

主管:中国科学院
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社
主办:中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所
出版:科学出版社


人类学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (06): 1028-1036.doi: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0038cstr: 32091.14.j.1000-3193/AAS.2022.0038
刘鑫1( ), 张兴华1(
), 张兴华1( ), 宇克莉1, 刘艳霞1, 包金萍2, 郑连斌1
), 宇克莉1, 刘艳霞1, 包金萍2, 郑连斌1
收稿日期:2021-08-12
修回日期:2022-03-14
出版日期:2022-12-15
发布日期:2022-12-19
通讯作者:
张兴华
作者简介:刘鑫,硕士研究生,主要从事体质人类学研究。E-mail: 基金资助:
LIU Xin1( ), ZHANG Xinghua1(
), ZHANG Xinghua1( ), YU Keli1, LIU Yanxia1, BAO Jinping2, ZHENG Lianbin1
), YU Keli1, LIU Yanxia1, BAO Jinping2, ZHENG Lianbin1
Received:2021-08-12
Revised:2022-03-14
Online:2022-12-15
Published:2022-12-19
Contact:
ZHANG Xinghua
摘要:
本文利用生物电阻抗法对广西京族的体成分进行了测定,初步分析了其体成分形成的原因。研究组于2020年12月在广西壮族自治区东兴市“京族三岛”测定了430例京族成人(男182例,女248例)的16项指标。结果表明,京族男、女性的体质量、总肌肉量、躯干肌肉量、推定骨量、总能量代谢与年龄呈显著负相关。体成分随年龄增长而发生的变化,主要是自然的生理变化和劳动强度下降所致。随着年龄增长,男性的体脂率升高,这主要是躯干脂肪增多造成的。京族男性的体质量、总肌肉量、推定骨量、总能量代谢、水分率、四肢和躯干肌肉量均大于女性,而体脂率、四肢和躯干脂肪率均小于女性。京族男性比女性拥有更大的体质量和更高比例的骨骼肌,这两方面因素再加上劳动强度的差异,可能导致男性肌肉量、骨量、脂肪率等体成分与女性存在差异。总体来看,京族成人身体偏胖,脂肪含量较高,身体含水量基本正常,体成分特征与同为南亚语系或同在沿海地区的其他中国族群并不相似,而相对更接近于中国蒙古族,并且表现在体质量、体脂率、水分率等方面接近。生活环境、社会经济、日常饮食和劳动强度等因素是导致京族成人体质量及体脂率较高的原因。
中图分类号:
刘鑫, 张兴华, 宇克莉, 刘艳霞, 包金萍, 郑连斌. 生物电阻抗法测定广西京族的体成分[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1028-1036.
LIU Xin, ZHANG Xinghua, YU Keli, LIU Yanxia, BAO Jinping, ZHENG Lianbin. Determination of body composition of the Jing in Guangxi using bioelectrical impedance analysis[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022, 41(06): 1028-1036.
| 指标Indicator | 18-44 a | 45-59 a | ≥60 a | 合计Total | F | 比较Com | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数n | 37 | 47 | 98 | 182 | |||
| 体质量m/kg | 67.1±11.6 | 67.4±11.2 | 64.6±10.2 | 65.8±10.8 | 1.352 | -0.209** | |
| 体脂率pfat/% | 21.7%±5.6% | 23.0%±5.9% | 25.1%±5.7% | 23.9%±5.9% | 5.255** | b | 0.192** |
| 总肌肉量mmus/kg | 49.3±5.8 | 48.7±5.3 | 45.5±5.5 | 47.1±5.7 | 9.126** | b, c | -0.393** |
| 推定骨量mbon/kg | 2.7±0.3 | 2.7±0.3 | 2.5±0.3 | 2.6±0.3 | 7.290** | b, c | -0.374** |
| 总能量代谢Mene/kcal | 2632.3±490.5 | 2524.0±397.5 | 2147.8±400.9 | 2343.4±469.5 | 23.767** | b, c | -0.560** |
| 水分率pwat/% | 52.3%±4.6% | 52.9%±5.1% | 53.1%±5.1% | 52.9%±5.0% | 0.395 | 0.091 | |
| 右上肢脂肪率pR-up-fat/% | 15.5%±4.6% | 15.8%±4.5% | 16.9%±5.7% | 16.4%±5.2% | 1.300 | 0.073 | |
| 右上肢肌肉量mR-up-lim-mus/kg | 2.6±0.5 | 2.7±0.4 | 2.5±0.7 | 2.6±0.6 | 1.100 | -0.182* | |
| 左上肢脂肪率pL-up-fat/% | 16.3%±4.5% | 16.7%±4.6% | 17.6%±5.9% | 17.1%±5.3% | 0.932 | 0.022 | |
| 左上肢肌肉量mL-up-lim-mus/kg | 2.5±0.4 | 2.5±0.4 | 2.4±0.6 | 2.5±0.5 | 0.801 | -0.097 | |
| 右下肢脂肪率pR-lo-fat/% | 22.3%±4.4% | 22.8%±4.7% | 22.2%±6.0% | 22.4%±5.4% | 0.211 | -0.105 | |
| 右下肢肌肉量mR-lo-lim-mus/kg | 8.4±1.3 | 8.6±1.4 | 8.5±1.4 | 8.5±1.4 | 0.067 | -0.062 | |
| 左下肢脂肪率pL-lo-fat/% | 22.1%±4.3% | 22.7%±4.5% | 21.5%±6.3% | 21.9%±5.5% | 0.671 | -0.151* | |
| 左下肢肌肉量mL-lo-lim-mus/kg | 8.4±1.3 | 8.5±1.3 | 8.6±1.3 | 8.5±1.3 | 0.151 | -0.021 | |
| 躯干脂肪率ptru-fat/% | 22.5%±6.6% | 24.4%±7.3% | 28.9%±6.8% | 26.4%±7.4% | 14.239** | b, c | 0.352** |
| 躯干肌肉量mtru-mus/kg | 27.2±2.9 | 26.4±2.2 | 23.4±2.6 | 24.9±3.1 | 39.874** | b, c | -0.644** |
表1 京族成年男性体质量和体成分指标的测量结果、年龄组间比较以及与年龄的相关性分析
Tab.1 Measurement comparison of age groups with correlated analysis with age of mass and body composition indicators in Jing adult males
| 指标Indicator | 18-44 a | 45-59 a | ≥60 a | 合计Total | F | 比较Com | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数n | 37 | 47 | 98 | 182 | |||
| 体质量m/kg | 67.1±11.6 | 67.4±11.2 | 64.6±10.2 | 65.8±10.8 | 1.352 | -0.209** | |
| 体脂率pfat/% | 21.7%±5.6% | 23.0%±5.9% | 25.1%±5.7% | 23.9%±5.9% | 5.255** | b | 0.192** |
| 总肌肉量mmus/kg | 49.3±5.8 | 48.7±5.3 | 45.5±5.5 | 47.1±5.7 | 9.126** | b, c | -0.393** |
| 推定骨量mbon/kg | 2.7±0.3 | 2.7±0.3 | 2.5±0.3 | 2.6±0.3 | 7.290** | b, c | -0.374** |
| 总能量代谢Mene/kcal | 2632.3±490.5 | 2524.0±397.5 | 2147.8±400.9 | 2343.4±469.5 | 23.767** | b, c | -0.560** |
| 水分率pwat/% | 52.3%±4.6% | 52.9%±5.1% | 53.1%±5.1% | 52.9%±5.0% | 0.395 | 0.091 | |
| 右上肢脂肪率pR-up-fat/% | 15.5%±4.6% | 15.8%±4.5% | 16.9%±5.7% | 16.4%±5.2% | 1.300 | 0.073 | |
| 右上肢肌肉量mR-up-lim-mus/kg | 2.6±0.5 | 2.7±0.4 | 2.5±0.7 | 2.6±0.6 | 1.100 | -0.182* | |
| 左上肢脂肪率pL-up-fat/% | 16.3%±4.5% | 16.7%±4.6% | 17.6%±5.9% | 17.1%±5.3% | 0.932 | 0.022 | |
| 左上肢肌肉量mL-up-lim-mus/kg | 2.5±0.4 | 2.5±0.4 | 2.4±0.6 | 2.5±0.5 | 0.801 | -0.097 | |
| 右下肢脂肪率pR-lo-fat/% | 22.3%±4.4% | 22.8%±4.7% | 22.2%±6.0% | 22.4%±5.4% | 0.211 | -0.105 | |
| 右下肢肌肉量mR-lo-lim-mus/kg | 8.4±1.3 | 8.6±1.4 | 8.5±1.4 | 8.5±1.4 | 0.067 | -0.062 | |
| 左下肢脂肪率pL-lo-fat/% | 22.1%±4.3% | 22.7%±4.5% | 21.5%±6.3% | 21.9%±5.5% | 0.671 | -0.151* | |
| 左下肢肌肉量mL-lo-lim-mus/kg | 8.4±1.3 | 8.5±1.3 | 8.6±1.3 | 8.5±1.3 | 0.151 | -0.021 | |
| 躯干脂肪率ptru-fat/% | 22.5%±6.6% | 24.4%±7.3% | 28.9%±6.8% | 26.4%±7.4% | 14.239** | b, c | 0.352** |
| 躯干肌肉量mtru-mus/kg | 27.2±2.9 | 26.4±2.2 | 23.4±2.6 | 24.9±3.1 | 39.874** | b, c | -0.644** |
| 指标Indicator | 18-44 a | 45-59 a | ≥60 a | 合计Total | F | 比较Com | r | u |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数n | 31 | 90 | 127 | 248 | ||||
| 体质量m/kg | 58.3±9.3 | 61.0±8.3 | 55.1±8.5 | 57.7±8.8 | 12.410** | c | -0.248** | 8.30** |
| 体脂率pfat/% | 34.8%±5.1% | 37.5%±5.9% | 36.4%±6.2% | 36.6%±6.2% | 2.414 | 0.049 | 21.58** | |
| 总肌肉量mmus/kg | 35.5±3.6 | 35.7±3.4 | 32.7±3.1 | 34.1±3.5 | 24.130** | b, c | -0.386** | 27.23** |
| 推定骨量mbon/kg | 2.1±0.3 | 2.1±0.2 | 1.9±0.3 | 2.0±0.3 | 28.558** | b, c | -0.420** | 20.49** |
| 总能量代谢Mene/kcal | 1949.2±314.0 | 2003.8±236.2 | 1663.8±285.3 | 1822.9±316.0 | 47.258** | b, c | -0.509** | 12.96** |
| 水分率pwat/% | 45.6%±2.8% | 45.9%±3.9% | 47.3%±4.3% | 46.6%±4.3% | 4.892** | b, c | 0.171** | 13.69** |
| 右上肢脂肪率pR-up-fat/% | 30.7%±6.4% | 33.5%±7.3% | 31.6%±7.0% | 32.2%±7.2% | 2.806 | -0.038 | 26.42** | |
| 右上肢肌肉量mR-up-lim-mus/kg | 1.7±0.3 | 1.8±0.3 | 1.6±0.3 | 1.7±0.3 | 7.899** | c | -0.166** | 18.60** |
| 左上肢脂肪率pL-up-fat/% | 31.8%±6.3% | 35.0%±6.8% | 32.0%±7.3% | 33.1%±7.3% | 5.326** | a, c | -0.112 | 26.33** |
| 左上肢肌肉量mL-up-lim-mus/kg | 1.6±0.3 | 1.7±0.4 | 1.6±0.4 | 1.6±0.3 | 4.144* | c | -0.050 | 21.60** |
| 右下肢脂肪率pR-lo-fat/% | 36.1%±3.8% | 37.9%±4.2% | 36.2%±4.8% | 36.8%±4.8% | 4.438* | c | -0.071 | 28.62** |
| 右下肢肌肉量mR-lo-lim-mus/kg | 5.8±0.6 | 6.1±0.7 | 5.8±0.7 | 5.9±0.7 | 4.504* | c | -0.128* | 23.03** |
| 左下肢脂肪率pL-lo-fat/% | 35.7%±4.1% | 37.7%±3.8% | 36.4%±3.9% | 36.8%±3.9% | 4.177* | a | -0.033 | 31.24** |
| 左下肢肌肉量mL-lo-lim-mus/kg | 5.7±0.6 | 6.1±1.0 | 5.7±0.7 | 5.8±0.9 | 9.014** | a, c | -0.127* | 24.10** |
| 躯干脂肪率ptru-fat/% | 34.6%±6.0% | 38.0%±7.3% | 37.3%±7.6% | 37.2%±7.6% | 2.545 | 0.085 | 14.78** | |
| 躯干肌肉量mtru-mus/kg | 20.8±2.2 | 20.0±2.0 | 18.1±2.1 | 19.1±2.2 | 32.475** | b, c | -0.502** | 21.57** |
表2 京族成年女性体质量和体成分指标的测量结果、年龄组间比较以及与年龄的相关性分析
Tab.2 Measurement comparison of age groups with age of mass and body composition indicators in Jing adult females
| 指标Indicator | 18-44 a | 45-59 a | ≥60 a | 合计Total | F | 比较Com | r | u |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数n | 31 | 90 | 127 | 248 | ||||
| 体质量m/kg | 58.3±9.3 | 61.0±8.3 | 55.1±8.5 | 57.7±8.8 | 12.410** | c | -0.248** | 8.30** |
| 体脂率pfat/% | 34.8%±5.1% | 37.5%±5.9% | 36.4%±6.2% | 36.6%±6.2% | 2.414 | 0.049 | 21.58** | |
| 总肌肉量mmus/kg | 35.5±3.6 | 35.7±3.4 | 32.7±3.1 | 34.1±3.5 | 24.130** | b, c | -0.386** | 27.23** |
| 推定骨量mbon/kg | 2.1±0.3 | 2.1±0.2 | 1.9±0.3 | 2.0±0.3 | 28.558** | b, c | -0.420** | 20.49** |
| 总能量代谢Mene/kcal | 1949.2±314.0 | 2003.8±236.2 | 1663.8±285.3 | 1822.9±316.0 | 47.258** | b, c | -0.509** | 12.96** |
| 水分率pwat/% | 45.6%±2.8% | 45.9%±3.9% | 47.3%±4.3% | 46.6%±4.3% | 4.892** | b, c | 0.171** | 13.69** |
| 右上肢脂肪率pR-up-fat/% | 30.7%±6.4% | 33.5%±7.3% | 31.6%±7.0% | 32.2%±7.2% | 2.806 | -0.038 | 26.42** | |
| 右上肢肌肉量mR-up-lim-mus/kg | 1.7±0.3 | 1.8±0.3 | 1.6±0.3 | 1.7±0.3 | 7.899** | c | -0.166** | 18.60** |
| 左上肢脂肪率pL-up-fat/% | 31.8%±6.3% | 35.0%±6.8% | 32.0%±7.3% | 33.1%±7.3% | 5.326** | a, c | -0.112 | 26.33** |
| 左上肢肌肉量mL-up-lim-mus/kg | 1.6±0.3 | 1.7±0.4 | 1.6±0.4 | 1.6±0.3 | 4.144* | c | -0.050 | 21.60** |
| 右下肢脂肪率pR-lo-fat/% | 36.1%±3.8% | 37.9%±4.2% | 36.2%±4.8% | 36.8%±4.8% | 4.438* | c | -0.071 | 28.62** |
| 右下肢肌肉量mR-lo-lim-mus/kg | 5.8±0.6 | 6.1±0.7 | 5.8±0.7 | 5.9±0.7 | 4.504* | c | -0.128* | 23.03** |
| 左下肢脂肪率pL-lo-fat/% | 35.7%±4.1% | 37.7%±3.8% | 36.4%±3.9% | 36.8%±3.9% | 4.177* | a | -0.033 | 31.24** |
| 左下肢肌肉量mL-lo-lim-mus/kg | 5.7±0.6 | 6.1±1.0 | 5.7±0.7 | 5.8±0.9 | 9.014** | a, c | -0.127* | 24.10** |
| 躯干脂肪率ptru-fat/% | 34.6%±6.0% | 38.0%±7.3% | 37.3%±7.6% | 37.2%±7.6% | 2.545 | 0.085 | 14.78** | |
| 躯干肌肉量mtru-mus/kg | 20.8±2.2 | 20.0±2.0 | 18.1±2.1 | 19.1±2.2 | 32.475** | b, c | -0.502** | 21.57** |
| 族群 Ethnic group | 男性Male | 女性Female | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数 n | 体质量m/kg | 体脂率pfat/% | 总肌肉量mmus/kg | 推定骨量mbon/kg | 总能量 代谢 Mene/kcal | 水分率pwat/% | 例数n | 体质量m/kg | 体脂率pfat/% | 总肌肉量mmus/kg | 推定骨量mbon/kg | 总能量 代谢 Mene/kcal | 水分率pwat/% | |
| 京族Jing | 182 | 65.8 | 23.9% | 47.1 | 2.6 | 2343.4 | 52.9% | 248 | 57.7 | 36.6% | 34.1 | 2.0 | 1822.9 | 46.6% |
| 佤族Va | 239 | 60.9 | 19.6% | 46.3 | 2.6 | 2024.1 | 55.5% | 324 | 54.8 | 33.3% | 34.1 | 2.0 | 1625.8 | 48.5% |
| 布朗族Blang | 248 | 58.6 | 19.5% | 44.3 | 2.5 | 1953.8 | 56.0% | 356 | 52.8 | 33.8% | 32.9 | 1.9 | 1544.1 | 48.6% |
| 黎族Li | 308 | 60.5 | 19.5% | 45.8 | 2.6 | 2049.8 | 55.0% | 299 | 52.9 | 31.2% | 34.0 | 2.0 | 1636.0 | 49.3% |
| 临高人 Lingao | 211 | 61.7 | 20.3% | 46.3 | 2.6 | 2037.0 | 54.6% | 204 | 54.5 | 32.8% | 34.4 | 2.1 | 1634.8 | 48.2% |
| 羌族Qiang | 299 | 66.5 | 22.5% | 49.0 | 2.7 | 2152.8 | 53.3% | 303 | 59.7 | 36.4% | 36.0 | 2.2 | 1741.3 | 46.5% |
| 基诺族Jino | 279 | 60.3 | 20.7% | 49.8 | 2.5 | 1962.9 | 55.2% | 321 | 52.8 | 33.4% | 33.0 | 1.9 | 1565.3 | 49.5% |
| 纳西族Naxi | 275 | 68.4 | 21.6% | 50.2 | 2.8 | 2230.9 | 54.8% | 301 | 57.2 | 33.0% | 35.8 | 2.2 | 1705.6 | 48.5% |
| 普米族Pumi | 216 | 66.0 | 19.3% | 50.2 | 2.8 | 2198.0 | 56.2% | 327 | 57.1 | 31.6% | 36.6 | 2.2 | 1736.4 | 49.3% |
| 桂林瑶族 Yao(Guilin) | 259 | 57.0 | 19.8% | 42.9 | 2.4 | 2145.4 | 55.8% | 278 | 50.6 | 30.2% | 31.9 | 2.0 | 1716.3 | 50.1% |
| 来宾瑶族 Yao(Laibin) | 275 | 59.9 | 22.3% | 43.4 | 2.4 | 2225.0 | 53.4% | 383 | 53.2 | 34.4% | 32.6 | 1.9 | 1799.0 | 48.0% |
| 蒙古族 Mongol | 1916 | 72.6 | 24.3% | 51.9 | 2.9 | 2442.1 | 52.7% | 2493 | 62.8 | 36.8% | 37.0 | 2.3 | 1872.5 | 46.7% |
表3 京族与中国其他11个族群成人体质量和体成分指标的均数
Tab.3 Means of mass and body composition indicators in Jing and 11 other ethnic groups in China
| 族群 Ethnic group | 男性Male | 女性Female | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数 n | 体质量m/kg | 体脂率pfat/% | 总肌肉量mmus/kg | 推定骨量mbon/kg | 总能量 代谢 Mene/kcal | 水分率pwat/% | 例数n | 体质量m/kg | 体脂率pfat/% | 总肌肉量mmus/kg | 推定骨量mbon/kg | 总能量 代谢 Mene/kcal | 水分率pwat/% | |
| 京族Jing | 182 | 65.8 | 23.9% | 47.1 | 2.6 | 2343.4 | 52.9% | 248 | 57.7 | 36.6% | 34.1 | 2.0 | 1822.9 | 46.6% |
| 佤族Va | 239 | 60.9 | 19.6% | 46.3 | 2.6 | 2024.1 | 55.5% | 324 | 54.8 | 33.3% | 34.1 | 2.0 | 1625.8 | 48.5% |
| 布朗族Blang | 248 | 58.6 | 19.5% | 44.3 | 2.5 | 1953.8 | 56.0% | 356 | 52.8 | 33.8% | 32.9 | 1.9 | 1544.1 | 48.6% |
| 黎族Li | 308 | 60.5 | 19.5% | 45.8 | 2.6 | 2049.8 | 55.0% | 299 | 52.9 | 31.2% | 34.0 | 2.0 | 1636.0 | 49.3% |
| 临高人 Lingao | 211 | 61.7 | 20.3% | 46.3 | 2.6 | 2037.0 | 54.6% | 204 | 54.5 | 32.8% | 34.4 | 2.1 | 1634.8 | 48.2% |
| 羌族Qiang | 299 | 66.5 | 22.5% | 49.0 | 2.7 | 2152.8 | 53.3% | 303 | 59.7 | 36.4% | 36.0 | 2.2 | 1741.3 | 46.5% |
| 基诺族Jino | 279 | 60.3 | 20.7% | 49.8 | 2.5 | 1962.9 | 55.2% | 321 | 52.8 | 33.4% | 33.0 | 1.9 | 1565.3 | 49.5% |
| 纳西族Naxi | 275 | 68.4 | 21.6% | 50.2 | 2.8 | 2230.9 | 54.8% | 301 | 57.2 | 33.0% | 35.8 | 2.2 | 1705.6 | 48.5% |
| 普米族Pumi | 216 | 66.0 | 19.3% | 50.2 | 2.8 | 2198.0 | 56.2% | 327 | 57.1 | 31.6% | 36.6 | 2.2 | 1736.4 | 49.3% |
| 桂林瑶族 Yao(Guilin) | 259 | 57.0 | 19.8% | 42.9 | 2.4 | 2145.4 | 55.8% | 278 | 50.6 | 30.2% | 31.9 | 2.0 | 1716.3 | 50.1% |
| 来宾瑶族 Yao(Laibin) | 275 | 59.9 | 22.3% | 43.4 | 2.4 | 2225.0 | 53.4% | 383 | 53.2 | 34.4% | 32.6 | 1.9 | 1799.0 | 48.0% |
| 蒙古族 Mongol | 1916 | 72.6 | 24.3% | 51.9 | 2.9 | 2442.1 | 52.7% | 2493 | 62.8 | 36.8% | 37.0 | 2.3 | 1872.5 | 46.7% |
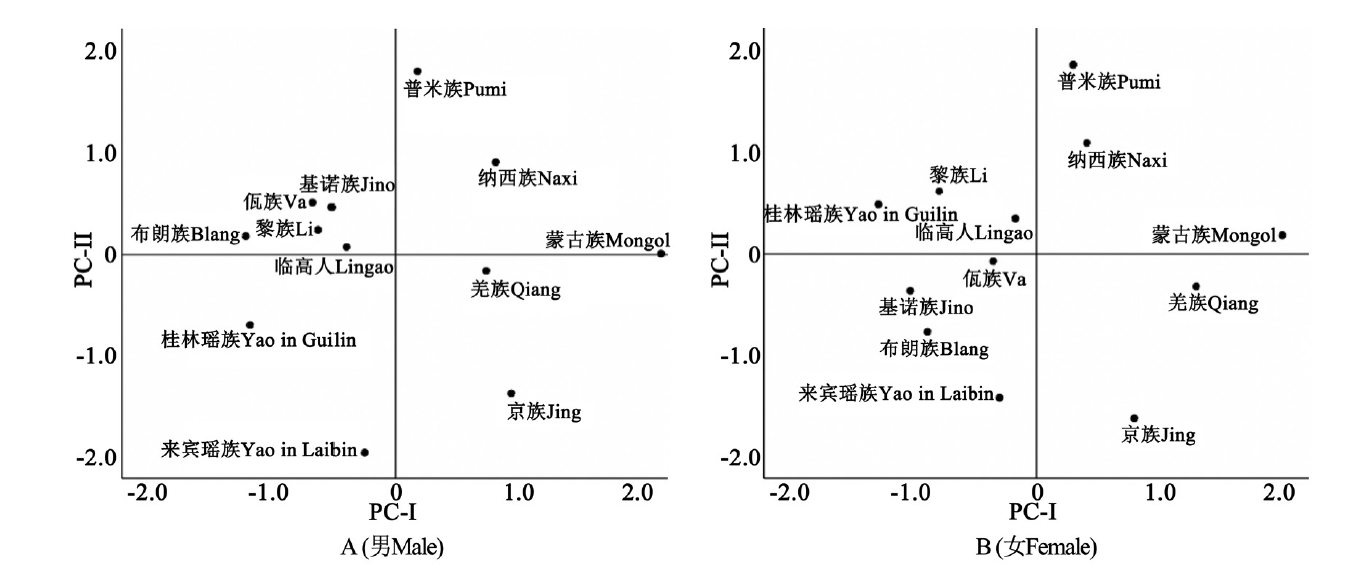
图1 京族与中国其他11个族群成人体质量和体成分指标的主成分分析
Fig.1 Principal component analysis of mass and body composition indicators of Jing and 11 other ethnic groups in China
| [1] | 颜其香, 周植志. 中国孟高棉语族语言与南亚语系[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2012 |
| [2] | 陈云. 京族海洋文化展现及其时代价值[J]. 今古文创, 2021(18): 105-106 |
| [3] | 邴强, 王健. 人体体成分的模型及检测方法研究进展[J]. 天津体育学院学报, 2001, 16(1): 51-55 |
| [4] | 张元通. 少年篮球运动员和普通中学生身体成分及骨密度比较:来源一所中学的数据[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(3): 341-347 |
| [5] |
Hung LS, Tidwell DK, Hall ME, et al. A meta-analysis of school-based obesity prevention programs demonstrates limited efficacy of decreasing childhood obesity[J]. Nutrition Research, 2015, 35(3): 229-240
doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2015.01.002 URL |
| [6] | Ross R, Blair SN, Arena R, et al. Importance of assessing cardiorespiratory fitness in clinical practice: A case for fitness as a clinical vital sign: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2016, 134(24): e653-e699 |
| [7] | 王雅萱, 李珊, 宇克莉, 等. 云南省佤族、拉祜族与哈尼族成人的体成分比较研究[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 39(3): 76-80 |
| [8] | 杜慧敏, 宇克莉, 刘琳. 西双版纳3个族群成人不同肥胖指标与血压的关系[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 38(5): 74-80 |
| [9] | 沈丽萍, 段一凡, 孙旭, 等. 生物电阻抗法和双能X射线吸收法测定健康成人体成分的对比研究[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2021, 27(10): 59-64 |
| [10] |
Kyle UG, Bosaeus I, Lorenzo A, et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-Part II: Utilization in clinical practice[J]. Clinical Nutrition, 2005, 23(6): 1430-1453
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2004.09.012 URL |
| [11] |
Böhm A, Heitmann BL. The use of bioelectrical impedance analysis for body composition in epidemiological studies[J]. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2013, 67(S3): S79-S85
doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2012.168 URL |
| [12] | 陈昭. 生物人类学和人体组成学的渊源关系[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(3): 264-273 |
| [13] | 廖彦博, 李坤, 郑连斌, 等. 广西京族体质人类学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(1): 100-102 |
| [14] | 李咏兰, 郑连斌, 金丹. 黎族的体成分与体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2019, 38(1): 77-87 |
| [15] | 杜慧敏, 孙泽阳, 张兴华, 等. 中国羌族身体体成分特点[J]. 解剖学报, 2018, 49(4): 540-542 |
| [16] | 宇克莉, 郑连斌, 李咏兰, 等. 海南临高人身体成分分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(1): 101-109 |
| [17] | 宇克莉, 贾亚兰, 郑连斌. 布朗族成人的身体成分分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2020, 39(2): 261-269 |
| [18] | 王雅萱, 张兴华, 宇克莉, 等. 中国基诺族的人体体成分研究[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 37(5): 66-69 |
| [19] | 李珊, 宋晴阳, 宇克莉, 等. 生物电阻抗法测量身体成分的可行性[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2019, 42(5): 480-486 |
| [20] | 席焕久, 陈昭. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010 |
| [21] | 向小雪, 宇克莉, 张兴华. 云南纳西族与普米族成人体成分分析[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 40(5): 75-80 |
| [22] | 孙思凡, 李咏兰. 桂林瑶族与来宾瑶族成人身体成分分析[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 40(4): 71-76 |
| [23] | 李咏兰, 郑连斌. 中国蒙古族体质人类学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018 |
| [24] | 于会新, 李咏兰, 郑连斌, 等. 中国少数民族体成分的变化[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(1): 36-50 |
| [25] | Slemenda CW, Miller JZ, Hui SL, et al. Role of physical activity in the development of skeletal mass in children[J]. Journal of Bone & Mineral Research, 2010, 6(11): 1227-1233 |
| [26] | 曾文真, 刘彬, 邓振兴, 等. 探讨高尿酸血症与生活相关性疾病的关系[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2015, 7(26): 56-58 |
