

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (06): 952-966.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0098cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0098
张伟林1( ), 颜茂都1,2, 昝金波1, 苗运法3, 宋香锁4, 张涛5, 徐尊铂1,2, 才让道吉1,2, 阮齐军6, 李浩1
), 颜茂都1,2, 昝金波1, 苗运法3, 宋香锁4, 张涛5, 徐尊铂1,2, 才让道吉1,2, 阮齐军6, 李浩1
收稿日期:2025-03-26
接受日期:2025-06-10
出版日期:2025-12-15
发布日期:2025-12-15
作者简介:张伟林,研究员,主要从事磁性地层学和构造地质学研究。E-mail: zhangwl@itpcas.ac.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Weilin1( ), YAN Maodu1,2, ZAN Jinbo1, MIAO Yunfa3, SONG Xiangsuo4, ZHANG Tao5, XU Zunbo1,2, Cairangdaoji 1,2, RUAN Qijun6, LI Hao1
), YAN Maodu1,2, ZAN Jinbo1, MIAO Yunfa3, SONG Xiangsuo4, ZHANG Tao5, XU Zunbo1,2, Cairangdaoji 1,2, RUAN Qijun6, LI Hao1
Received:2025-03-26
Accepted:2025-06-10
Online:2025-12-15
Published:2025-12-15
摘要:
对元谋猿人遗址及其周边地区的地貌形成演化以及水系地表侵蚀过程的研究,可深入揭示青藏高原东南缘构造隆升与气候-生态环境-古人类活动的耦合关系。本研究以磁性地层年代学、构造事件和岩相变化为基石,系统阐述了元谋猿人遗址及其周边地区古夷平面、内部古水系以及河流阶地等地貌发育、形成和演化过程。研究结果表明,元谋猿人遗址及周边地区在新生代以来至少经历了从渐新世晚期至中新世早期、晚中新世早期、上新世早期、早更新世晚期、中更新世、晚更新世以及全新世等不同时期的重大构造事件和水系重组事件,最终演化成现今的地貌格局。另外,元谋猿人遗址的形成过程与三级古夷平面的形成和河流阶地的发育高度相关,反映了古人类活动与构造运动、水系变迁及其控制的地貌演化模式的密切关系。本研究为探讨地貌过程和生态环境变化对元谋猿人及其他古人类生存活动的影响机制提供了重要的地质证据,并为元谋猿人遗址及周边区域今后的古人类和旧石器考古工作提供了重要的参考依据。
中图分类号:
张伟林, 颜茂都, 昝金波, 苗运法, 宋香锁, 张涛, 徐尊铂, 才让道吉, 阮齐军, 李浩. 元谋猿人遗址区域新生代地貌演化[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 952-966.
ZHANG Weilin, YAN Maodu, ZAN Jinbo, MIAO Yunfa, SONG Xiangsuo, ZHANG Tao, XU Zunbo, Cairangdaoji , RUAN Qijun, LI Hao. Evolution of Cenozoic geomorphology in the Yuanmou hominin site area[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2025, 44(06): 952-966.

图1 青藏高原东南缘构造地质概况 A-B.青藏高原东南缘位置与区域构造 Location and Regional tectonics of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau; C.元谋盆地地貌概况 Geomorphic overview of the Yuanmou Basin; D.青藏高原东南部三大阶梯地形,具体位置a-a′见图1:A Three gradient terrains of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau with specific locations a-a′ shown in Fig.1A; E.元谋盆地地形,具体位置b-b′见图1:C Topography of the Yuanmou Basin with specific locations b-b′ shown in Fig.1C
Fig.1 Tectonic and geological overview of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau
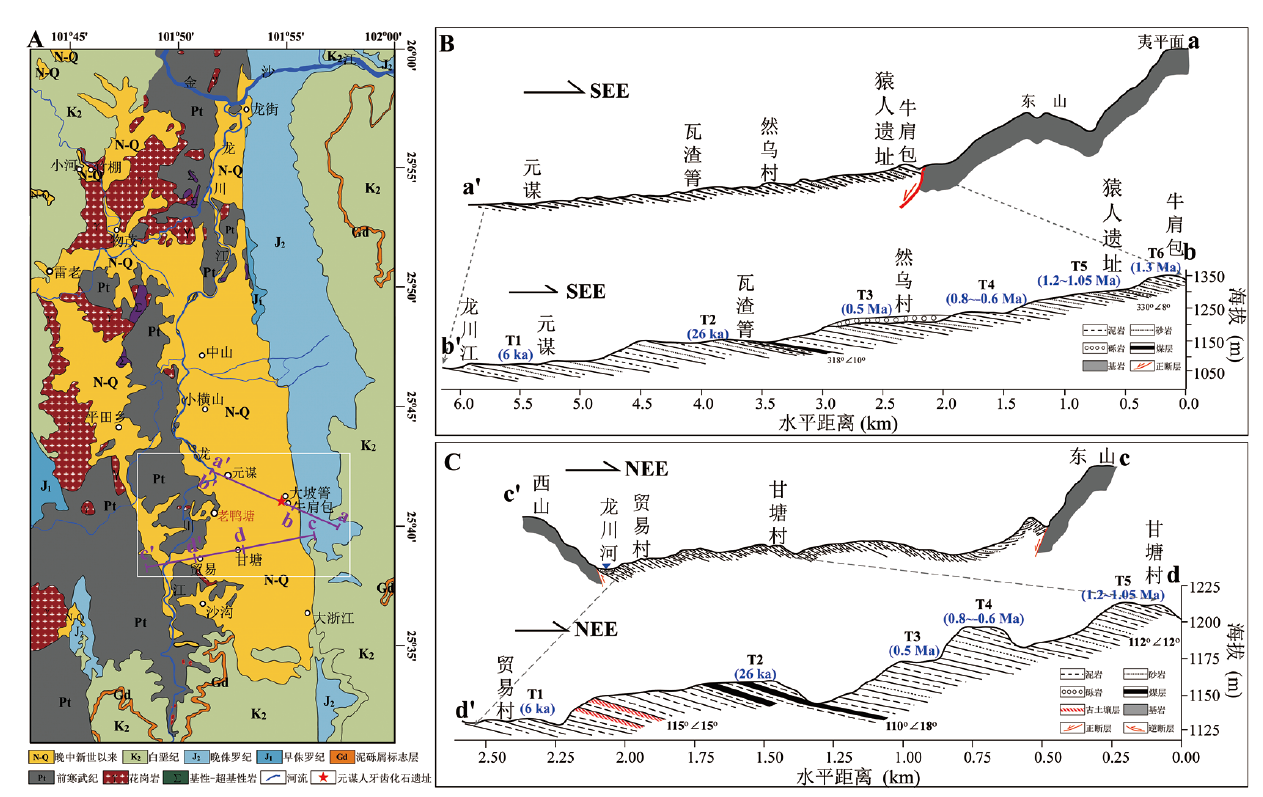
图2 元谋盆地及其周边地层分布 A.元谋盆地及其周边区域地质图 Geological map of the Yuanmou Basin and its surrounding regions; B.横跨元谋盆地a-a’和b-b’的水平剖面图 Cross sections of a-a’ and b-b’ spanning the Yuanmou Basin; C.横跨元谋盆地c-c’和d-d’的水平剖面图 Cross sections of c-c’ and d-d’ spanning the Yuanmou Basin
Fig.2 Stratigraphic distribution in the Yuanmou basin and its surrounding regions
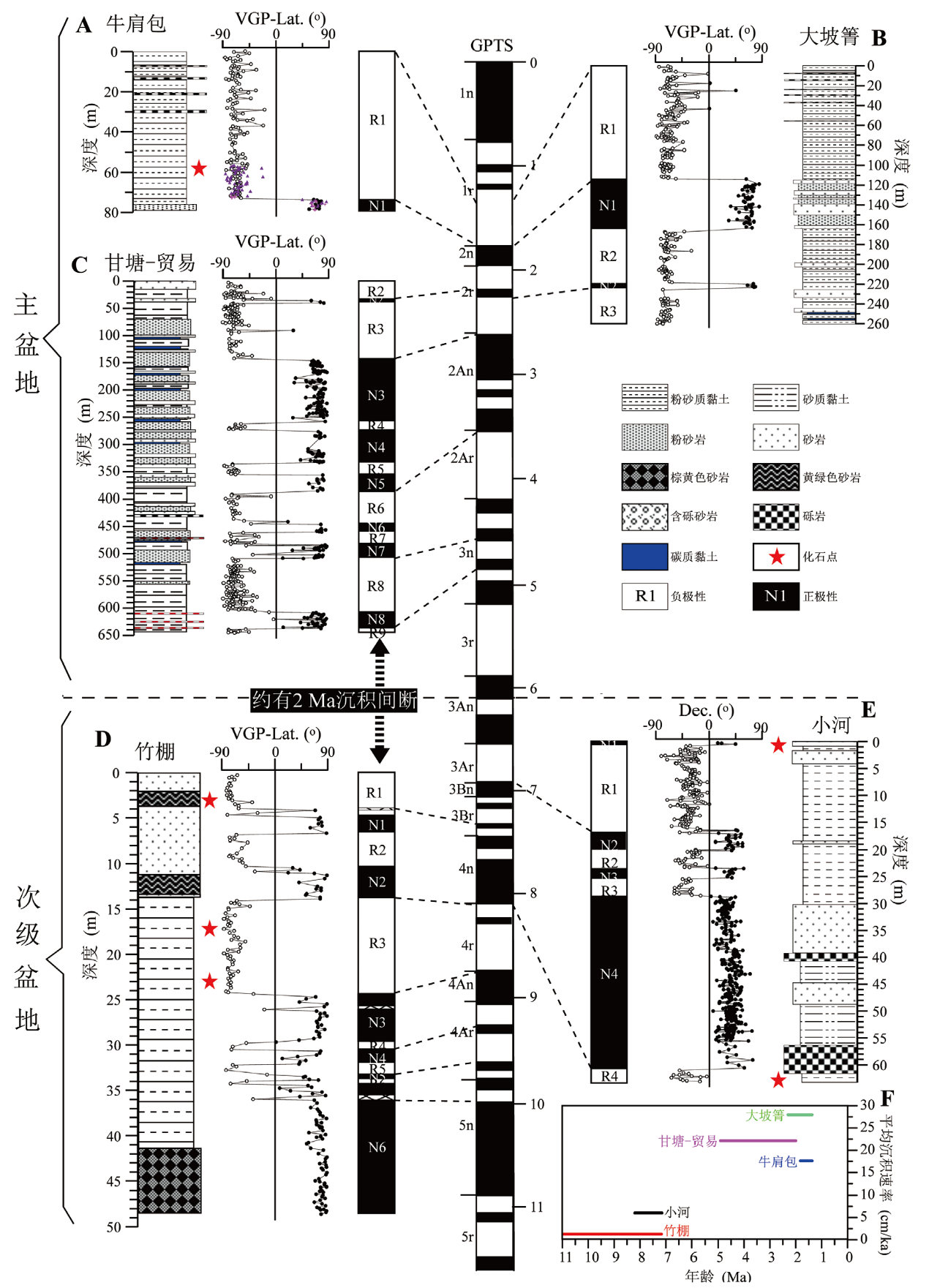
图3 青藏高原东南缘元谋盆地磁性地层年代 A-C.主盆地The main basin[40,58]; D-E.次级盆地The sub-basin[44,46]; F.平均沉积速率The average sedimentary rate
Fig.3 Magnetostratigraphic age of the Yuanmou basin in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau
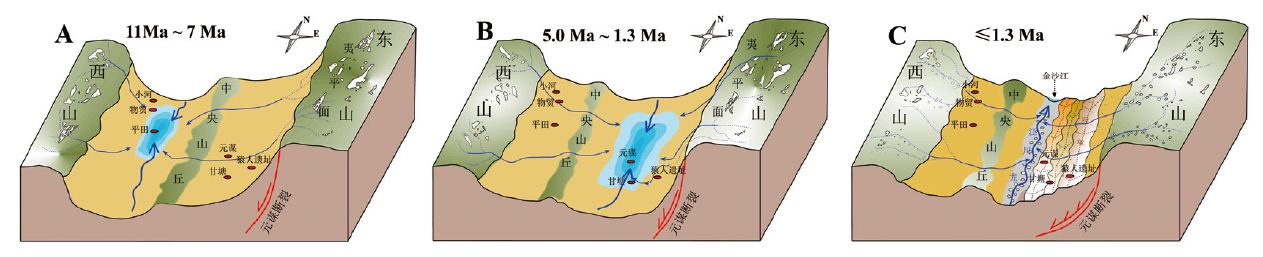
图4 青藏高原东南缘元谋盆地内部水系演化模型 A.第一阶段(11 Ma~7 Ma)/The first stage from 11 Ma to 7 Ma;B.第二阶段(5.0 Ma~1.3 Ma)/The second stage from 5.0 Ma to 1.3 Ma; C.第三阶段(≤1.3 Ma)/The third stage after 1.3 Ma
Fig.4 Internal drainage evolutionary model for the Yuanmou Basin in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau
| [1] |
Antonelli A, Kissling WD, Flantua SGA, et al. Geological and climatic influences on mountain biodiversity[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11(10): 718-725
doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0236-z |
| [2] |
Huang S, Meijers MJM, Eyres A, et al. Unravelling the history of biodiversity in mountain ranges through integrating geology and biogeography[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 2019, 46(8): 1777-1791
doi: 10.1111/jbi.13622 |
| [3] |
Valdes P, Scotese C, Lunt D. Deep ocean temperatures through time[J]. Climate of the Past, 2021, 17: 1483-1506
doi: 10.5194/cp-17-1483-2021 |
| [4] |
Salles T, Husson L, Lorcery M, et al. Landscape dynamics and the Phanerozoic diversification of the biosphere[J]. Nature, 2023, 624: 115-121
doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06777-z |
| [5] | Wang E, Burchfiel BC, Royden LH, et al. Late Cenozoic Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang, Red River, and Dali fault systems of Southwestern Sichuan and Central Yunnan. China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1998, 327: 1-108 |
| [6] |
Li SH, Deng CL, Yao HT, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of the Dali Basin in Yunnan and implications for late Neogene rotation of the southeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2013, 118: 791-807
doi: 10.1002/jgrb.v118.3 URL |
| [7] |
Zhang WL, Yan MD, Fang XM, et al. High-resolution paleomagnetic constraint on the oldest hominoid- fossil bearing sequence in the Xiaolongtan Basin, southeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau and its geologic implications[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019, 182: 103001
doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.103001 URL |
| [8] | Xie SP, Sun BN, Wu JY, et al. Palaeoclimatic Estimates for the Late Pliocene Based on Leaf Physiognomy from Western Yunnan, China[J]. Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 2012, 12: 251-261 |
| [9] |
Ji XP, Jablonski NG, Su DF, et al. Juvenile hominoid cranium from the terminal Miocene of Yunnan, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(31): 3771-3779
doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-6021-x URL |
| [10] |
Li YJ, Oskolski AA, Jacques FMB, et al. New middle Miocene fossil wood of Wataria (malvaceae) from southwest China[J]. IAWA Journal, 2015, 36(3): 345-357
doi: 10.1163/22941932-20150105 URL |
| [11] |
Tapponnier P, Xu ZQ, Roger F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growths of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294: 1671-1677
pmid: 11721044 |
| [12] | Leloup PH, Tapponnier P, Lacassin R, et al. Discussion on the role of the Red River shear zone, Yunnan and Vietnam, in the continental extrusion[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(6): 1253-1260 |
| [13] |
Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Ledain AY, et al. Propagating Extrusion Tectonics in Asia - New Insights from Simple Experiments with Plasticine[J]. Geology, 1982, 10(12): 611-616
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1982)10<611:PETIAN>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [14] |
Zhang HP, Oskin ME, Liu ZJ, et al. Pulsed exhumation of interior eastern Tibet: Implications for relief generation mechanisms and the origin of high-elevation planation surfaces[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 449: 176-185
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.05.048 URL |
| [15] |
Zhu CY, Wang GC, Leloup PH, et al. Role of the Early Miocene Jinhe-Qinghe Thrust Belt in the building of the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau topography[J]. Tectonophysics, 2021, 811: 228871
doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2021.228871 URL |
| [16] |
Wang Y, Zhang B, Schoenbohm LM, et al. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Ailao Shan-Red River fault (SE Tibet): Implications for kinematic change during plateau growth[J]. Tectonics, 2016, 35(8): 1969-1988
doi: 10.1002/tect.v35.8 URL |
| [17] | 许志琴, 王勤, 李忠海, 等. 印度-亚洲碰撞:从挤压到走滑的构造转换[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(1): 1-23 |
| [18] |
Clark MK, House MA, Royden LH, et al. Late Cenozoic uplift of southeastern Tibet[J]. Geology, 2005, 33: 525-528
doi: 10.1130/G21265.1 URL |
| [19] |
Kirby E, Whipple KX. Expression of active tectonics in erosional landscapes[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2012, 44: 54-75
doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2012.07.009 URL |
| [20] | 张会平, 杨农, 张岳桥, 等. 岷江水系流域地貌特征及其构造指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 1: 126-135 |
| [21] | 王洋, 王岳军, 张培震, 等. 青藏高原东南缘断裂体系新生代构造演化[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2022, 52(5): 777-802 |
| [22] | 吴锡浩. 青藏高原东南部地貌边界与金沙江水系发育[J]. 山地学报, 1989, 7(2): 75-84 |
| [23] | 刘静, 曾令森, 丁林, 等. 青藏高原东南缘构造地貌、活动构造和下地壳流动假说[J]. 地质科学, 2009, 44(4): 1227-1255 |
| [24] | Kirby E, Reiners PW, Krol MA, et al. Late Cenozoic evolution of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Inferences from 40Ar/39Ar and (U‐Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 2002, 21(1): TC1001. |
| [25] |
Wang E, Kirby E, Furlong KP, et al. Two‐phase growth of high topography in eastern Tibet during the Cenozoic[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(9): 640-645
doi: 10.1038/ngeo1538 |
| [26] |
Leloup PH, Lacassin R, Tapponnier P, et al. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone (Yunnan, China), Tertiary transform boundary of Indochina[J]. Tectonophysics, 1995, 251: 3-84
doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(95)00070-4 URL |
| [27] |
Clark MK, Royden LH. Topographic ooze: Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(8): 703-706
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [28] |
Huang YJ, Zong HR, Zhang ST, et al. Higher palaeoelevation in the Baoshan Basin: Implications for landscape evolution at the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2024, 13(3): 563-580
doi: 10.1016/j.jop.2024.05.004 URL |
| [29] | Brookfield MB. The evolution of the great river systems of southern Asia during the Cenozoic India-Asia collision: Rivers draining southwards[J]. Geomorphology, 1998, 22(3): 258-312 |
| [30] | Clark MK, Schoenbohm LM, Royden LH, et al. Surface uplift, tectonics, and erosion of eastern Tibet from large-scale drainage patterns[J]. Tectonics, 2004, 23(1): TC1006 |
| [31] | Clift PD, Blusztajn J, Duc NA. Large-scale drainage capture and surface uplift in eastern Tibet SW China before 24 Ma inferred from sediments of the Hanoi Basin, Vietnam[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33: L19403 |
| [32] | Yan Y, Carter A, Huang CY, et al. Constraints on Cenozoic regional drainage evolution of SW China from the provenance of the Jianchuan Basin[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2012, 13: Q03001 |
| [33] |
Zheng HB, Clift PD, Wang P, et al. Pre-Miocene birth of the Yangtze River[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 2013, 110(19): 7556-7561
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216241110 URL |
| [34] |
Zhao M, Shao L, Liang JS, et al. No Red River capture since the late Oligocene: Geochemical evidence from the northwestern South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 185-194
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.02.029 URL |
| [35] |
Chen Y, Yan MD, Fang XM, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb geochronological and sedimentological study of the Simao Basin, Yunnan: Implications for the Early Cenozoic evolution of the Red River[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 476: 22-33
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.07.025 URL |
| [36] |
Zhao XD, Zhang HP, Hetzel R, et al. Existence of a continental-scale river system in eastern Tibet during the late Cretaceous-early Palaeogene[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 7231
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27587-9 pmid: 34903729 |
| [37] | 张叶春, 李吉均, 朱俊杰, 等. 晚新生代元谋盆地演化与河谷发育研究[J]. 兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 1999, 35(1): 199-205 |
| [38] |
Liu FL, Gao HS, Pan BT, et al. Quantitative analysis of planation surfaces of the upper Yangtze River in the Sichuan-Yunnan Region, Southwest China[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2019, 13(1): 55-74
doi: 10.1007/s11707-018-0707-y |
| [39] |
Schoenbohm LM, Burchfiel BC, Chen LZ, et al. Miocene to present activity along the Red River fault, China, in the context of continental extrusion, upper-crustal rotation, and lower-crustal flow[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2006, 118(5-6): 672-688
doi: 10.1130/B25816.1 URL |
| [40] |
Zhu RX, Potts R, Pan YX, et al. Paleomagnetism of the Yuanmou Basin near the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and its constraints on late Neogene sedimentation and tectonic rotation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 272(1): 97-104
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.04.016 URL |
| [41] | 宗冠福, 潘悦容, 姜础, 等. 元谋盆地含古猿化石地层初步划分[J]. 人类学学报, 1991, 10(2): 155-166 |
| [42] | 宗冠福. 元谋盆地的新第三纪地层[J]. 地层学杂志, 1996, 20(2): 138-145 |
| [43] | 张云翔, 邱占祥, 郑良, 等. 云南元谋小河盆地含古猿化石地层的沉积特点与对比[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(1): 85-89 |
| [44] | 岳乐平, 张云翔, 祁国琴, 等. 云南元谋盆地含古猿化石层古地磁年龄及古生物意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(11): 1069-1075 |
| [45] | 董为, 刘建辉, 潘悦容. 云南元谋晚中新世真角鹿化石一新种及其古环境探讨[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(3): 271-278 |
| [46] |
Zhu RX, Liu QS, Yao HT, et al., Magnetostratigraphic dating of hominoid-bearing sediments at Zhupeng, Yuanmou Basin, southwestern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 236: 559-568
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.05.039 URL |
| [47] | 钱方. 关于元谋人的地质时代问题——与刘东生等同志商榷[J]. 人类学学报, 1965, 4(4): 324-332 |
| [48] | 胡承志. 云南元谋发现的猿人牙齿化石[J]. 地质学报, 1973, 1: 65-71 |
| [49] | 李普, 钱方, 马醒华, 等. 用古地磁方法对元谋人化石年代的初步研究[J]. 中国科学, 1976, 6: 579-591 |
| [50] | 浦庆余, 钱方. 对元谋人化石层-元谋组的研究[J]. 地质学报, 1977, 1: 89-99 |
| [51] | 梁其中, 江能人, 孙荣. 元谋盆地晚新生代地层的磁性地层学研究[J]. 云南地质, 1988, 3(7): 46-57 |
| [52] | 江能人, 孙荣, 梁其中. 云南元谋盆地晚新生代地层和古生物[J]. 云南地质, 1989, (增刊): 1-107 |
| [53] | 钱方, 周国兴. 元谋第四纪地质与古人类[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991 |
| [54] | 张宗祜, 刘平贵, 钱方, 等. 元谋盆地晚新生代地质研究的新进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1994, 14(2): 1-17 |
| [55] | 程国良, 李素玲, 林金录. “元谋人”的年代和松山早期事件的商榷[J]. 地质科学, 1997, 1: 34-43 |
| [56] | 刘东生, 丁梦林. 关于元谋人化石地质时代的讨论[J]. 人类学学报, 1983, 2(1): 40-48 |
| [57] | 尤玉柱, 刘后一, 潘悦容. 云南元谋、班果盆地晚新生代地层与脊椎动物化石.见:中国地质科学院地层古生物论文集编委会.地层古生物论文集(第七辑)[C]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1978 |
| [58] |
Zhu RX, Potts R, Pan YX, et al. Early evidence of the genus Homo in East Asia[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2008, 55: 1075-1085
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2008.08.005 pmid: 18842287 |
| [59] | Hyodo M, Nakaya H, Urabe A, et al. Paleomagnetic dates of hominid remains from Yuanmou, China, and other Asian sites[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2002, 43: 27-41 |
| [60] | 刘泽纯, 李庆辰. 关于元谋盆地的沉积特征与地层划分[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1988, 8(4): 65-75 |
| [61] | 高星. “元谋人”的年龄及相关的年代问题讨论[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(4): 442-450 |
| [62] | Zhang WL, Fang XM, Zhang T, et al. Eocene Rotation of the Northeastern Central Tibetan Plateau Indicating Stepwise Compressions and Eastward Extrusions[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(17): 1-14 |
| [63] |
Li SH, van Hinsbergen DJJ, Najman Y, et al. Does pulsed Tibetan deformation correlate with Indian plate motion changes?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 536: 116144
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2020.116144 URL |
| [64] |
Su T, Spicer RA, Li SH, et al. Uplift, climate and biotic changes at the Eocene-Oligocene transition in south-eastern Tibet[J]. National Science Review, 2018, 6(3): 495-504
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwy062 URL |
| [65] |
He SL, Ding L, Xiong ZY, et al. A distinctive Eocene Asian monsoon and modern biodiversity resulted from the rise of eastern Tibet[J]. Science Bulletin, 2022, 67: 2245-2258
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2022.10.006 pmid: 36546000 |
| [66] | Ni XJ, Li Q, Deng T, et al. New Yuomys rodents from southeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau indicate low elevation during the Middle Eocene[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2023, 10: 1018675 |
| [67] | Bai B. Reappraisal of some perissodacyl fossils from the Middle Eocene of the Lijiang Basin, Yunnan, China with a revision of tapiroid Diplolophodon[J]. Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2023, 61(1): 26-42 |
| [68] | Gourbet L, Leloupa PH, Paquette JL, et al. Reappraisal of the Jianchuan Cenozoic basin stratigraphy and its implica tions on the SE Tibetan plateau evolution[J]. Tectonophysics, 2017, (700-701): 162-179 |
| [69] |
Fang XM, Yan MD, Zhang WL, et al. Paleogeography control of Indian monsoon intensification and expansion at 41 Ma[J]. Science Bulletin, 2021, 66: 2320-2328
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2021.07.023 URL |
| [70] |
Zheng H, Clift PD, He MY, et al. Formation of the First Bend in the late Eocene gave birth to the modern Yangtze River, China[J]. Geology, 2020, 49: 35-39
doi: 10.1130/G48149.1 URL |
| [71] |
Cao K, Leloup PH, Wang GC, et al. Thrusting, exhumation, and basin fill on the western margin of the South China block during the India-Asia collision[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2021, 133(1-2): 74-90
doi: 10.1130/B35349.1 URL |
| [72] |
Linnemann U, Su T, Kunzmann L, et al. New U-Pb dates show a Paleogene origin for the modern Asian biodiversity hot spots[J]. Geology, 2018, 46(1): 3-6
doi: 10.1130/G39693.1 URL |
| [73] | Li SH, Su T, Spicer RA, et al. Oligocene deformation of the Chuandian terrane in the SE margin of the Tibetan Plateau related to the extrusion of Indochina[J]. Tectonics, 2020, 39: e2019TC005974 |
| [74] |
Ni X, Li Q, Li L, et al. Oligocene primates from China reveal divergence between African and Asian primate evolution[J]. Science, 2016, 352: 673-677
doi: 10.1126/science.aaf2107 pmid: 27151861 |
| [75] |
Tian YM, Spicer RA, Huang J, et al. New early oligocene zircon U-Pb dates for the ‘Miocene’ Wenshan Basin, Yunnan, China: Biodiversity and paleoenvironment[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2021, 565: 116929
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2021.116929 URL |
| [76] |
Socquet A, Pubellier M. Cenozoic deformation in western Yunnan (China-myanmar border)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24(4): 495-515
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.03.006 URL |
| [77] |
Tanaka K, Mu CL, Sato K, et al. Tectonic deformation around the eastern Himalayan syntaxis: constraints from the Cretaceous paleomagnetic data of the Shan-Thai Block[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2008, 175: 713-728
doi: 10.1111/gji.2008.175.issue-2 URL |
| [78] |
Wang JH, Yin A, Harrison TM, et al. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 188(1-2): 123-133
doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00315-6 URL |
| [79] |
Spurlin MS, Yin A, Horton BK, et al. Structural evolution of the Yushu-Nangqian region and its relationship to syncollisional igneous activity, east-central Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2005, 117(9-10): 1293-1317
doi: 10.1130/B25572.1 URL |
| [80] |
Lu YJ, Kerrich R, Cawood PA, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of potassic felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China: constraints on the relationship of magmatism to the Jinsha suture[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(2): 737-747
doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.016 URL |
| [81] |
Xu Y, Zhu J, Hu R, et al. Heterogeneous lithospheric mantle beneath the Southeastern Tibetan plateau: Evidence from Cenozoic high-Mg potassic volcanic rocks in the Jinshajiang-Ailaoshan Cenozoic magmatic belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 180: 103849
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.04.018 URL |
| [82] |
Sun XL, Ding WN, Kuiper KF, et al. New early Oligocene age for the Mouding Basin, Southwestern China: Source and paleoenvironment[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2024, 636: 111983
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111983 URL |
| [83] |
Zhang GH Tian, YT, Li R, et al. Progressive tectonic evolution from crustal shortening to mid-lower crustal expansion in the southeast Tibetan Plateau: a synthesis of structural and thermochronological insights[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022, 226: 103951
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.103951 URL |
| [84] |
Zhao LC, Wang YF, Liu CJ, et al. Climatic implications of fruit and seed assemblage from Miocene of Yunnan, southwestern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2004, 117: 81-89
doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00118-6 URL |
| [85] |
Jacques FMB, Guo SX, Su T, et al. Quantitative reconstruction of the Late Miocene monsoon climates of southwest China: A case study of the Lincang flora from Yunnan Province[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 304: 318-327
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.04.014 URL |
| [86] |
Li SH, Deng CL, Dong W, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of the Xiaolongtan Formation bearing Lufengpithecus keiyuanensis in Yunnan, southwestern China: Constraint on the initiation time of the southern segment of the Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 655: 213-226
doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.06.002 URL |
| [87] |
Nie JS, Ruetenik G, Gallagher K, et al. Rapid Incision of the Mekong River in the Middle Miocene Linked to Monsoonal Precipitation[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11: 944-948
doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0244-z |
| [88] | 郑勇, 王亚军, 孔屏. 四川攀枝花昔格达组及其下伏河流砾石的地球化学特征以及对物源的制约[J]. 地质科学, 2009, 44(3): 1036-1051 |
| [89] | 姚海涛, 邓成龙, 吕连清. 元谋盆地河湖相沉积物磁性地层学研究综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2005, 20(2): 518-523 |
| [90] | 张进江, 钟大赉, 周勇. 东南亚及哀牢山红河构造演化的讨论[J]. 地质论评, 1999, 45: 337-344 |
| [91] | 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 肖华国, 等. 四川泸定昔格达组时代及其新构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 1999, 73(1): l-6 |
| [92] | 孔屏. 金沙江何时开始东流[J]. 地质科学, 2009, 44(4): 1256-1265 |
| [93] | 李朝柱, 蒋复初, 傅建利, 等. 云南元谋龙街粉砂层的形成时代研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(5): 933-934 |
| [94] | 黄万波, 王景文, 邱铸鼎, 等. 元谋组、龙街组及昔格达组的时代对比[A].见:中国地质科学院地层古生物论文集编委会(主编).地层古生物论文集(第七辑)[C]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1978 |
| [95] |
Kong P, Granger DE, Wu FY, et al. Cosmogenic nuclide burial ages and provenance of the Xigeda paleo-lake: Implications for evolution of the Middle Yangtze River[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 278(1-2): 131-141
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.12.003 URL |
| [96] |
刘芬良, 高红山, 李宗盟, 等. 金沙江巧家-蒙姑段的阶地发育与河谷地貌演化[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75(5): 1095-1105
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202005015 |
| [97] | 黄成敏, 王成善, 何毓蓉, 等. 元谋盆地古红土的土壤发生学特征及古环境意义[J]. 土壤通报, 2004, 35(3): 251-256 |
| [98] | 杨达源, 韩志勇, 葛兆帅, 等. 金沙江石鼓-宜宾河段的贯通与深切地貌过程的研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(4): 564-568 |
| [99] |
McPhillips D, Hoke GD, Liu ZJ, et al. Dating the incision of the Yangtze River gorge at the First Bend using three nuclide burial ages[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(1): 101-110
doi: 10.1002/grl.v43.1 URL |
| [100] | 闵隆瑞, 尹占国, 张金起. 龙街粉砂层形成时代及其古环境[J]. 第四纪研究, 1990, 4: 354-362 |
| [1] | 孙博阳, 史勤勤, 侯素宽, 李雨, 孟月, 关建宇, 魏金凯, 阮齐军. 元谋猿人遗址大哺乳动物群生态学与动物地理意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 967-977. |
| [2] | 阮齐军, 李田广, 车德才, 和金梅, 孙博阳, 史勤勤, 侯素宽, 张双权, 王国付, 李俊, 永春, 张飞, 石俊雯, 张雯静, 贾真秀, 李浩. 云南元谋猿人遗址2023年度发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 939-951. |
| [3] | 阮齐军, 王幼平. 元谋猿人遗址发现及研究历史回顾与展望[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 927-938. |
| [4] | 贾真秀, 赤列次仁, 李浩, 童艳, 夏格旺堆, 陈发虎. 西藏拉萨堆龙曲流域2021-2022年旧石器考古调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(06): 1083-1093. |
| [5] | 张晓凌, 王呈祥, 谭韵瑶, 靳英帅, 杨紫衣, 王社江. 青藏高原旧石器时代考古发现与研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(06): 967-978. |
| [6] | 丁曼雨, 何伟, 王恬怡, 夏格旺堆, 张明, 曹鹏, 刘峰, 戴情燕, 付巧妹. 中国西藏拉托唐古墓地古代居民线粒体全基因组研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 1-11. |
| [7] | 陈宥成, 侯光良, 高靖易, 陈晓良. 青藏高原冬给措纳湖畔新发现的细石器及其同周边地区的技术关系[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 28-39. |
| [8] | 王社江;张晓凌;陈祖军;仪明洁;葛俊逸;达娃;何伟;张建林;栗静舒;洛桑;哈比卜;李林辉;高星. 藏北尼阿木底遗址发现的似阿舍利石器——兼论晚更新世人类向青藏高原的扩张[J]. 人类学学报, 2018, 37(02): 253-269. |
| [9] | 张晓凌;王社江;陈祖军. 西藏旧石器考古调查取得丰硕成果[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(01): 86-86. |
| [10] | 王頠. 广西布兵盆地河流阶地新发现的史前石器遗址[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(03): 270-284. |
| [11] | 席焕久;温有锋;张海龙;李文慧;任甫;黄克强;肖艳杰;叶丽平;李春山;陈昭;. 青藏高原与安第斯高原地区儿童青少年的身高、体重和胸围的对比[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(02): 198-213. |
| [12] | 仪明洁; 高星; 张晓凌; 孙永娟; P.Jeffrey Brantingham; David B.Madsen; David Rhode. 青藏高原边缘地区史前遗址2009年调查试掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2011, 30(02): 124-136. |
| [13] | 王幼平. 青藏高原隆起与东亚旧石器文化的发展[J]. 人类学学报, 2003, 22(03): 192-200. |
| [14] | 袁宝印,侯亚梅,王頠,鲍立克,郭正堂,黄慰文. 百色旧石器遗址的若干地貌演化问题[J]. 人类学学报, 1999, 18(03): 215-224. |
| [15] | 黄培华,R. Grün. 元谋猿人遗址牙化石埋藏年代的初步研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1998, 17(03): 165-170. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3