

河北汉族成年男性身高与足迹的相关性
收稿日期: 2023-07-30
修回日期: 2023-11-16
网络出版日期: 2024-08-13
基金资助
2023年河北省公安厅科技计划项目“当代人群足迹与身高相关关系研究”(HBGAT2023009)
Correlation between height and footprint of the adult Han men in Hebei
Received date: 2023-07-30
Revised date: 2023-11-16
Online published: 2024-08-13
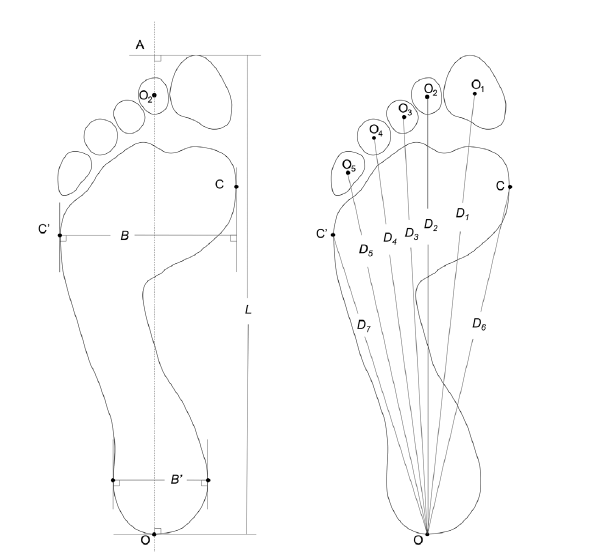
为了研究河北省当代汉族成年男性身高与足迹的相关性,本文采集了205名河北省籍19~51 a成年男性赤足足迹数据并进行统计分析。结果表明:河北省当代汉族成年男性体足比左侧均值为7.336 (6.806~7.848),右侧均值为7.350 (6.755~7.883),明显大于四十多年前统计得出的通用体足比系数6.876或7;左右两足对称性整体表现为左足大于右足,但两者差别并不大;赤足足迹全长与新确定的7个足迹测量特征均与身高显著相关,且第四趾测量值与身高相关系数最高(左侧0.758,右侧0.769);得出的一元线性回归方程组计算身高误差范围为-46~48 mm,利用第四趾测量值计算误差最小(-28~22 mm)。研究结果提示河北省当代汉族男性人群体足比随着时代的变迁而增大,已超过7.33,整体呈现“大个小脚”的变化趋势。
李彦雷 . 河北汉族成年男性身高与足迹的相关性[J]. 人类学学报, 2024 , 43(04) : 657 -667 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0026
Footprint itself has will ‘leave a trace’ characteristics, and has the incomparable superiority than other trace evidences when used to estimate individual characteristics such as stature. Traditionally, forensic scientists use the stature-footprint length ratio (h/L) to calculate stature through footprint. The h/L (6.876 or 7) now we are using today was developed more than 40 years ago, but populations are dynamic, which means stature estimation standards should be constantly revised, thus ensuring the most accurate estimations are made. Research has shown that h/L has changed. Past statistical studies showed that h/L are greatly influenced by regional, national. However, h/L have not been seen studied in north China, especially in Hebei province in recent years. Therefore, this study focuses on the modern Han adults in Hebei province, establish the correlation between footprint and stature through footprints collecting, measuring and data analyzing, then build regression equation models of stature to estimate the contemporary Han adult male population in Hebei Province accurately and to compare the contribution degree of multiple footprint measurements, give recommendations on the order of the measurements, in order to solve problems more effectively. The sample comprises 205 Han male adults in Hebei province (age 19~51). A stature measurement was collected, and ten linear measurements were then extracted from bilateral footprints. Prior to data collection, a precision test was conducted to determine the repeatability of linear measurement acquisition. What’s more, the environmental factors such as temperature and time were controlled throughout the study. Results show: 1) The mean value h/L of left is 7.336 (6.806~7.848), the right side 7.350 (from 6.755~7.883), both left and right h/L are bigger than 7.33, is greater than the current ratio which is obviously not suitable for people of Hebei province today. 2) The bilateral difference of footprint measurements is significant, and the overall performance for the left foot is greater than the right foot, but less than 2 mm. 3) The length from forth toe to the pternion (D4) show significantly correlation with stature, and has the highest correlation coefficient (left side 0.758, right side 0.769). It was the most accurate single variable in the simple linear regressions to calculate stature with associated error rates of -28 mm to 22 mm. It is concluded that h/L based on noncontemporary individuals which we are using today is not suitable for modern populations, and the D4 measurement is recommended for stature calculation first.