| [27] | Ichida K, Matsuo H, Takada T, et al. Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3(1): 1811-1821 |
| [28] |
Kedar E, Gardner GC. Lipid-associated rheumatologic syndromes[J]. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America, 2013, 39(2): 481-493
doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2013.02.014 |
| [29] | 谢薇, 王志红, 何丹. 佤族成人身体素质及相关因素的调查[J]. 云南中医学院学报, 2006, 29(S1): 38-40 |
| [30] | 明伟. 西双版纳山区的民族——布朗族[J]. 中国民族教育, 2010(4): 25 |
| [31] | 秀丽. 农耕文明的北上与蒙古族饮食文化的变迁[J]. 内蒙古大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2020, 52(4): 10-17 |
| [1] | 白静雅, 程鹏, 马斌, 欧阳思维, 魏栋, 海向军. 甘肃临夏保安族成人的体成分[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(04): 536-548. |
| [2] | 高新颖, 宇克莉, 张兴华, 姚玥彤, 肖瑶, 程智, 高雯芳, 刘鑫, 包金萍. 云南佤族三大方言族群的体成分[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 458-469. |
| [3] | 曾浩然, 刘康康, 罗亚平. 指纹皱纹研究的现状及展望[J]. 人类学学报, 2024, 43(03): 518-528. |
| [4] | 何嘉宁, 冉智宇. 中国史前人类的头骨变形[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(05): 575-589. |
| [5] | 孙蕾, 李彦桢, 武志江. 河南郑州站马屯遗址仰韶晚期人骨的颅面形态[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 331-341. |
| [6] | 王邦彦, 王久存, 文少卿. 古代强直性脊柱炎的诊断标准及国内研究回顾[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 422-434. |
| [7] | 付卫伟, 王晓卫, 杨晨希, 王程亮, 贺树军, 李保国. 非人灵长类早期发育阶段行为偏侧的研究进展[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(03): 435-444. |
| [8] | 贺乐天, 王永强, 魏文斌. 新疆哈密拉甫却克墓地人的颅面部测量学特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1017-1027. |
| [9] | 沙仁高娃, 程慧珍, 韦兰海. 达斡尔语分支早期在蒙古语族中的地位[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1037-1046. |
| [10] | 宋焕庭, 唐玮, 张丽梅, 张忠良, 张嘉宇, 陈世韬. 指纹与年龄相关性的量化分析[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1047-1057. |
| [11] | 邢松. 现代人出现和演化的化石证据[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1069-1082. |
| [12] | 饶慧芸. 古蛋白质分析在东亚古人类演化中的应用前景[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1083-1096. |
| [13] | 李小强. 农业的起源、传播与影响[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(06): 1097-1108. |
| [14] | 刘武, 吴秀杰. 中更新世晚期中国古人类化石的形态多样性及其演化意义[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 563-575. |
| [15] | 倪喜军. 新证据下的现代人起源模型[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(04): 576-592. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京ICP证05002819号-3
京ICP证05002819号-3