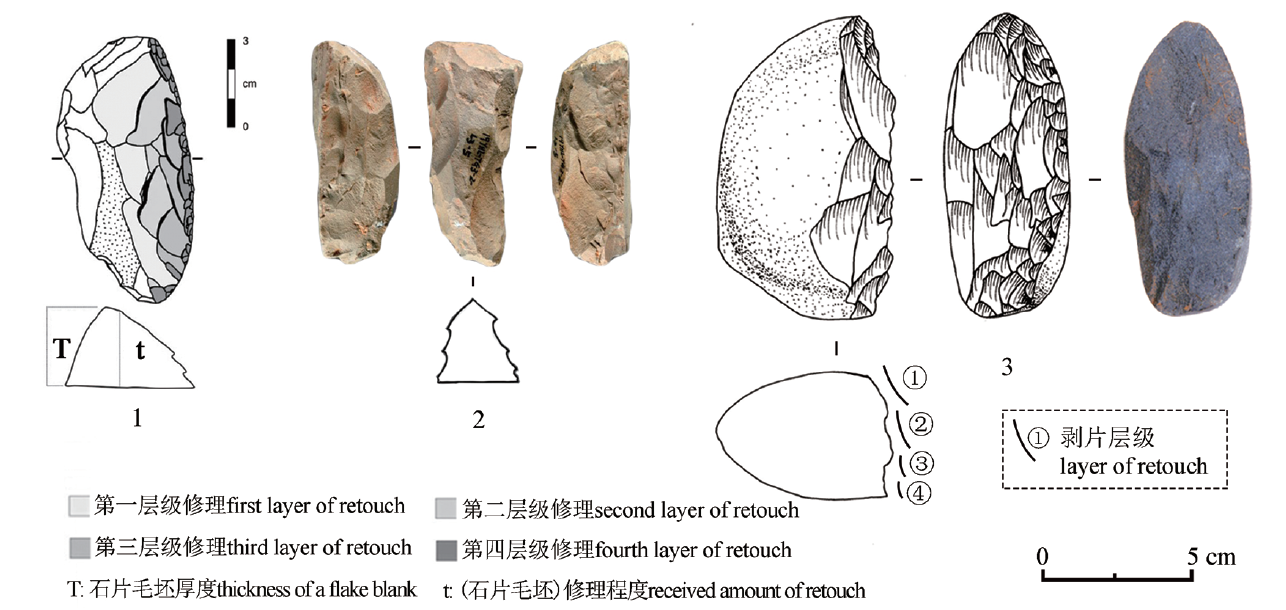
图1 基纳型修理的刮削器与单向多层级剥片的陡刃砾石石器 1.基纳型刮削器的多层级修理示意图[16] Illustration of the multiple “lines” of retouch on Quina scrapers;2.云南鹤庆龙潭遗址的基纳型刮削器[6] Quina scraper from the Longtan open-air site in Heqing, Yunnan;3.广东英德青塘遗址黄门岩2号洞地点的陡刃砾石石器Steep-edged cobble tool from the Huangmenyan cave 2 of the Qingtang site in Yingde, Guangdong
Fig.1 Quina scrapers and steep-edged cobble tools with unidirectional hierarchical retouch
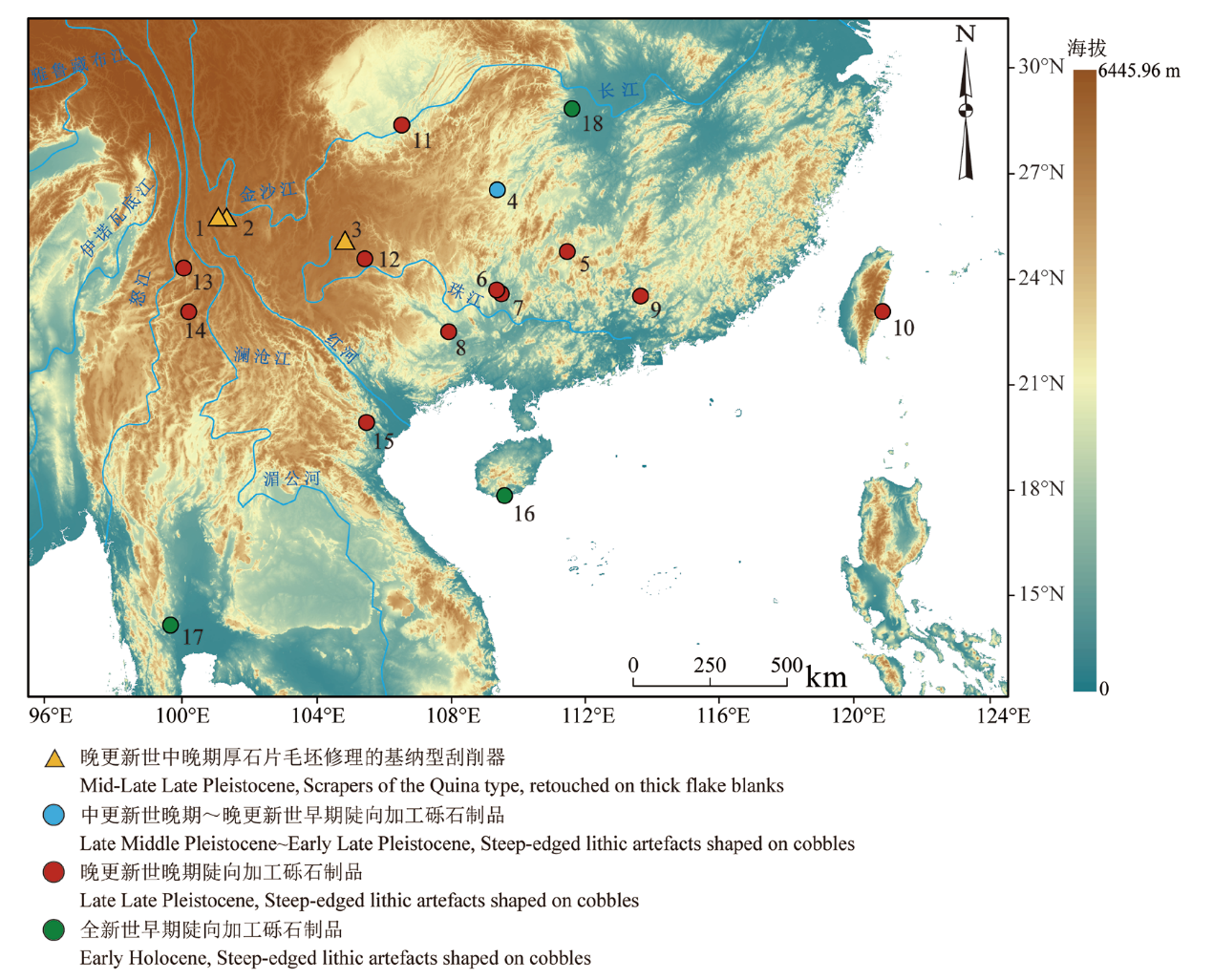
图2 本文讨论涉及的主要遗址 1.云南鹤庆龙潭Longtan open-air site in Heqin, Yunnan; 2.云南鹤庆天华洞Tianhuadong cave site in Heqing, Yunnan; 3.云南富源大河Dahe cave site in Fuyuan, Yunnan; 4.湖南潕水文化类群Wushui River Valley Cultural Complex in Hunan; 5.湖南道县玉蟾岩Yuchanyan cave site in Daoxian, Hunan; 6.广西柳州凤岩Fengyan cave site in Liuzhou, Guangxi; 7.广西柳州白莲洞Bailiandong cave site in Liuzhou, Guangxi; 8.广西隆安娅怀洞Yahuaidong cave site in Liuzhou, Guangxi; 9.广东英德青塘Qingtang cave site in Yingde, Guangdong; 10.台湾八仙洞Baxiandong cave site in Taiwan; 11.重庆铜梁Tongliang open-air site in Chongqing; 12.贵州兴义猫猫洞Maomaodong cave site in Xingyi, Guizhou; 13.云南保山老虎洞Laohudong cave site in Baoshan, Yunnan; 14.云南沧源硝洞Xiaodong rockshelter site in Cangyuan, Yunnan; 15.越南Dieu岩厦Dieu rockshelter site in northern Vietnam; 16.海南三亚落笔洞Luobidong cave site in Sanya, Hainan; 17.泰国Sai Yok I岩厦Sai Yok I rockshelter site in western Thailand;18.湖南澧县彭头山Pengtoushan open-air site in Lixian, Hunan
Fig.2 Main sites discussed in the text

图3 中国西南地区所见基纳型修理特征的刮削器类 标本来源:1.云南鹤庆龙潭[6] Longtan open-air site in Heqing, Yunnan;2.云南鹤庆天华洞[7] Tianhuadong cave site in Heqing, Yunnan;3.云南富源大河[17] Dahe cave site in Fuyuan, Yunnan
Fig.3 Scrapers of the Quina type in Southwest China
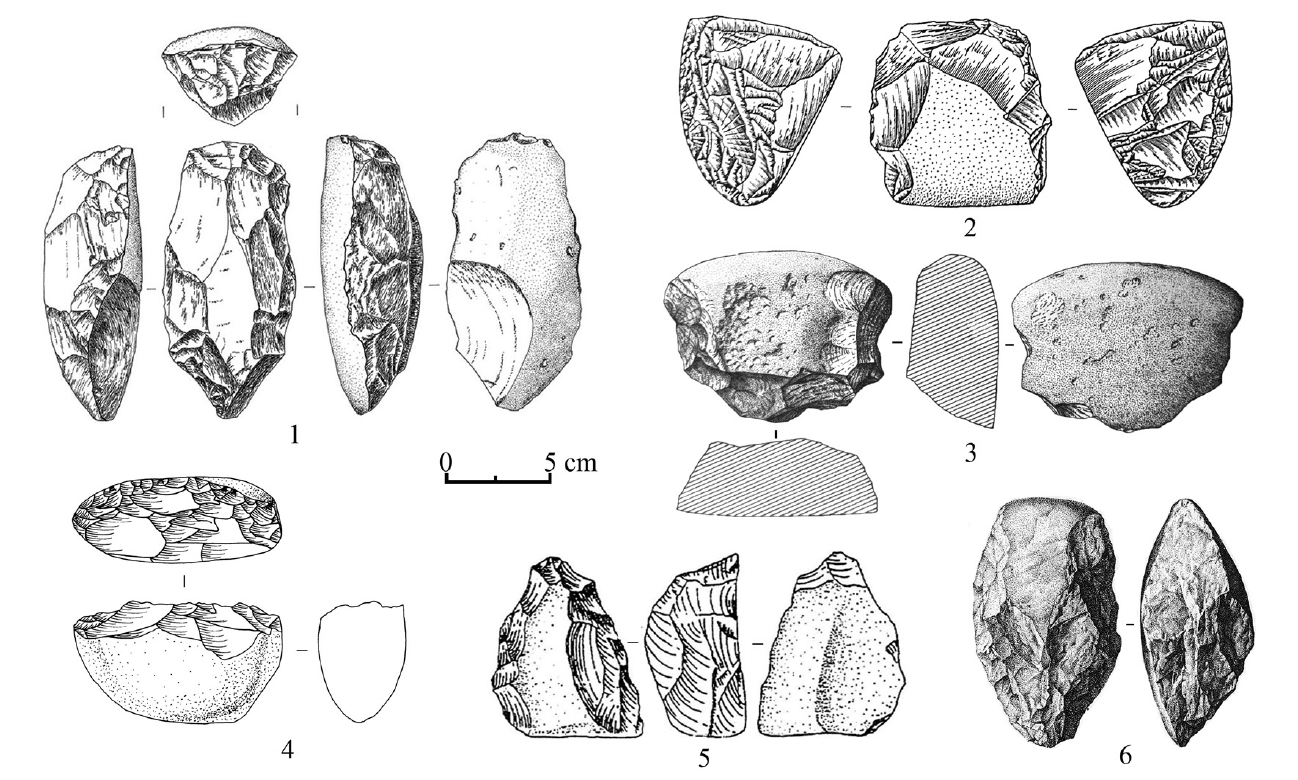