Key words: Hebei province; Contemporary people; Han; Footprint Length; Stature
| [1] | 姜东, 闫文柱, 刘素伟, 等. 辽宁农村汉族成人手长、足长与身高的关系[J]. 解剖学报, 2011, 42(2): 249-252 |
| [2] | 樊晓光, 丁士海. 山东半岛地区大学生手长足长与身高关系的研究[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 1997, 12(2): 98-100 |
| [3] | 余舰, 夏君, 王万麟, 等. 贵州地区汉族特定人群男性手长、足长与身高的关系[J]. 遵义医学院学报, 2003, 26,(6): 515-516 |
| [4] | 熊伟, 赵英. 湖南省青年大学生手长、足长与身高的相关关系[J]. 南华大学学报, 2001, 29,(4): 351-352 |
| [5] | 吴旭芒, 高以群. 足迹学[M]. 北京: 警官教育出版社, 1996 |
| [6] | 罗亚平. 痕迹检验教程[M]. 北京: 中国人民公安大学出版社, 2014, 166 |
| [7] | Robbins LM. Estimating height and weight from size of footprints[J]. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 1986, 31(1): 143-152 |
| [8] | Robbins LM. The individuality of human footprints[J]. Journal of Forensic Science, 1978, 23(11): 778-785 |
| [9] | Kennedy RB, Pressman S, Chen S, et al. Statistical Analysis of Barefoot Impressions[J]. Forensic Sci, 2003, 48(1): 1-9 |
| [10] | Kennedy RB. Uniqueness of bare feet and its use as a possible means of identification[J]. Forensic Science International, 1996, 82(1): 81-87 |
| [11] | Kennedy RB. A large-scale statistical analysis of barefoot impressions[J]. Journal of Forensic Science, 2005, 50(5): 71-80 |
| [12] | Naomi H, Ambika F, Daniel F, et al. Estimation of stature using anthropometry of feet and footprints in a Western Australian population[J]. Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine, 2013, 20: 435-441 |
| [13] | 马立广, 曹彦荣, 徐玖瑾, 等. 中国102个人群的身高与地理环境相关性研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2008, 27(3): 223-231 |
| [14] | 张振标. 现代中国人身高的变异[J]. 人类学学报, 1988, 7(2): 112-120 |
| [15] | 唐锡麟, 王志强, 王冬妹. 中国汉族青年身高水平的地域分布[J]. 人类学学报, 1994, 13(2): 143-148 |
| [16] | 张迎修. 中国沿海11省市儿童青少年的生长发育状况[J]. 人类学学报, 2004, 23(2): 159-163 |
| [17] | 朱鹏, 张洪波, 黄锟, 等. 安徽省7-18岁学生1985-2005年身高变化趋势研究[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2006, 27(7): 567-569 |
| [18] | 杨晓光, 李艳平, 马冠生, 等. 中国2002年居民身高和体重水平及近10年变化趋势分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2005, 26(7): 489-493 |
| [19] | 内蒙古自治区昭乌达盟公安处编. 足迹检验[M]. 北京: 群众出版社, 1982, 123 |
| [20] | 顾仲生, 高凯燕. 单个平面赤足迹中支撑压痕总长、宽度与身高、体重相关规律的综合定量分析[J]. 上海公安高等专科学校学报, 2001, 11(2): 45-50 |
| [21] | 李力. 回归法推断手印和足迹与身高和体重的关系[J]. 法医学杂志, 2005, 21(4): 252-254 |
| [22] | 刘玉文, 刘俊峰. 赤足平面足迹推断身高的实验研究[J]. 四川警官高等专科学校学报, 2005, 17(6):70-73 |
| [23] | 汤澄清, 董佳英, 姚力, 等. 关于身高的分析[J]. 辽宁警专学报, 2006, 33(5): 62-64 |
| [24] | 李力. 依据手足印推算身高体重的可行性研究[J]. 刑事技术, 2007, 1: 22-24 |
| [25] | Kanchan T, Krishan K, Sundar SS, et al. Analysis of footprint and its parts for stature estimation in Indian population[J]. The Foot. 2012, 22: 175-180 |
| [26] | Schultz AH. Proportions, variability and asymmetries of the long bones of the limbs and the clavicles in man and apes[J]. Human Biology, 1937, 9(3): 281-328 |
| [27] | Latimer HB, Lowrance EW. Bilateral asymmetry in weight and in length of human bones[J]. The Anatomical Record, 1965, 152(2): 217-224 |
| [28] | Auerbach BM, Ruff CB. Limb bone bilateral asymmetry: variability and commonality among modern humans[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2006, 50(2): 203-218 |
| [29] | 郑连斌, 贾淑媛, 韩在柱, 等. 人类的不对称行为特征[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学报), 2001, 21(3): 58-61 |
| [30] | 皮建辉, 邓莉, 雷鸣枝, 等. 湖南汉族一侧优势行为特征研究[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2007, 13(3): 244-246 |
| [31] | 范迎, 徐国昌, 席焕久, 等. 河南汉族7项不对称行为特征的研究[J]. 生物学通报, 2012, 47(10): 4-9 |
| [32] | 张瑜珂, 李咏兰, 陆舜华, 等. 浙江汉族7项不对称行为特征[J]. 解剖学报, 2013, 44(2): 284-291 |
| [33] | 胡向阳, 姚慧芳, 林建辉. 身高与足迹长度相关关系综合研究[J]. 法医学杂志, 2005, 21(1): 15-18 |
| [34] | 解云, 张书杰, 兰绍江, 等. 中国刑事科学技术大全:痕迹检验[M]. 北京: 中国人民公安大学出版社, 2003, 150 |
| [35] | 李仁, 刘树元. 青少年足长与身长关系的研究[J]. 人类学学报, 1987, 6(4): 361 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |