

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (01): 165-180.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0019cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0019
• 综述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-09-15
修回日期:2023-11-15
出版日期:2025-02-15
发布日期:2025-02-13
作者简介:雷帅,复旦大学人类表型组研究院博士后,主要从事生物考古学研究。E-mail: 1710976265@qq.com
基金资助:Received:2023-09-15
Revised:2023-11-15
Online:2025-02-15
Published:2025-02-13
摘要:
本文详细论述了人类牙釉质同位素研究涉及的重要理论方法问题。首先,梳理了人类牙釉质的生长发育机制、主要化学组成及抵抗成岩作用的优越性。其次,回顾和评述了牙釉质多同位素方法对于人类生活史、居住史及健康史三大科学主题的研究现状。最后,强调了在新时代中国特色考古学理论体系建设的大背景下,快速发展牙釉质多同位素研究的迫切性,并结合国际生物考古学界已有的研究经验和不足,对中国今后如何开展此项研究进行了展望。
中图分类号:
雷帅. 人类牙釉质同位素研究的进展与展望[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(01): 165-180.
LEI Shuai. Progress and perspectives of the isotope research of human tooth enamel[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2025, 44(01): 165-180.
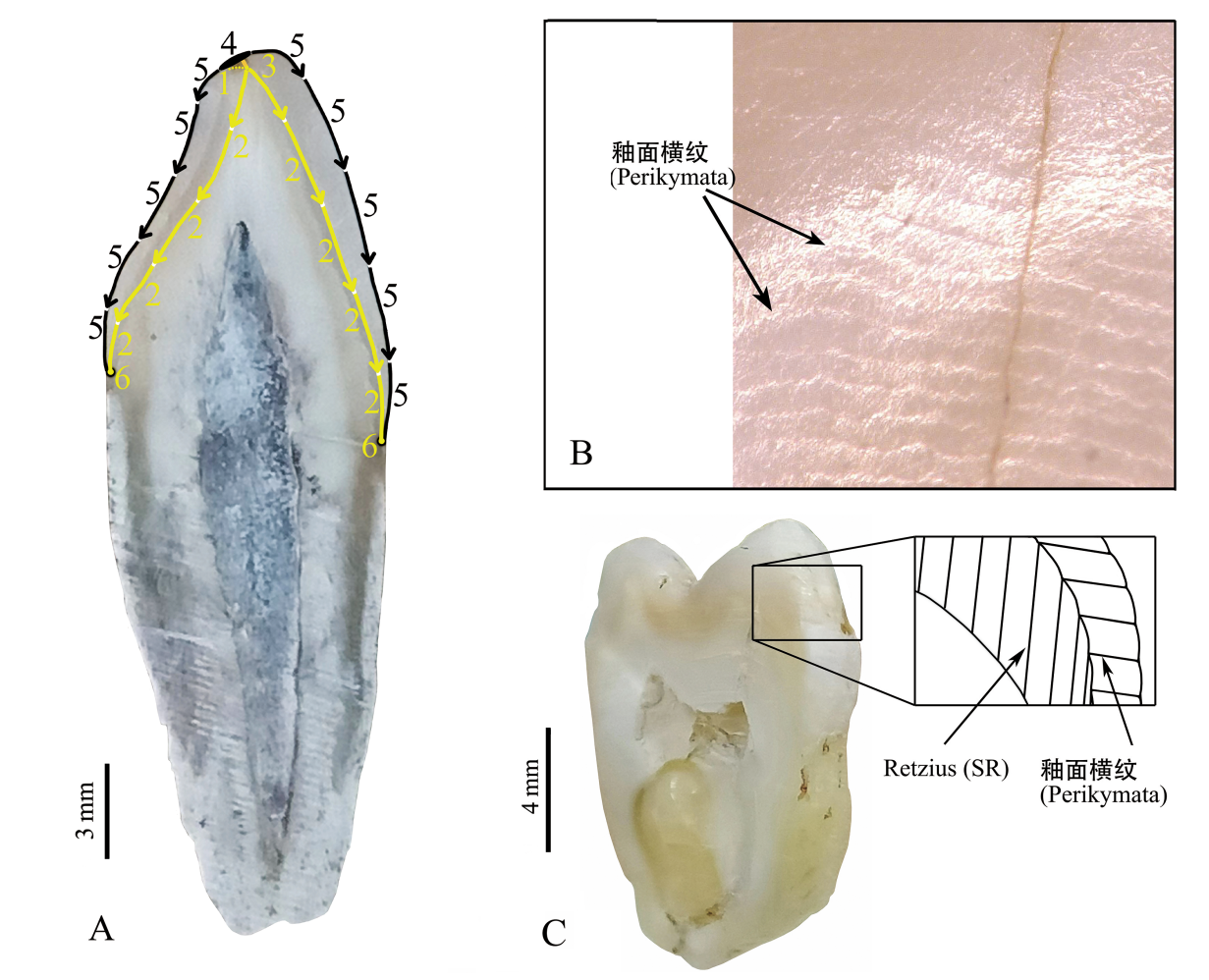
图1 成釉细胞的分化模式和牙釉质增量条纹 A.修改自文献[9⇓-11]/modified from reference [9⇓-11],图中数字按时间顺序从早到晚依次表示成釉细胞分泌和成熟过程中的不同点位Numbers in the figure indicate, in chronological order from early to late, the different points in the secretion and maturation process of enamel-forming cells。B. 超景深电子显微镜 (KEYENCEVHX-2000)下牙釉质表面的釉面横纹(Perikymata)/Enamel transverse striations (Perikymata) of the enamel surface under an ultra-deep field electron microscope (KEYENCEVHX-2000);C.牙釉质切面上的长周期增量条纹(Retzius),延伸到牙釉质表面又称釉面横纹(Perikymata)/ Long-period incremental streaks in enamel sections (Retzius) extend to the surface of the enamel, also known as transverse enamel lines (Perikymata)
Fig.1 Patterns of enamel-forming cell differentiation, and incremental streaking of tooth enamel
| [1] | Dean MC, Liversidge HM, Elamin F. Combining radiographic and histological data for dental development to compare growth in the past and the present[J]. Annals Human Biology, 2014, 41(4): 336-347 |
| [2] | 雷帅, 郭怡. 生物考古学视野下人类的牙齿与饮食[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(3): 501-513 |
| [3] | Nanci A. Enamel:Composition, formation, and structure[A]. In: Nanci A (Ed.). Ten Cate’s oral histology development, structure, and function[M]. Missouri: Elsevier Mosby, 2008: 141-190 |
| [4] |
Beaumont J, Montgomery J. Oral histories: A simple method of assigning chronological age to isotopic values from human dentine collagen[J]. Annals of Human Biology, 2015, 42(4): 407-414
pmid: 26225904 |
| [5] | Hillson S. Tooth Development in Human Evolution and Bioarchaeology[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014: 28-68 |
| [6] |
AlQahtani SJ, Hector MP, Liversidge HM. Brief communication: the London Atlas of Human Tooth Development and Eruption[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2010, 142(3): 481-490
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21258 pmid: 20310064 |
| [7] | Smith CE. Cellular and chemical events during enamel maturation[J]. Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine, 1998, 9(2): 128-161 |
| [8] | Fincham AG, Simmer JP. Amelogenin proteins of developing dental enamel[J]. Dental Enamel, 1997, 205: 118-134 |
| [9] |
Radlanski RJ, Renz H. A possible interdependency between the wavy path of enamel rods, distances of Retzius lines, and mitotic activity at the cervical loop in human teeth: a hypothesis[J]. Medical hypotheses, 2004, 62(6): 945-949
pmid: 15142654 |
| [10] | Birch W, Dean C. Rates of enamel formation in human deciduous teeth[J]. Comparative Dental Morphology, 2009, 13: 116-120 |
| [11] |
Simmer JP, Papagerakis P, Smith CE, et al. Regulation of Dental Enamel Shape and Hardness[J]. Journal Of Dental Research, 2010, 89(10): 1024-1038
doi: 10.1177/0022034510375829 pmid: 20675598 |
| [12] |
Newman HN, Poole DF. Observations with scanning and transmission electron microscopy on the structure of human surface enamel[J]. Archives Of Oral Biology, 1974, 19(12): 1135-1143
pmid: 4531875 |
| [13] |
FitzGerald CM. Do enamel microstructures have regular time dependency? Conclusions from the literature and a large-scale study[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 1998, 35(4-5): 371-386
pmid: 9774500 |
| [14] |
Reid DJ, Ferrell RJ. The relationship between number of striae of Retzius and their periodicity in imbricational enamel formation[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2006, 50(2): 195-202
pmid: 16263151 |
| [15] | Nanci A. Development of the tooth and its supporting tissues[A]. In: Nanci A (Ed.). Ten Cate’s Oral Histology Development, Structure, and Function[M]. Missouri: Elsevier Mosby, 2008: 79-107 |
| [16] | Beynon AD, Dean MC, Reid DJ. On thick and thin enamel in hominoids[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1991, 86(2): 295-309 |
| [17] |
Lacruz RS, Bromage TG. Appositional enamel growth in molars of South African fossil hominids[J]. Journal of Anatomy, 2006, 209(1): 13-20
pmid: 16822265 |
| [18] |
Kodaka T, Sano T, Higashi S. Structural and calcification patterns of the neonatal line in the enamel of human deciduous teeth[J]. Scanning Microscopy, 1996, 10(3): 737-743
pmid: 9813636 |
| [19] |
Dean MC, Scandrett AE. The relation between long-period incremental markings in dentine and daily cross-striations in enamel in human teeth[J]. Archives Of Oral Biology, 1996, 41(3): 233-241
pmid: 8735009 |
| [20] |
Beaumont J, Craig-Atkins E, Buckberry J, et al. Comparing apples and oranges: Why infant bone collagen may not reflect dietary intake in the same way as dentine collagen[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2018, 167(3): 524-540
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.23682 pmid: 30187451 |
| [21] | Hubbard MJ. Calcium transport across the dental enamel epithelium[J]. Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine, 2000, 11(4): 437-466 |
| [22] |
Krachler M, Rossipal E, Micetic-Turk D. Trace element transfer from the mother to the newborn: Investigations on triplets of colostrum, maternal and umbilical cord sera[J]. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 1999, 53(6): 486-494
pmid: 10403586 |
| [23] |
Rossipal E, Krachler M, Li F, et al. Investigation on the transport of trace elements across barriers in humans: Studies of placental and mammary transfer[J]. Acta Paediatrica, 2000, 89(10): 1190-1195
pmid: 11083374 |
| [24] | Humphrey LT, Dean MC, Jeffries TE, et al. Unlocking evidence of early diet from tooth enamel[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2008, 105(19): 6834-6839 |
| [25] |
Wilson PR, Beynon AD. Mineralization differences between human deciduous and permanent enamel measured by quantitative microradiography[J]. Archives Of Oral Biology, 1989, 34(2): 85-88
doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(89)90130-1 pmid: 2783050 |
| [26] |
Wong FSL, Anderson P, Fan H, et al. X-ray microtomographic study of mineral concentration distribution in deciduous enamel[J]. Archives of Oral Biology, 2004, 49(11): 937-944
pmid: 15353251 |
| [27] |
Lacruz RS, Habelitz S, Wright JT, et al. Dental enamel formation and implications for oral health and disease[J]. Physiological Reviews, 2017, 97(3): 939-993
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2016 pmid: 28468833 |
| [28] | Kohn MJ, Schoeninger MJ, Barker WW. Altered states: Effects of diagenesis on fossil tooth chemistry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(18): 2737-2747 |
| [29] |
Kubota T, Nakamura A, Toyoura K, et al. The effect of chemical potential on the thermodynamic stability of carbonate ions in hydroxyapatite[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2014, 10(8): 3716-3722
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.05.007 pmid: 24821142 |
| [30] | Munro LE, Longstaffe FJ, White CD. Effects of heating on the carbon and oxygen-isotope compositions of structural carbonate in bioapatite from modern deer bone[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2008, 266(3-4): 142-150 |
| [31] | Koch PL. Isotopic reconstruction of past continental environments[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1998, 26: 573-613 |
| [32] | Luz B, Kolodny Y, Horowitz M. Fractionation of oxygen isotopes between mammalian bone-phosphate and environmental drinking water[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(8): 1689-1693 |
| [33] | Iacumin P, Nikolaev V, Ramigni M, et al. Oxygen isotope analyses of mammal bone remains from Holocene sites in European Russia: palaeoclimatic implications[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2004, 40(1-2): 169-176 |
| [34] | Bryant JD, Froelich PN. Oxygen isotope composition of human tooth enamel from medieval Greenland: Linking climate and society: Comment[J]. Geology, 1996, 24(5): 477-478 |
| [35] | Iacumin P, Bocherens H, Mariotti A, et al. Oxygen isotope analyses of co-existing carbonate and phosphate in biogenic apatite: A way to monitor diagenetic alteration of bone phosphate?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 142(1-2): 1-6 |
| [36] | Koch PL, Behrensmeyer AK, Tuross N, et al. Isotopic fidelity during bone weathering and burial[J]. Annual Report of the Director of the Geophysical Laboratory, Carnegie Institution of Washington, 1990, 105 |
| [37] | Dupras TL. Biogeochemical Approaches to Paleodietary Analysis[J]. American Antiquity, 2002, 67(1): 174-175 |
| [38] |
Daux V, Lecuyer C, Heran MA, et al. Oxygen isotope fractionation between human phosphate and water revisited[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2008, 55(6): 1138-1147
doi: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2008.06.006 pmid: 18721999 |
| [39] |
Chenery CA, Pashley V, Lamb AL, et al. The oxygen isotope relationship between the phosphate and structural carbonate fractions of human bioapatite[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2012, 26(3): 309-319
doi: 10.1002/rcm.5331 pmid: 22223318 |
| [40] | Mascarenhas RD, Sena-Souza JP, Bernasconi SM, et al. Building an isoscape based on tooth enamel for human provenance estimation in Brazil[J]. Forensic Science International, 2022, 330: 1-10 |
| [41] | Ambrose SH, Norr L. Experimental evidence for the relationship of the carbon isotope ratios of whole diet and dietary protein to those of bone collagen and carbonate[A]. In: Grupe G, Lambert JL (Eds). Prehistoric Human Bone Archaeology at the Molecular Level[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1993: 1-13 |
| [42] | Tieszen LL, Fagre T. Effects of diet quality and composition of respiratory CO2, bone collagen, bioapatite, and soft tissues[A]. In: Grupe G, Lambert JL (Eds). Prehistoric Human Bone Archaeology at the Molecular Level[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1993: 123-135 |
| [43] | Krueger HW, Sullivan CH. Models for carbon isotope fractionation between diet and bone[J]. Acs Symposium Series, 1984, 258: 205-220 |
| [44] | Lee-Thorp JA, Sealey JC, van der Merwe NJ. Stable carbon isotope ratio differences between bone collagen and bone apatite, and their relationship to diet[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1989, 16(6): 585-599 |
| [45] | 吴晓桐, 张兴香. 关于锶同位素考古研究的几个问题[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(3): 535-550 |
| [46] | 唐自华, 王学烨, 陈相龙, 等. 凤翔雍山血池遗址北斗坊地点牛、马牙釉质的锶同位素研究[J]. 考古与文物, 2020(6): 122-125 |
| [47] | Kohn MJ, Cerling TE. Stable Isotope Compositions of Biological Apatite[J]. Phosphates: Geochemical, Geobiological, and Materials Importance, 2008, 48: 455-488 |
| [48] | Smith CI, Nielsen-Marsh CM, Jans MME, et al. The strange case of Apigliano: early ‘fossilization’ of medieval bone in southern Italy[J]. Archaeometry, 2002, 44: 405-415 |
| [49] | Hedges REM. Bone diagenesis: An overview of processes[J]. Archaeometry, 2002, 44: 319-328 |
| [50] | Nielsen-Marsh C, Hedges REM. Patterns of diagenesis in bone I: the effects of site environments[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2000, 27(12): 1139-1150 |
| [51] | Nielsen-Marsh C, Hedges REM. Patterns of diagenesis in bone II: effects of acetic acid treatment and removal of diagenetic CO32-[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2000, 27(12): 1151-1159 |
| [52] | Bartsiokas A, Middleton AP. Characterization and dating of recent and fossil bone by X-ray diffraction[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1992, 19(1): 63-72 |
| [53] | Person A, Bocherens H, Saliège JF, et al. Early diagenetic evolution of bone phosphate: an X-ray diffractometry analysis[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1995, 22(2): 211-221 |
| [54] | Krueger HW. Exchange of carbon with biological apatite[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1991, 18(3): 355-361 |
| [55] | Hoppe KA, Koch PL, Furutani TT. Assessing the preservation of biogenic strontium in fossil bones and tooth enamel[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2003, 13(1-2): 20-28 |
| [56] | Price TD, Blitz J, Burton JH, et al. Diagenesis in prehistoric bone: problems and solutions[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1992, 19(5): 513-529 |
| [57] | 胡耀武, 王昌燧, 何德亮, 等. 古代人骨羟磷灰石的去污染研究[J]. 考古, 2006(7): 68-74 |
| [58] | Lee-Thorp JA, van der Merwe NJ. Aspects of the chemistry of modern and fossil biological apatites[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1991, 18(3): 343-354 |
| [59] | Margolis HC, Kwak SY, Yamazaki H. Role of mineralization inhibitors in the regulation of hard tissue biomineralization: Relevance to initial enamel formation and maturation[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2014, 5: 1-10 |
| [60] |
Dorozhkin SV. Calcium orthophosphates: occurrence, properties, biomineralization, pathological calcification and biomimetic applications[J]. Biomatter, 2011, 1(2): 121-164
doi: 10.4161/biom.18790 pmid: 23507744 |
| [61] | Perry MA, Provan M, Tykot RH, et al. Using dental enamel to uncover the impact of childhood diet on mortality in Petra, Jordan[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 2020, 29: 1-13 |
| [62] | Koch PL, Tuross N, Fogel M. The Effects of Sample Treatment and Diagenesis on the Isotopic Integrity of Carbonate in Biogenic Hydroxylapatite[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 1997, 24(5): 417-429 |
| [63] | Kohn MJ, Cerling TE. Stable Isotope Compositions of Biological Apatite[J]. Phosphates: Geochemical, Geobiological, and Materials Importance, 2002, 48: 455-488 |
| [64] | Zazzo A, Mariotti A, Lécuyer C, et al. Heintz, Intra-tooth isotope variations in late Miocene bovid enamel from Afghanistan: Paleobiological, taphonomic, and climatic implications[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2002, 186(1-2): 145-161 |
| [65] |
Wright LE, Schwarcz HP. Stable carbon and oxygen isotopes in human tooth enamel: Identifying breastfeeding and weaning in prehistory[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 1998, 106(1): 1-18
pmid: 9590521 |
| [66] | Dabrowski P, Kulus M, Grzelak J, et al. Assessing weaning stress-Relations between enamel hypoplasia, delta δ18O and delta δ13C values in human teeth obtained from early modern cemeteries in Wroclaw, Poland[J]. Annals Of Anatomy-anatomischer Anzeiger, 2020, 232: 1-13 |
| [67] | Velasco MC, Tung TA. Shaping dietary histories: Exploring the relationship between cranial modification and childhood feeding in a high-altitude Andean population (1100-1450 CE)[J]. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 2021, 62: 1-19 |
| [68] |
Pryor AJE, Insoll T, Evis L. Laser ablation strontium isotope analysis of human remains from Harlaa and Sofi, eastern Ethiopia, and the implications for Islamisation and mobility[J]. Science and Technology of Archaeological Research, 2020, 6(1): 113-136
doi: 10.1080/20548923.2020.1843266 |
| [69] | Smith TM, Austin C, Green DR, et al. Wintertime stress, nursing, and lead exposure in Neanderthal children[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(10): 1-9 |
| [70] | Bryant JD, Froelich PN, Showers WJ, et al. A tale of two quarries: biologic and taphonomic signatures in the oxygen isotope composition of tooth enamel phosphate from modern and Miocene equids[J]. Palaios, 1996, 11(4): 397-408 |
| [71] | Wright LE. Examining childhood diets at Kaminaljuyu, Guatemala, through stable isotopic analysis of sequential enamel microsamples[J]. Archaeometry, 2013, 55(1): 113-133 |
| [72] | Roberts SB, Coward WA, Ewing G, et al. Effect of weaning on accuracy of doubly labeled water method in infants[J]. American Journal of Physiology Anthropology, 1988, 254(4): 622-627 |
| [73] | Tsutaya T, Yoneda M. Reconstruction of Breastfeeding and Weaning Practices Using Stable Isotope and Trace Element Analyses: A Review[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2015, 156: 2-21 |
| [74] | Martin JE, Vance D, Balter V. Magnesium stable isotope ecology using mammal tooth enamel[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2015, 112(2): 430-435 |
| [75] | Sponheimer M, Loudon JE, Codron D, et al. Reply to Fontes-Villalba et al.: On a reluctance to conjecture about animal food consumption[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2013, 110(43): E4056 |
| [76] | Lei S, Gu WF, Wu Q, et al. Early childhood nurturing strategies in groups of the Yellow River's middle reaches from the late Yangshao culture (3500-2800 BC): A stable isotope perspective[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2023, 33(5): 920-938 |
| [77] | Chu NC, Henderson GM, Belshaw NS, et al. Establishing the potential of Ca isotopes as proxy for consumption of dairy products[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2006, 21(10): 1656-1667 |
| [78] | Jaouen K, Villalba-Mouco V, Smith GM, et al. A Neandertal dietary conundrum: Insights provided by tooth enamel Zn isotopes from Gabasa, Spain[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2022, 119(43): 1-9 |
| [79] | Bourgon N, Jaouen K, Bacon AM, et al. Trophic ecology of a Late Pleistocene early modern human from tropical Southeast Asia inferred from zinc isotopes[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2021, 161: 1-10 |
| [80] | Jaouen K, Beasley M, Schoeninger M, et al. Zinc isotope ratios of bones and teeth as new dietary indicators: Results from a modern food web (Koobi Fora, Kenya)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 1-8 |
| [81] |
Jaouen K, Pouilloux L, Balter V, et al. Dynamic homeostasis modeling of Zn isotope ratios in the human body[J]. Metallomics, 2019, 11(6): 1049-1059
doi: 10.1039/c8mt00286j pmid: 30848262 |
| [82] | Jaouen K, Colleter R, Pietrzak A, et al. Tracing intensive fish and meat consumption using Zn isotope ratios: Evidence from a historical Breton population (Rennes, France)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 1-12 |
| [83] | Jaouen K, Szpak P, Richards MP. Zinc isotope ratios as indicators of diet and trophic level in Arctic marine mammals[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3): 1-13 |
| [84] | Costas-Rodríguez M, Van Heghe L, Vanhaecke F. Evidence for a possible dietary effect on the isotopic composition of Zn in blood via isotopic analysis of food products by multi-collector ICP-mass spectrometry[J]. Metallomics, 2014, 6(1): 139-146. |
| [85] | Jaouen K, Pons ML, Balter V. Iron, copper and zinc isotopic fractionation up mammal trophic chains[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 374: 164-172 |
| [86] | Tacail T, Thivichon-Prince B, Martin JE, et al. Assessing human weaning practices with calcium isotopes in tooth enamel[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2017, 114(24): 6268-6273 |
| [87] | Li Q, Nava A, Reynard LM, et al. Spatially-Resolved Ca Isotopic and Trace Element Variations in Human Deciduous Teeth Record Diet and Physiological Change[J]. Environmental Archaeology, 2022, 27(5): 474-483 |
| [88] | Martin JE, Vance D, Balter V, et al. Natural variation of magnesium isotopes in mammal bones and teeth from two South African trophic chains[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 130: 12-20 |
| [89] |
Ungar PS, Sponheimer M. The diets of early hominins[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6053): 190-193
doi: 10.1126/science.1207701 pmid: 21998380 |
| [90] | Cerling TE, Mbua E, Kirera FM. Diet of Paranthropus boisei in the early Pleistocene of East Africa[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 2011, 108(23): 9337-9341 |
| [91] |
Balter V, Martin JE, Tacail T, et al. Calcium stable isotopes place Devonian conodonts as first level consumers[J]. Geochemical Perspectives Letters, 2019, 10: 36-39
doi: 10.7185/geochemlet.1912 |
| [92] |
Cloquet C, Carignan J, Lehmann MF, et al. Variation in the isotopic composition of zinc in the natural environment and the use of zinc isotopes in biogeosciences: a review[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2008, 390(2): 451-463
pmid: 17952419 |
| [93] |
Podlesak DW, Bowen GJ, O’Grady S, et al. Delta δ2H and delta δ18O of human body water: a GIS model to distinguish residents from non-residents in the contiguous USA[J]. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 2012, 48(2): 259-279
doi: 10.1080/10256016.2012.644283 pmid: 22397457 |
| [94] | Ugan A, Neme G, Gil A, et al. Geographic variation in bone carbonate and water delta δ18O values in Mendoza, Argentina and their relationship to prehistoric economy and settlement[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2012, 39(8): 2752-2763 |
| [95] | Gil A, Neme G, Ugan A, et al. Oxygen isotopes and human residential mobility in central western Argentina[J]. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 2014, 24(1): 31-41 |
| [96] | 李大伟, 王伟, 廖卫. 广西更新世早期么会洞遗址动物牙釉质的C、O稳定同位素分析——试析华南地区直立人的生存环境[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 42(4): 212-222 |
| [97] |
Pollard AM, Pellegrini M, Lee-Thorp JA. Technical Note: Some Observations on the Conversion of Dental Enamel delta δ18OpValues to delta δ18Ow to Determine Human Mobility[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2011, 145(3): 499-504
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21524 pmid: 21541927 |
| [98] | Terzer S, Wassenaar LI, Araguás-Araguás LJ, et al. Global isoscapes for delta δ18O and delta δ2H in precipitation: improved prediction using regionalized climatic regression models[J]. Hydrology And Earth System Sciences, 2013, 17(11): 4713-4728 |
| [99] | West AG, February EC, Bowen GJ. Spatial analysis of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes ("isoscapes") in ground water and tap water across South Africa[J]. Journal Of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 145: 213-222 |
| [100] | 董宁宁. 动物牙釉质氧同位素分析:一种季节性研究的新方法[J]. 江汉考古, 2016(2): 53-61 |
| [101] | Longinelli A. Oxygen isotopes in mammal bone phosphate: A new tool for paleohydrological and paleoclimatological research?[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(2): 385-390 |
| [102] | Levinson AA, Luz B, Kolodny Y. Variations in oxygen isotopic compositions of human teeth and urinary stones[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1987, 2(4): 367-371 |
| [103] | Keller AT, Regan LA, Lundstrom CC, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of spatiotemporal Pb isoscapes for provenancing of human remains[J]. Forensic Science International-Genetics, 2016, 261: 83-92 |
| [104] |
Warner MM, Plemons AM, Herrmann NP, et al. Refining Stable Oxygen and Hydrogen Isoscapes for the Identification of Human Remains in Mississippi[J]. Journal Of Forensic Sciences, 2018, 63(2): 395-402
doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.13575 pmid: 28664651 |
| [105] | Bowen GJ, Wilkinson B. Spatial distribution of δ18O in meteoric precipitation[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(4): 315-318 |
| [106] | Bowen GJ, Revenaugh J. Interpolating the isotopic composition of modern meteoric precipitation[J]. Water Resources Research, 2003, 30(4): 315-318 |
| [107] | Zhao SH, Hu HC, Tian FQ, et al. Divergence of stable isotopes in tap water across China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 1-14 |
| [108] | Chesson LA, Tipple BJ, Mackey GN, et al. Strontium isotopes in tap water from the coterminous USA[J]. Ecosphere, 2012, 3(7): 1-17 |
| [109] |
Ammer STM, Bartelink EJ, Vollner JM, et al. Spatial Distributions of Oxygen Stable Isotope Ratios in Tap Water From Mexico for Region of Origin Predictions of Unidentified Border Crossers[J]. Journal Of Forensic Sciences, 2020, 65(4): 1049-1055
doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.14283 pmid: 31999362 |
| [110] | Daux V, Minster B, Cauquoin A, et al. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic composition of tap waters in France[J]. Geological Society Special Publication, 2021, 507(1): 47-61 |
| [111] | Gautam MK, Song BY, Shin WJ, et al. Spatial variations in oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in waters and human hair across South Korea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 726: 1-12 |
| [112] |
Reitsema LJ, Crews DE. Brief communication: oxygen isotopes as a biomarker for sickle-cell disease? Results from transgenic mice expressing human hemoglobin S genes[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2011, 145(3): 495-498
doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21513 pmid: 21541922 |
| [113] | Warinner C, Tuross N. Alkaline Cooking and Stable Isotope Tissue-diet Spacing in Swine: Archaeological Implications[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2009, 36(8): 1690-1697 |
| [114] | Brettell R, Montgomery J, Evans J. Brewing and Stewing: The Effect of Culturally Mediated Behavior on the Oxygen Isotope Composition of Ingested Fluids and the Implications for Human Provenance Studies[J]. Journal Of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2012, 27(5): 778-785 |
| [115] | Kennedy BP, Folt CL, Blum JD, et al. Natural isotope markers in salmon[J]. Nature, 1997, 387(6635): 766-767 |
| [116] | Beard BL, Johnson CM. Strontium isotope compositions of skeletal material can determine the birth place and geographic mobility of animals and humans[J]. Journal of Forensic Science, 2000, 45(5): 1049-1061 |
| [117] | Slovak NM, Paytan A. Applications of Sr Isotopes in Archaeology[A]. In: Baskaran M (Ed.). Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 743-768 |
| [118] | Wang XY, Tang ZX, Dong XX. Distribution of strontium isotopes in river waters across the Tarim Basin: a map for migration studies[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2018, 175(6): 967-973 |
| [119] | Budd P, Montgomery J, Barreiro B, et al. Differential diagenesis of strontium in archaeological human dental tissues[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(5): 687-694 |
| [120] | Kusaka S, Nakano T, Yumoto T, et al. Strontium isotope evidence of migration and diet in relation to ritual tooth ablation: A case study from the Inariyama Jomon site, Japan[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2011, 38(1): 166-174 |
| [121] | Giblin J, Knudson K, Bereczki Z, et al. Strontium isotope analysis and human mobility during the Neolithic and Copper Age: a case study from the Great Hungarian Plain[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2013, 40(1): 227-239 |
| [122] | 丛德新, 赵春燕, 贾伟明. 新疆阿敦乔鲁遗址人类迁移行为与食物结构的初步研究[J]. 江汉考古, 2021(6): 233-239 |
| [123] | Laffoon JE, Shuler KA, Millard AR, et al. Isotopic evidence for anthropogenic lead exposure on a 17th/18th century Barbadian plantation[J]. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2019, 171(3): 529-538 |
| [124] | Evans JA, Pashley V, Mee K, et al. Applying lead (Pb) isotopes to explore mobility in humans and animals[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(10): 1-17 |
| [125] | Munkittrick TJA, Varney TL, Grimes V. The use and abuse of Pb in bioarchaeological studies: A review of Pb concentration and isotope analyses of teeth[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2023, 156: 1-14 |
| [126] | Montgomery J, Budd P, Evans J. Reconstructing the lifetime movements of ancient people: A Neolithic case study from southern England[J]. European Journal of Archaeology, 2000, 3(3): 370-385 |
| [127] |
Gulson BL, Mizon KJ, Korsch MJ, et al. Mobilization of lead from human bone tissue during pregnancy and lactation-a summary of longterm research[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2003, 303(1-2): 79-104
pmid: 12568766 |
| [128] | Ishida LY, de Faria RA, Barros FS, et al. Isotope Analysis in Human Teeth as a Tool for Forensic Identification and Georeferencing[J]. XXVI Brazilian Congress on Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 70(2): 699-705 |
| [129] | Evans JA, Pashley V, Chenery CA, et al. Lead isotope analysis of tooth enamel from a Viking age mass grave in southern Britain and the constraints in places on the origin of the individuals[J]. Archaeometry, 2018, 60(4): 859-869 |
| [130] | Kamenov GD, Logaro EM, Goad G, et al. Trace elements in modern and archaeological human teeth: implications for human metal exposure and enamel diagenetic changes[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2018, 99: 27-34 |
| [131] |
Shepherd TJ, Dirks W, Roberts NMW, et al. Tracing fetal and childhood exposure to lead using isotope analysis of deciduous teeth[J]. Environmental Research, 2016, 146: 145-153
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2015.12.017 pmid: 26752082 |
| [132] | Boethius A, Kjällquist M, Kielman-Schmitt M, et al. Early Holocene Scandinavian foragers on a journey to affluence: Mesolithic fish exploitation, seasonal abundance and storage investigated through strontium isotope ratios by laser ablation (LA-MC-ICP-MS)[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(1): 1-29 |
| [133] | Boethius A, Ahlström T, Kielman-Schmitt M, et al. Assessing laser ablation multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry as a tool to study archaeological and modern human mobility through strontium isotope analyses of tooth enamel[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2022, 14(5): 1-28 |
| [134] | 赵春燕, 王明辉, 叶茂林. 青海喇家遗址人类遗骸的锶同位素比值分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2016, 35(2): 212-222 |
| [135] |
Kohn MJ. You are what you eat[J]. Science, 1999, 283(5400): 335-336
pmid: 9925492 |
| [136] |
Reitsema LJ. Beyond Diet Reconstruction: Stable Isotope Applications to Human Physiology, Health, and Nutrition[J]. American Journal of Human Biology, 2013, 25(4): 445-456
doi: 10.1002/ajhb.22398 pmid: 23784719 |
| [137] | Fuller BT, Fuller JL, Sage NE, et al. Nitrogen balance and δ15N: why you’re not what you eat during pregnancy[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2004, 18(23): 2889-2896 |
| [138] | Kuo TC, Wang CH, Lin HC, et al. Assessment of renal function by the stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in human blood plasma[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(2): 1-9 |
| [139] | Li Q, Thirlwall M, Müller W. Ca Isotopic Analysis of Laser-Cut Microsamples of (Bio) Apatite Without Chemical Purification[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 422: 1-12 |
| [140] | Coudray C, Feillet-Coudray C, Rambeau M, et al. Stable isotopes in studies of intestinal absorption, exchangeable pools and mineral status: the exampleof magnesium[J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2005, 19(1): 97-103 |
| [141] | Richards MP, Montgomery J. Isotope analysis and paleopathology:a short review and future developments[A]. In: Buikstra J, Roberts C (Eds). The Global History of Paleopathology: Pioneers and Prospects[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2012: 718-731 |
| [142] | 胡耀武. 稳定同位素生物考古学的概念、简史、原理和目标[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(3): 526-534 |
| [1] | 马姣, 付永旭, 陈相龙, 武仙竹, 胡耀武. 贵州牛坡洞遗址动物骨骼的碳氮稳定同位素变化[J]. 人类学学报, 2025, 44(04): 688-700. |
| [2] | 朱语桐, 张国文, 郑万泉, 张燕. 四川宁南钟家梁子遗址人骨的稳定同位素[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 767-779. |
| [3] | 黄嫣, 胡耀武. 陶器脂肪酸揭示古人类食谱的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(05): 865-880. |
| [4] | 周立刚, 曹艳朋, 楚小龙, 孙蕾. 河南淅川下寨遗址人骨的C和N稳定同位素[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 405-414. |
| [5] | 赵文杰, 贾真秀, 李三灵, 李浩. 2020年江西高安上湖旧石器遗址发掘报告[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 373-380. |
| [6] | 雷帅, 郭怡. 生物考古学视野下人类的牙齿与饮食[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(03): 501-513. |
| [7] | 吴晓桐, 张兴香. 关于锶同位素考古研究的几个问题[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(03): 535-550. |
| [8] | 张全超, 孙语泽, 侯亮亮, 吉平, 朱永刚. 哈民忙哈遗址人和动物骨骼的C、N稳定同位素分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 261-273. |
| [9] | 赵东月, 吕正, 张泽涛, 刘波, 凌雪, 万杨, 杨帆. 通过稳定同位素分析云南大阴洞遗址先民的生业经济方式[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(02): 295-307. |
| [10] | 王宁, 桑哲成, 刘效彬, 吴倩. 商代前期中原地区多品种农作物种植制度的初探:以河南新郑望京楼遗址为例[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(01): 96-107. |
| [11] | 刘晓迪, 魏东, 王婷婷, 张昕煜, 胡耀武. 内蒙古东南部战国时期的农业经济及人群融合[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(05): 764-775. |
| [12] | 何欣龙, 梅宏成, 王继芬, 朱军, 郭鹏然, 胡灿, 何亚, 龚晓晓, 胡展纶. 新疆和田、哈密和阿勒泰市居民指甲中氢、氧稳定同位素的比较[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(05): 888-894. |
| [13] | 徐哲, 马姣, 裴树文. 哺乳动物牙釉质碳氧稳定同位素揭示早期人类演化与环境关系[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(03): 454-468. |
| [14] | 胡耀武. 稳定同位素生物考古学的概念、简史、原理和目标[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(03): 526-534. |
| [15] | 周立刚, 韩朝会, 孙蕾, 呼国强. 河南淇县宋庄东周墓地人骨稳定同位素分析——东周贵族与殉人食谱初探[J]. 人类学学报, 2021, 40(01): 63-74. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3