图4 中国南方至东南亚大陆地区所见陡向加工砾石制品 1.云南沧源硝洞 Xiaodong rockshelter site in Cangyuan, Yunnan[8];2.广西柳州白莲洞Bailiandong cave site in Liuzhou[14], Guangxi;3.中国台湾八仙洞 Baxiandong cave site in Taiwan, China[31];4.广东英德青塘Qingtang cave site in Yingde, Guangdong;5.越南北部Dieu岩厦遗址Dieu rockshelter site in northern Vietnam[26] ;6.泰国Sai Yok Ⅰ 岩厦遗址 Sai Yok Ⅰ rockshelter site in western Thailand[30]
Fig.4 Unidirectionally worked cobble tools with steep edges in southern China and Mainland Southeast Asia
| [1] | 四川省文物考古研究院, 北京大学考古文博学院. 四川稻城县皮洛旧石器时代遗址[J]. 考古, 2022, 7: 3-14 |
| [2] | 四川省文物考古研究院, 中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所. 中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所.四川资阳市濛溪河旧石器时代遗址[J]. 考古, 2024, 10: 3-16 |
| [3] |
Zhang DJ, Xia H, Chen FH, et al. Denisovan DNA in Late Pleistocene sediments from Baishiya Karst Cave on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6516): 584-587
doi: 10.1126/science.abb6320 pmid: 33122381 |
| [4] |
Zhang XL, Ha B, Wang SJ, et al. The earliest human occupation of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau 40 thousand to 30 thousand years ago[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6418): 1049-1051
doi: 10.1126/science.aat8824 pmid: 30498126 |
| [5] | 西藏自治区文物保护研究所, 中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所, 阿里文化局, 等. 世界屋脊上的远古家园——西藏阿里地区革吉县梅龙达普史前洞穴遗址[N]. 中国文物报,2024-01-19(008) |
| [6] | Ruan QJ, Li H, Xiao PY, et al. Quina lithic technology indicates diverse Late Pleistocene human dynamics in East Asia[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2025, 22(14): e2418029122 |
| [7] | 阮齐军, 刘建辉, 胡越, 等. 云南鹤庆天华洞旧石器遗址石制品研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(2): 166-181 |
| [8] |
Ji XP, Kuman K, Clark RJ, et al. The oldest Hoabinhian technocomplex in Asia (43.5 ka) at Xiaodong rockshelter, Yunnan Province, southwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2016, 400: 166-174
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.09.080 URL |
| [9] | 蔡奕芝, 刘春喜, 邱立诚. 英德青塘洞穴文化遗存的研究[J].见:英德市博物馆,中山大学人类学系,广东省文物考古研究所(编).英德史前考古报告[C].广州:广东人民出版社, 1999, 214-226 |
| [10] | 邱立诚, 宋方义, 王令红. 广东阳春独石仔新石器时代洞穴遗址发掘[J]. 考古, 1982, 5: 456-475 |
| [11] | 宋方义, 邱立诚, 张镇洪, 等. 广东封开黄岩洞遗址综述[A].见:封开县博物馆,广东省文物考古研究所,广东省博物馆,等(编).纪念黄岩洞遗址发现三十周年论文集[C].广州: 广东旅游出版社, 1991, 1-12 |
| [12] | 谌世龙. 桂林庙岩洞穴遗址的发掘与研究[A]. 见:英德市博物馆,中山大学人类学系,广东省博物馆(编).中石器文化及有关问题研讨会论文集[C]. 广州: 广东人民出版社, 1999, 150-165 |
| [13] | 中国社会科学院考古研究所. 桂林甑皮岩[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2003 |
| [14] | 广西柳州白莲洞洞穴科学博物馆. 柳州白莲洞[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009 |
| [15] | Bui V. The Stone Age archaeology in Viet Nam: Achievements and general model[A]. In: Manguin PY (Ed.). Southeast Asian Archaeology 1994: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference of the European Association of Southeast Asian Archaeologist[C]. Hull: Centre for Southeast Asian Studies, University of Hull, 1994, 1: 5-12 |
| [16] | Hiscock P, Turq A, Faivre J, et al. Quina procurement and tool production[A]. In: Adams B, Blades BS (Eds.). Lithic Materials and Paleolithic Societies[C]. West Sussex: Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2009, 232-246 |
| [17] | 石晶. 云南富源大河遗址石制品研究[D]. 博士学位论文, 长春: 吉林大学, 2016 |
| [18] |
Hu Y, Marwick B, Zhang JF, et al. Late Middle Pleistocene Levallois stone-tool technology in southwest China[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7737): 82-85
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0710-1 |
| [19] | 黄慰文, 侯亚梅, 斯信强. 盘县大洞——贵州旧石器初期遗址综合研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012 |
| [20] |
Li F, Li YH, Gao X, et al. A refutation of reported Levallois technology from Guanyindong Cave in South China[J]. National Science Review, 2019, 6: 1094-1096
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz115 URL |
| [21] | Li YH, Boëda E, Forestier H, et al. Lithic Technology, typology and cross-regional comparison of Pleistocene lithic industries: Comment on the earliest evidence of Levallois in East Asia[J]. L’Anthropologie, 2019, 123: 769-781 |
| [22] | 李浩. 中国旧石器时代早、中期石器技术多样性研究的新进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(4): 602-612 |
| [23] | 王幼平. 现代人扩散南线的考古学观察[J]. 南方文物, 2023, 3: 147-156 |
| [24] | 李昱龙. 岭南地区陡刃砾石石器的加工技术[J]. 考古, 2018, 5: 70-80 |
| [25] | Nguyen KS. Stone Age archaeology in Vietnam[J]. Vietnam Archaeology, 2007, 2: 53-64 |
| [26] | Nguyen GD. Results of recent research into the lithic industries from Late Pleistocene-Early Holocene sites in northern Vietnam[J]. Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association Bulletin (Taipei Papers, volume 3), 2005, 25: 95-97 |
| [27] | 王幼平. 更新世环境与中国南方旧石器文化发展[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1997 |
| [28] |
Zhou YD, Forestier H, Wu Y, et al. Final Pleistocene-Early Holocene (-40-8 ka) lithic industries in Southern China and their implications for understanding the prehistory of Mainland Southeast Asia[J]. Lithic Technology, 2023, 49: 242-260
doi: 10.1080/01977261.2023.2247645 URL |
| [29] | 郝思德, 黄万波. 三亚落笔洞遗址[M]. 海口: 南方出版社, 1998 |
| [30] | van Heekeren HR, Knuth CE. The Thai-Danish Prehistoric Expedition 1960-62: Archaeological Excavations in Thailand, Vol. I, Sai-Yok, Stone Age Settlement in the Kanchanaburi Province[M]. Copenhagen: Munksgaard, 1967 |
| [31] | 臧振华. 八仙洞考古的新发现兼论台湾旧石器文化的年代与类缘问题[A].见: 陈光祖, 臧振华(编). 第四届国际汉学会议论文集:东亚考古的新发现[C].中国台北: 台湾“中央”研究院, 2013, 379-416 |
| [32] | Lien C. Chang-pin Culture of Taiwan and characteristics of its lithic industry[A]. In: Kaifu Y, Izuho M, Goebel T, et al (Eds.). Emergence and Diversity of Modern Human Behavior in Paleolithic Asia[C]. Texas: Texas A&M University Press, 2015, 239-249 |
| [33] | 阮齐军, 周建威, 和金梅, 等. 云南鹤庆龙潭旧石器遗址2019—2020年度发掘简报[J]. 南方文物, 2021, 1: 105-118 |
| [34] | 吉学平, 敖秀娟, 徐兴兰, 等. 云南富源大河出土一批莫斯特文化特征石制品[N]. 中国文物报,2006-08-18(002) |
| [35] | 朱之勇, 吉学平. 云南保山老虎洞旧石器遗址石器研究[A].见:教育部人文社会科学重点研究基地吉林大学边疆考古研究中心(编).边疆考古研究(第9辑)[C].北京:科学出版社, 2010, 1-8 |
| [36] | 曹泽田. 猫猫洞旧石器之研究[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1982, 2: 155-164 |
| [37] | 中国社会科学院考古研究所华南一队, 广西文物保护与考古研究所, 柳州白莲洞洞穴科学博物馆, 等. 广西柳州市凤岩遗址2023年发掘简报[J]. 考古, 2025, 2: 3-18 |
| [38] | 广东省文物考古研究所, 北京大学考古文博学院, 英德市博物馆. 广东英德市青塘遗址[J]. 考古, 2019, 7: 3-15 |
| [39] | 广东省珠江文化研究会岭南考古研究专业委员会, 中山大学地球科学系, 英德市人民政府, 等. 英德牛栏洞遗址:稻作起源与环境综合研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013 |
| [40] | 谢光茂, 余明辉, 卢杰英. 广西隆安娅怀洞遗址发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(3): 365-388 |
| [41] | 袁家荣. 湖南旧石器时代文化与玉蟾岩遗址[M]. 长沙: 岳麓书社, 2013 |
| [42] | 吴小红, 伊莉莎贝塔·博阿雷托以, 袁家荣, 等. 湖南道县玉蟾岩遗址早期陶器及其地层堆积的碳十四年代研究[J]. 南方文物, 2012, 3: 6-15 |
| [43] | 湖南省文物考古研究所. 彭头山与八十垱[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006 |
| [44] | 李宣民, 张森水. 铜梁旧石器文化之研究[J]. 古脊椎动物与古人类, 1981, 4: 359-371 |
| [45] | Debénath A, Dibble HL. Handbook of Paleolithic Typology, Volume One: Lower and Middle Paleolithic of Europe[M]. Philadelphia: University Museum University of Pennsylvania, 1994 |
| [46] |
Bordes F. Mousterian Cultures in France[J]. Science, 1961, 134(3482): 803-810
pmid: 17817388 |
| [47] | Stringer C. Coasting out of Africa[J]. Nature, 2000, 405: 24-27 |
| [48] |
Anil D, Chauhan N, Ajithprasad P, et al. An early presence of Modern human or convergent evolution: A 247 ka Middle Paleolithic assemblage from Andhra Pradesh, India[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2022, 45: 103565
doi: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2022.103565 URL |
| [49] |
Blinkhorn J, Achyuthan H, Petraglia M, et al. Middle Paleolithic occupation in the Thar Desert during the Upper Pleistocene: the signature of a modern human exit out of Africa?[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 77: 233-238
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.06.012 URL |
| [50] |
Blinkhorn J, Ajithprasad P, Mukherjee A, et al. The first directly dated evidence for Palaeolithic occupation on the Indian coast at Sandhav, Kachchh[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 224: 105975
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.105975 URL |
| [51] |
Clarkson C, Harris C, Li B, et al. Human occupation of northern India spans the Toba super-eruption -74,000 years ago[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 961
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14668-4 pmid: 32098950 |
| [52] |
Field J, Petraglia MD, Lahr MM. The southern dispersal hypothesis and the South Asian archaeological record: examination of dispersal routes through GIS analysis[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 2007, 26: 88-108
doi: 10.1016/j.jaa.2006.06.001 URL |
| [53] | 于建军, 王幼平, 何嘉宁, 等. 新疆吉木乃县通天洞遗址[J]. 考古, 2018, 7: 3-14 |
| [54] |
Li F, Kuhn SL, Chen F, et al. The easternmost Middle Paleolithic (Mousterian) from Jinsitai Cave, North China[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2018, 114: 76-84
doi: S0047-2484(17)30303-2 pmid: 29447762 |
| [55] |
Li F, Petraglia M, Roberts P, et al. The northern dispersal of early modern humans in eastern Eurasia[J]. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(20): 1699-1701
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2020.06.026 pmid: 36659239 |
| [56] |
Nguyen DT, Clarkson C. Typological transformation among Late Paleolithic flaked core tools in Vietnam: An examination of the Pa Muoi assemblage[J]. Journal of Indo-Pacific Archaeology, 2016, 40: 32-41
doi: 10.7152/jipa.v40i0.14963 URL |
| [57] |
Liu W, Martinon-torres M, Cai Y, et al. The earliest unequivocally modern humans in southern China[J]. Nature, 2015, 526: 696-699
doi: 10.1038/nature15696 |
| [58] | 金昌柱, 潘文石, 张颖奇, 等. 广西崇左江州木榄山智人洞古人类遗址及其地质时代[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(19): 2848-2856 |
| [59] | Demeter F, Shackelfor LL, Bacon A, et al. Anatomically modern human in Southeast Asia (Laos) by 46 ka[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(36): 14375-14380 |
| [60] | Demeter F, Shackelfor LL, Westaway KE, et al. Early modern humans from Tam Pa Ling, Laos[J]. Current Anthropology, 2017, 58(Supplement 17): S527-S538 |
| [61] |
Demeter F, Zanolli C, Westaway KE, et al. A Middle Pleistocene Denisovan molar from the Annamite Chain of northern Laos[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 2557
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29923-z pmid: 35581187 |
| [62] | Curnoe D, Ji XP, Herries AIR, et al. Human remains from the Pleistocene-Holocene transition of Southwest China suggest a complex evolutionary history for East Asians[J]. PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(3): e31918 |
| [63] |
Turq A. Approche technologique et economique du facies Mousterien de type Quina[J]. Bulletin de la Societe Prehistorique Francaise, 1989, 86: 244-256
doi: 10.3406/bspf.1989.9390 URL |
| [64] | 曲彤丽. 世界不同地区现代人及现代行为的出现与区域特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2012, 31(3): 269-278 |
| [65] | 李浩. 探究早期现代人的南方扩散路线[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(4): 630-648 |
| [1] | 杜瑞妍, 吉学平, 周振宇, 关莹, 张茂林, 周晓燕, 邢松. 云南马鹿洞和塘子沟遗址古人类牙齿残留物中的淀粉粒[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 1072-1082. |
| [2] | 胡越. 贵州观音洞遗址的石核剥片策略和修理技术[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 1019-1033. |
| [3] | 肖培源, 阮齐军, 李浩. 中国西南基纳型旧石器中期技术的发现与研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 1009-1018. |
| [4] | 慕占雄, 陈国科, 杜水生, 王辉. 甘肃环县楼房子遗址2018年发掘简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(01): 121-134. |
| [5] | 邓婉文, 刘锁强, 巫幼波, 刘拓, 李文成, 何嘉宁, 王幼平. 广东英德青塘遗址黄门岩2号洞地点2016年度的发掘[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(01): 64-73. |
| [6] | 何乃汉,覃圣敏. 试论岭南中石器时代[J]. 人类学学报, 1985, 4(04): 308-313. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3